2-Minute Neuroscience: Early Neural development
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers a concise overview of early neural development, starting from the formation of the neural plate in the third week of embryonic development to the emergence of the brain's primary and secondary vesicles. It details the fusion into the neural tube, which develops into the brain and spinal cord, and the subsequent growth and subdivision into distinct brain regions by the 11th week, highlighting the remarkable journey of the brain's structural formation before birth.
Takeaways
- 🕒 The development of the nervous system starts at the third week of embryonic development.
- 🌱 The ectoderm thickens to form the neural plate, which folds inward to create the neural groove.
- 🤝 The neural folds come together and fuse by the end of the third week, forming the neural tube by the fourth week.
- 🧠 The neural tube will develop into the brain and spinal cord.
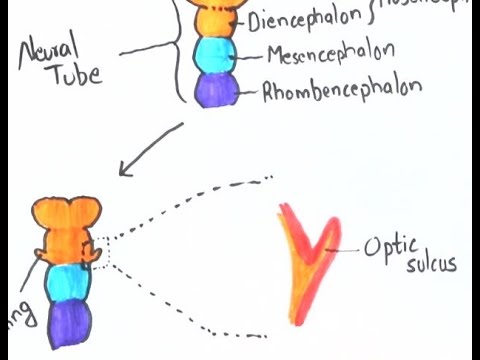
- 📍 During the fourth week, the neural tube bulges form the primary vesicles: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon.
- 🧠 The prosencephalon will develop into the cerebrum, the mesencephalon into the midbrain, and the rhombencephalon into the brainstem and cerebellum.
- 🔍 The prosencephalon further divides into the telencephalon and diencephalon, with the telencephalon becoming the cerebral hemispheres.
- 🧠 The diencephalon will include structures like the thalamus and hypothalamus.
- 🌐 The rhombencephalon divides into the metencephalon (pons and cerebellum) and myelencephalon (medulla).
- 📈 The telencephalon grows rapidly, and by 11 weeks, the brain's shape is similar to that at birth.
- 👶 Although the brain continues to develop post-birth, its structure at birth is fundamentally complete.
Q & A
What is the '2 minute neuroscience' series about?
-The '2 minute neuroscience' series is about providing simple explanations of neuroscience topics within a short duration of 2 minutes or less.
When does the development of the nervous system begin?
-The development of the nervous system begins around the third week of embryonic development.
What is the initial formation of the nervous system called?
-The initial formation of the nervous system is called the neural plate, which is an area of the ectoderm that thickens.
What is the groove formed by the folding inward of the neural plate?
-The groove formed by the folding inward of the neural plate is called the neural groove.
What happens to the neural groove by the end of the third week of embryonic development?
-By the end of the third week, the sides of the neural groove, known as neural folds, begin to come together and start to fuse.
When are the neural folds completely fused together?
-The neural folds are completely fused together by the end of the fourth week to form the neural tube.
What will the neural tube eventually become?
-The neural tube will eventually become the brain and spinal cord.
What are the three primary vesicles that appear during the fourth week of neural tube development?
-The three primary vesicles are the prosencephalon, which forms the cerebrum; the mesencephalon, which becomes the midbrain; and the rhombencephalon, which develops into the rest of the brainstem and cerebellum.
How does the prosencephalon further subdivide during brain development?
-The prosencephalon subdivides into the telencephalon and diencephalon, with the telencephalon becoming the cerebral hemispheres and the diencephalon consisting of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and other structures.
What parts of the brain does the rhombencephalon subdivide into?
-The rhombencephalon subdivides into the metencephalon, which becomes the pons and cerebellum, and the myelencephalon, which becomes the medulla.
At what stage does the brain start to resemble its shape at birth?
-The brain starts to resemble its shape at birth by 11 weeks of development, with the telencephalon growing more rapidly than other parts of the neural tube.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Development of the Face and Palate

Divisões embriológicas do Encéfalo (Sistema Nervoso Central) - Neuroanatomia - VideoAula 070
Development of EYE : Visual Learning: Easy learning

EMBRIOLOGI SISTEM SARAF PUSAT Pt 2 Brain dan Spinal Cord #SistemSaraf

Neurulation - Neural Tube formation - Third Week Embryology

The Central Nervous System: The Brain and Spinal Cord
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)