Windows vs 100 latest ransomware
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the creator tests Windows Defender's ability to protect against ransomware, using the latest ransomware samples. Despite its cloud analysis and real-time protection, Windows Defender fails to block one ransomware strain, 'Nebula,' which successfully encrypts all files. However, Defender does block 98-99% of the threats. The video emphasizes the ongoing vulnerability of Windows 11 to sophisticated ransomware, recommending additional protections like ransomware control and folder access. The creator also touches on other tools like Threat Locker, which uses whitelisting to block ransomware from executing.
Takeaways
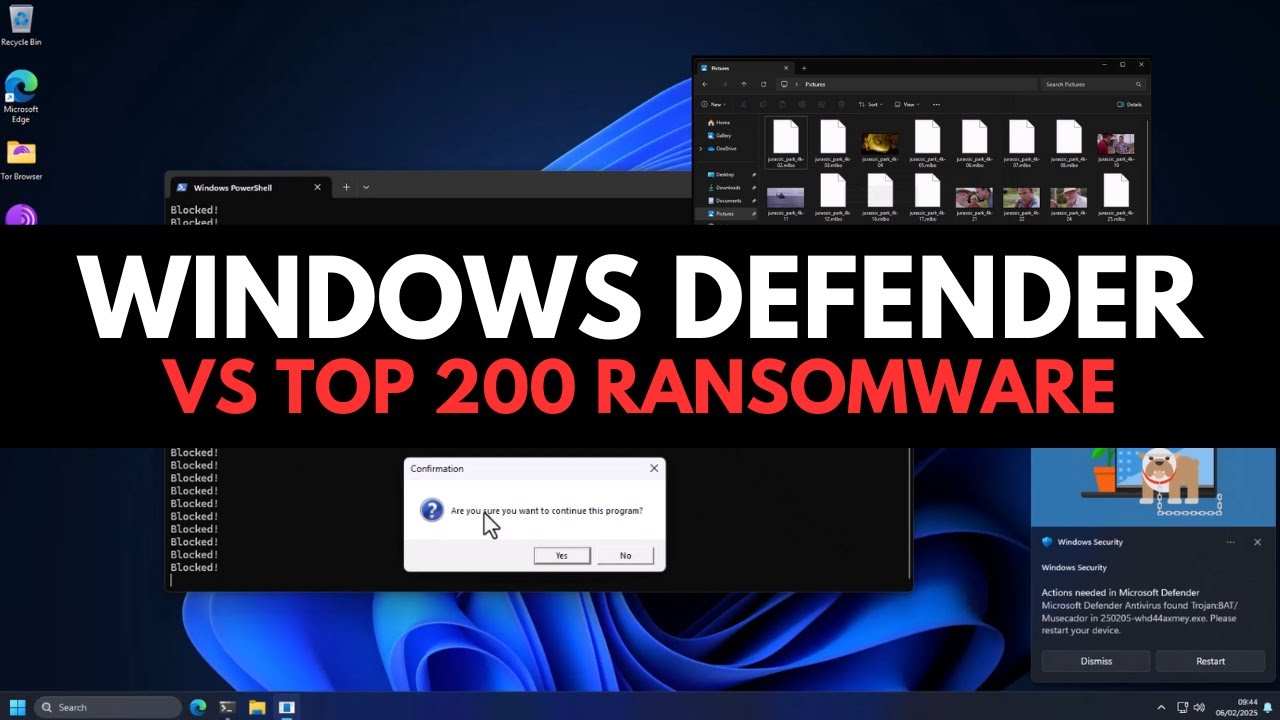
- 😀 Windows Defender blocked 98-99 ransomware attempts but still failed to block one, allowing data encryption.
- 😀 Despite Windows Defender's improvements, modern ransomware can still bypass protection and cause damage.
- 😀 Nebula ransomware successfully encrypted all test data despite Microsoft Defender's cloud analysis and definitions.
- 😀 Windows Defender performed better than Macaffy, blocking 75 out of 100 ransomware attempts.
- 😀 Ransomware protection settings, such as 'control folder access,' can help protect crucial data but may cause access issues with legitimate apps.
- 😀 Smart App Control is a feature that blocks untrusted or unsigned files, but it is not a guaranteed fix against ransomware.
- 😀 Windows Defender lacks sophisticated behavioral protection, making it less effective against more complex ransomware attacks.
- 😀 The 'test' feature of Threat Locker successfully blocked ransomware execution by reducing the attack surface with application whitelisting.
- 😀 Despite improvements, no antivirus software is fully immune to sophisticated, modern ransomware attacks.
- 😀 Ransomware protection needs to be complemented by user vigilance, such as using control folder access settings for sensitive data.
- 😀 Even with blocking 98-99% of ransomware, Windows Defender still requires improvements to counteract evolving threats.
Q & A
What happened during the previous test with McAfee antivirus?
-The test with McAfee antivirus failed because it was unable to stop ransomware from executing and encrypting files. The system was compromised despite McAfee being active, highlighting its lack of effectiveness against modern ransomware.
What ransomware was executed during this test with Windows Defender?
-The ransomware executed during this test was a new type called Nebula ransomware. It encrypted files and displayed a ransom message, demanding payment within 72 hours.
How did Windows Defender perform in this test against ransomware?
-Windows Defender blocked 98 out of 99 ransomware attempts, which is a significant improvement over McAfee. However, it still allowed one ransomware (Nebula) to execute and encrypt files.
Why did Windows Defender allow the Nebula ransomware to execute?
-Windows Defender was not able to block the Nebula ransomware because it was a sophisticated threat that bypassed the system's detection, highlighting the limitations of signature-based protection and behavioral analysis.
What is the ransomware protection feature in Windows 11?
-The ransomware protection feature in Windows 11 includes 'Control Folder Access,' which helps prevent unauthorized apps from accessing certain sensitive folders, such as Documents or Pictures, in the event of a ransomware attack. However, it doesn't block ransomware entirely.
What is 'Smart App Control' in Windows Defender, and how does it help with ransomware?
-Smart App Control is a new feature that blocks untrusted or unsigned applications from running. While it can reduce the attack surface by preventing some malware from executing, it is not a foolproof solution, as some ransomware may still bypass this protection if it is signed.
How effective is the 'Smart App Control' feature in blocking ransomware?
-Based on the test results, 'Smart App Control' is not very effective against ransomware because it only checks if files are signed, and some signed ransomware can still bypass this protection.
What steps can users take to better protect their data from ransomware in Windows 11?
-Users can enable 'Control Folder Access' in Windows Defender to protect critical folders like Documents and Pictures. Additionally, they can use the 'Ransomware Protection' settings to further secure their files. While these tools are not perfect, they help reduce the risk of data loss.
What is the key takeaway from this test regarding Windows Defender's effectiveness?
-The key takeaway is that Windows Defender has improved over time but is still not foolproof. While it blocked most of the ransomware in the test, it allowed one to slip through and encrypt files, indicating that modern ransomware is still a significant threat.
How does Threat Locker differ from Windows Defender in protecting against ransomware?
-Threat Locker uses a 'default deny' approach, blocking any unapproved applications from running. It employs whitelisting and application control, making it much more effective at preventing ransomware attacks compared to traditional antivirus programs like Windows Defender.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)