IGCSE Physics (2023-2025) + PYQ - C18/25: Electrical Quantities
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores fundamental electrical quantities such as current, voltage, resistance, and power in the context of IGCSE physics. It delves into the definitions, formulas, and practical applications of these concepts, using examples to illustrate how they are measured and calculated. The video also discusses the difference between ohmic and non-ohmic resistors and concludes with real-world applications like calculating electricity bills.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the definition of electric current?
-Electric current is the rate at which electric charge (electrons) passes a point in a circuit. It requires a complete circuit and a driving force, such as a battery or power supply, to push the charges around the circuit.
What are the three instruments used to measure electric current?
-The three instruments used to measure electric current are the analog ammeter, the digital ammeter, and the galvanometer, which is specifically used to measure tiny currents.
How is an ammeter connected in a circuit?
-An ammeter is connected in series with the circuit to measure the current flowing through it.
What is the conventional current flow direction?
-Conventionally, current is thought to flow from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, although in reality, it is the electrons that move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
How is the amount of electric charge related to the current in amperes?
-One ampere is defined as the amount of charge that passes through a circuit in one second. It is equivalent to the charge of approximately 1.6 × 10^19 electrons.
What is the definition of voltage?
-Voltage can be defined as the work done by charge passing through an electrical component or as the difference in electrical potential between two points, also known as potential difference.
How does the connection of batteries affect the total voltage?
-When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up. However, if connected incorrectly, such as in opposite directions, the voltages can cancel each other out.
What is the formula for calculating the electromotive force (EMF) of a battery?
-The formula for calculating the EMF of a battery is the work done divided by the charge (Q), or EMF = Work Done / Q.
How is resistance defined in an electrical circuit?
-Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for an electric current to flow through a device or component. It is defined as the potential difference (voltage) across a component divided by the current flowing through it.
What is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit?
-The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit is given by Ohm's Law, which states that V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
How does the resistance of a wire change with its length and thickness?
-The resistance of a wire increases with its length and decreases with its thickness. Doubling the length of a wire doubles its resistance, while doubling the diameter of a wire halves its resistance.
What is the unit for electromotive force (EMF)?
-The unit for electromotive force (EMF) is the volt.
How is power calculated in an electrical circuit?
-Power in an electrical circuit is calculated using the formula P = VI, where P is the power in watts, V is the voltage in volts, and I is the current in amperes.
What is the significance of a kilowatt hour (kWh) in measuring energy consumption?
-A kilowatt hour (kWh) is a unit of energy equivalent to one kilowatt of power being used for one hour. It is commonly used to measure the energy consumption of electrical appliances and is the standard unit for billing electricity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

APA ITU ARUS LISTRIK, TEGANGAN, RESISTANSI, DAN DAYA LISTRIK
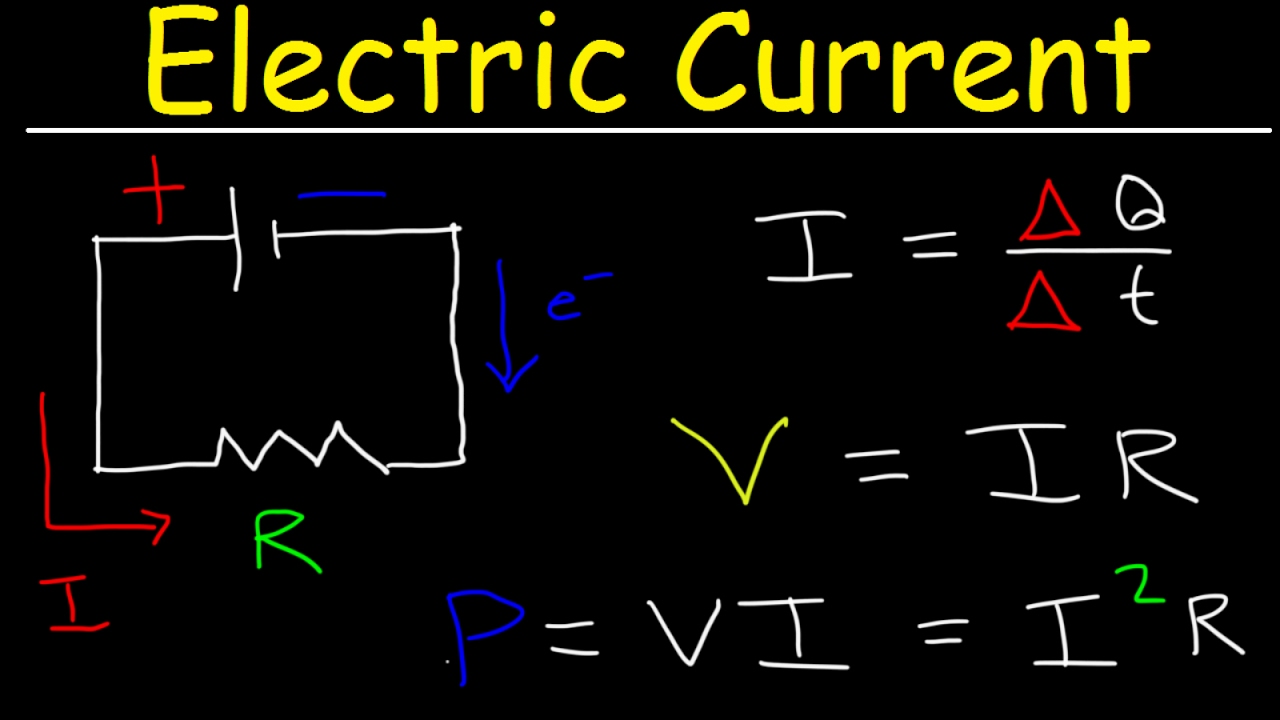
Electric Current & Circuits Explained, Ohm's Law, Charge, Power, Physics Problems, Basic Electricity

Satuan, Besaran dan Simbol Dalam Listrik
DC Series circuits explained - The basics working principle
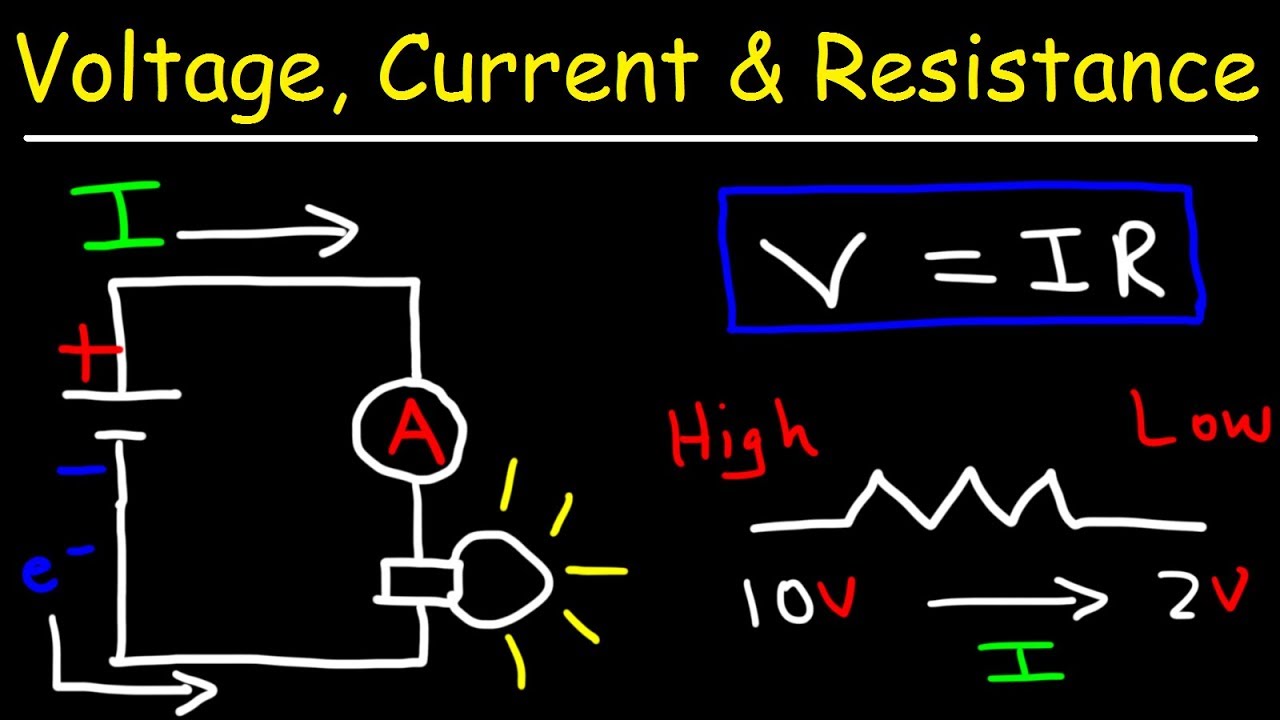
Voltage Current and Resistance

Alat Ukur dan Pengukuran Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)