#1. Introduction To Data Warehouse and features of Data Warehouse |DWDM|
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the topic of Data Warehouse, explaining its purpose and four defining features: subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, and time-variant. The presenter contrasts data warehouses with traditional databases—highlighting larger storage, historical data retention, and support for management decision-making across organizations. Each feature is clarified with examples: focusing on a specific subject (like sales), integrating data from multiple sources and resolving inconsistencies, preventing alteration once data is stored, and maintaining long-term historical records. The video closes by promising future lessons on OLTP vs. OLAP, and invites viewers to like, comment, subscribe, and contact the creator for notes or questions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Data Warehousing is a subject that will be covered in-depth, with the first chapter focused entirely on this topic.
- 😀 The video also introduces the concept of Data Mining, which will be discussed starting from Chapter 2.
- 😀 Data Warehouses are used to store large amounts of data, unlike databases, which store limited information.
- 😀 Key features of Data Warehouses include: subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, and time-variant.
- 😀 Data Warehouses focus on a single subject (e.g., sales, production) instead of the entire organization.
- 😀 The data in a Data Warehouse is integrated from multiple sources, ensuring consistency and meaningful organization.
- 😀 Non-volatile means once data is entered into the Data Warehouse, it cannot be modified, deleted, or updated.
- 😀 Time-variant allows Data Warehouses to store historical data, even extending back several years.
- 😀 Data Warehouses are useful for management’s decision-making, with data readily accessible for analysis.
- 😀 The next video will explain the differences between operational databases (OLTP) and Data Warehouses (OLAP).
- 😀 The creator encourages viewers to subscribe, like, comment, and reach out via contact details provided for further inquiries.
Q & A
What is a Data Warehouse?
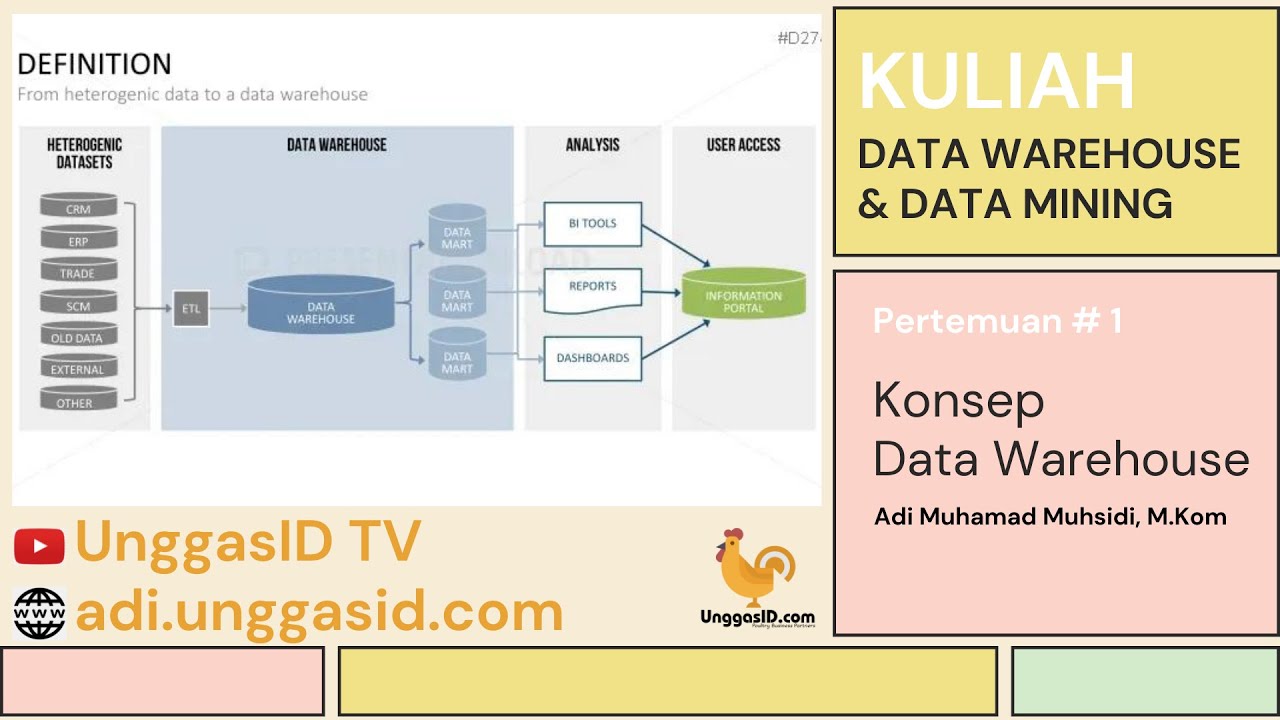
-A Data Warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, and time-variant collection of data, designed to support management's decision-making processes. It stores large amounts of historical data from various sources to assist in business analysis and decision-making.
How does a Data Warehouse differ from a regular database?
-A database typically stores smaller, more transactional data focused on day-to-day operations, whereas a Data Warehouse stores vast amounts of historical, aggregated data from various sources, allowing for complex queries and business analysis.
What are the key features of a Data Warehouse?
-The key features of a Data Warehouse are: 1) Subject-Oriented, meaning it focuses on specific areas such as sales or production; 2) Integrated, meaning it consolidates data from various sources; 3) Non-Volatile, meaning once data is stored, it cannot be altered or deleted; and 4) Time-Variant, meaning it stores historical data over a long period.
What does 'Subject-Oriented' mean in the context of Data Warehousing?
-Subject-Oriented means that a Data Warehouse is designed to focus on specific subjects or areas, such as sales, production, or customer behavior, rather than encompassing the entire organization. This allows for in-depth analysis of each subject.
What does 'Integrated' mean in a Data Warehouse?
-Integrated refers to the process of combining data from different sources into a unified, consistent view. This includes resolving inconsistencies and transforming data from various formats into a common structure for easier analysis.
Why is Data Warehouse data considered Non-Volatile?
-Data in a Data Warehouse is considered Non-Volatile because once data is entered, it cannot be changed, updated, or deleted. This ensures the integrity of historical data for accurate analysis and reporting.
What is meant by Time-Variant in the context of a Data Warehouse?
-Time-Variant means that a Data Warehouse can store data from different time periods, including historical data that spans years. This allows organizations to analyze long-term trends and changes over time, which is not typically possible with regular databases.
Can you provide an example of how data is integrated in a Data Warehouse?
-For example, data from various accounts like salary accounts, savings accounts, and current accounts would be integrated under one category called 'Accounts.' This integration combines various related data sources into a single view for better analysis.
What is the importance of Data Warehouse in management decision-making?
-A Data Warehouse is crucial for management decision-making as it provides easy access to vast amounts of organized data from various sources. This helps managers analyze trends, make informed decisions, and identify areas for improvement in the organization.
What is the difference between OLTP and OLAP systems, as mentioned in the video?
-OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems are focused on managing real-time transactional data, while OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems, like Data Warehouses, are designed to perform complex queries and analyses on large volumes of historical data.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)