Transport across the Cell Membrane / Plasma Membrane | Active and Passive Transport
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses various aspects of transport, including active and passive transport mechanisms, energy requirements, and the Facilitated Diffusion Act of 1965. It mentions the importance of membrane proteins in transport processes and touches upon the role of sodium-potassium pumps in maintaining concentration gradients. The script also urges viewers to subscribe to the channel for more content on transport and related topics.
Takeaways
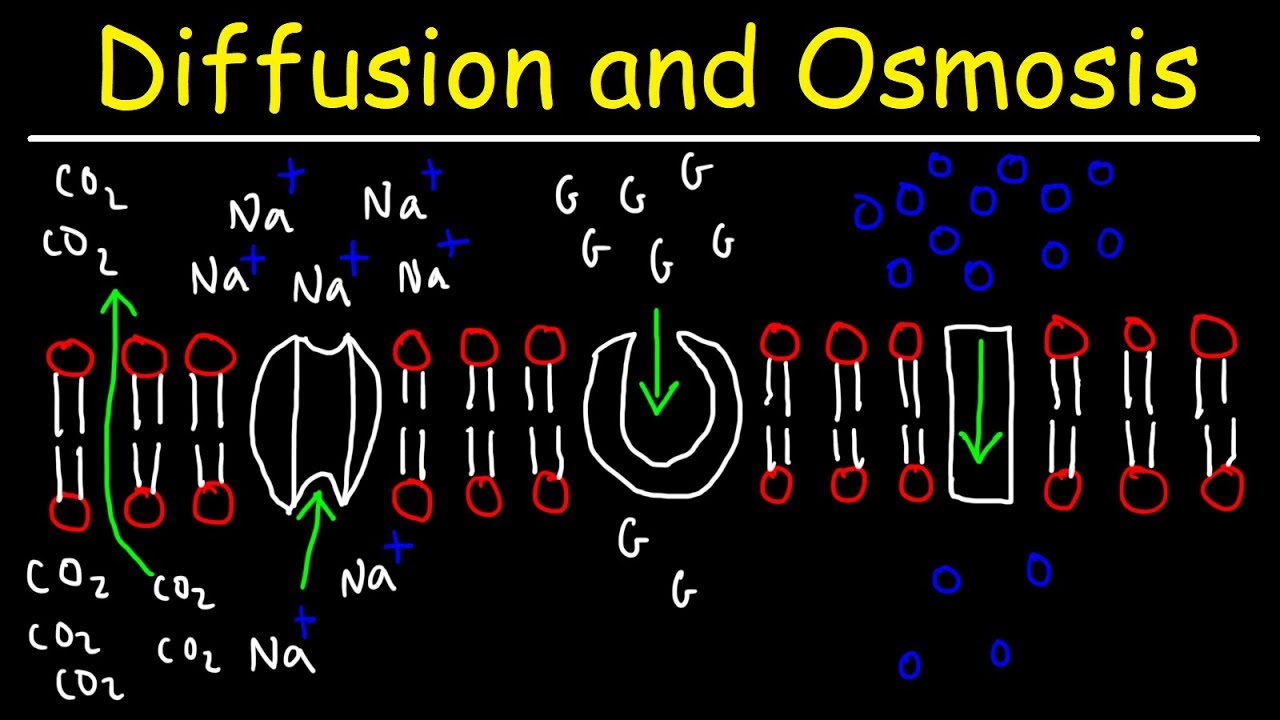
- 🔄 There are two main types of transport across cell membranes: passive and active transport.
- 🔋 Passive transport does not require energy and includes processes like simple diffusion.
- ⚡ Active transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient.
- 🚶 Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport where molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration without the need for energy.
- 🛠 Facilitated diffusion is also passive transport but involves carrier proteins to help move substances across the membrane.
- ⚙️ Active transport involves specific proteins like the sodium-potassium pump to maintain concentration gradients across the membrane.
- 🌬 Oxygen and carbon dioxide typically move across cell membranes through simple diffusion due to their small size and nonpolarity.
- 🔑 Carrier proteins play a crucial role in facilitated diffusion by allowing larger or polar molecules to pass through the membrane.
- 💡 Primary active transport directly uses metabolic energy to transport molecules.
- 🔋 Secondary active transport uses the energy from the electrochemical gradient created by primary active transport to move other substances.
- 🔍 Sodium-potassium pumps are essential for maintaining cell potential and the proper function of nerve and muscle cells.
Q & A
What are the different types of transport mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions various types of transport including active transport, facilitated diffusion, passive transport, and transport in and out of the cell membrane.
What is active transport and how does it relate to energy requirements?
-Active transport is a process that requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient. It is mentioned in the script as a type of transport that requires energy.
What is facilitated diffusion and how does it differ from active transport?
-Facilitated diffusion is a passive transport process that involves the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins, without the need for energy, unlike active transport.
What is the role of carrier proteins in transport across the cell membrane?
-Carrier proteins assist in the transport of substances across the cell membrane, particularly in facilitated diffusion and active transport, by providing a specific binding site for the molecules to be transported.
How is the sodium-potassium pump related to the transport process discussed in the script?
-The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport that moves sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient, which is powered by ATP.
What is the significance of the concentration gradient in transport processes?
-The concentration gradient is crucial in transport processes as it determines the direction in which substances naturally move, from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
What does the script imply about the importance of energy in cellular transport?
-The script implies that energy, often in the form of ATP, is essential for active transport processes, which move substances against their concentration gradient.
How does the script relate the transport of substances to the function of the cell?
-The script suggests that transport processes are integral to cell function, allowing for the movement of necessary substances into the cell and waste products out of the cell.
What is the role of the transport mechanism in maintaining cell homeostasis?
-The transport mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining cell homeostasis by regulating the movement of ions and molecules, ensuring a stable internal environment.
What does the script suggest about the complexity of transport systems within cells?
-The script suggests that transport systems within cells are complex, involving various mechanisms and proteins to facilitate the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
How does the script connect the transport of substances to the broader context of cellular metabolism?
-The script connects the transport of substances to cellular metabolism by mentioning that energy from metabolic processes, such as ATP, is required for active transport.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How do things move across a cell membrane? | Cells | MCAT | Khan Academy

General Biology I - Transport Mechanisms - Part I

Transport melaui membran sel
Diffusion and Osmosis - Passive and Active Transport With Facilitated Diffusion

Transportasi pada membran sel - Biologi kelas 11 SMA

Active transport vs. PassiveTransport
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)