Logistics Fundamentals Lecture One - An Introduction
Summary
TLDRIn this introductory lecture on logistics, Chris Lee, a seasoned logistics professional with nearly 20 years of experience, provides an overview of the field. He explains the origins and definitions of logistics, highlighting its importance in both military and modern business contexts. The lecture covers the role of logistics in supply chain management, the significance of information flow, and the economic impact of efficient logistics. Lee also discusses the concept of economic utility and its various types, as well as the evolving consumer behaviors that affect logistics. The session concludes with an invitation to explore the impact of information technology on logistics in the next lecture.
Takeaways
- 🚚 Logistics is crucial in both military and commercial sectors, with a significant role in supply chain management.
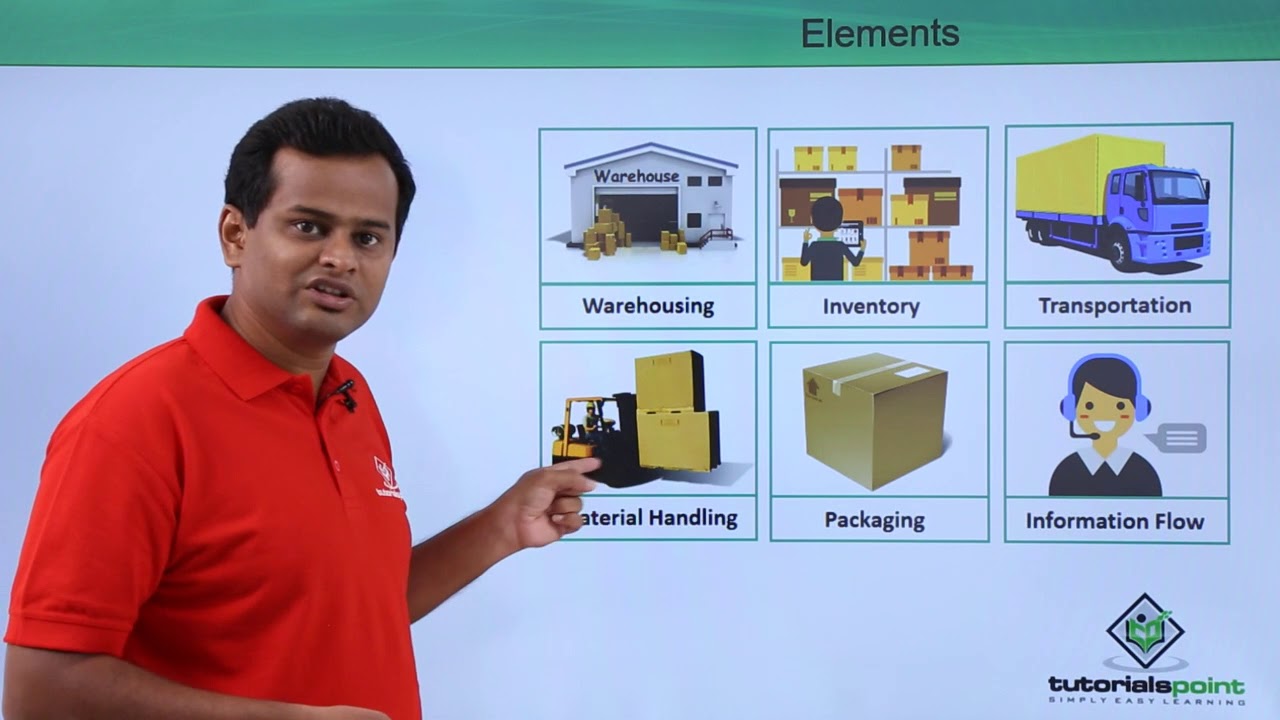
- 🌐 Modern logistics integrates forward and reverse flows, ensuring efficient movement and storage of goods and information.
- 🏢 Logistics management involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow and storage of goods and services from origin to consumption.
- 📦 The effectiveness of logistics impacts business functions like marketing, operations, production, and finance.
- 📊 The economic utility of logistics includes possession, form, time, and place, all contributing to customer satisfaction and economic development.
- 🛠️ Advancements in information technology and deregulation have transformed logistics, enhancing its economic opportunities and operational efficiency.
- 👨👩👧👦 Changing consumer behaviors and family dynamics influence logistics, demanding more convenience and tailored services.
- 🔄 Mass customization allows companies to meet specific customer needs, reflecting the shift towards more personalized logistics services.
- 🛒 Efficient logistics reduce costs and improve GDP, highlighting the direct relationship between logistics efficiency and economic growth.
- 📈 The logistics job market is robust, offering various roles from analysts to managers, driven by the growing importance of supply chain management.
Q & A
Who is the presenter of the logistics lecture series?
-The presenter is Chris Lee.
What background does Chris Lee have in logistics?
-Chris Lee has almost 20 years of experience in logistics, beginning with the United States military, and has worked globally in the field.
How does the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP) define logistics?
-CSCMP defines logistics as part of supply chain management that plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet customer requirements.
What is the main focus of logistics according to the Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport?
-The Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport focuses on getting the right product to the right place in the right quantity, at the right time, in the best condition, and at an acceptable cost.
Why is the flow and storage of information important in modern logistics?
-Information in logistics is crucial because it allows for efficient management and can substitute for inventory, enabling companies to reorder products as they are sold rather than keeping them in storage.
What are the 'eight R's' of logistics mentioned in the lecture?
-The 'eight R's' of logistics involve getting the right product, in the right quantity and quality, to the right place, at the right time, for the right customer, at the right cost, in the right way.
How does logistics impact economic development and GDP?
-Efficient logistics reduce costs, which allows for greater economic development. Higher logistics costs can limit economic progress and directly affect a nation's GDP.
What are the four types of economic utility in logistics?
-The four types of economic utility are possession utility, form utility, time utility, and place utility.
What role do changing family roles and rising customer expectations play in logistics?
-Changes in family roles, such as more dual-income households, increase the demand for convenience in logistics, while rising customer expectations require continuous improvement in logistics services to meet evolving demands.
What is the significance of reverse logistics in today's logistics field?
-Reverse logistics, which deals with the return of products from the point of consumption, is crucial for managing returns, recycling, and disposal, and is now as important as forward logistics.
What professional opportunities are available in the logistics and supply chain management field?
-Career opportunities in logistics and supply chain management include roles such as logistics analysts, consultants, customer service managers, international logistics managers, supply chain software managers, purchasing managers, transportation managers, and warehouse operations managers.
What are the systems and total cost approaches in logistics?
-The systems approach in logistics recognizes the interdependence of various organizational functions, while the total cost approach ensures that material management and distribution are coordinated in the most cost-efficient way.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

International Trade : Logistics & Sourcing - I
Logistics Management - Introduction

Logixtics ULIP Hackathon 2.0 Kick Off Event | NLDS x Atal Innovation Mission x Startup India

История и философия науки 1

MATERI KELAS XI MPLB "MANAJEMEN LOGISTIK"

Become a CONCEPT ARTIST for video games - What to practice?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)