simple present tense (verbal)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the simple present tense is explained, covering its use for habits, permanent situations, general truths, and fixed plans. The video demonstrates how the present tense is used in positive, negative, and interrogative sentences, with examples. It also explains the rules for subject-verb agreement, including when to add 's' or 'es' to verbs. The video includes examples from both English and Indonesian to illustrate how the tense works in both languages. It provides a clear and accessible overview of the simple present tense for learners.
Takeaways
- 😀 The simple present tense is used to describe habits, routines, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed plans.
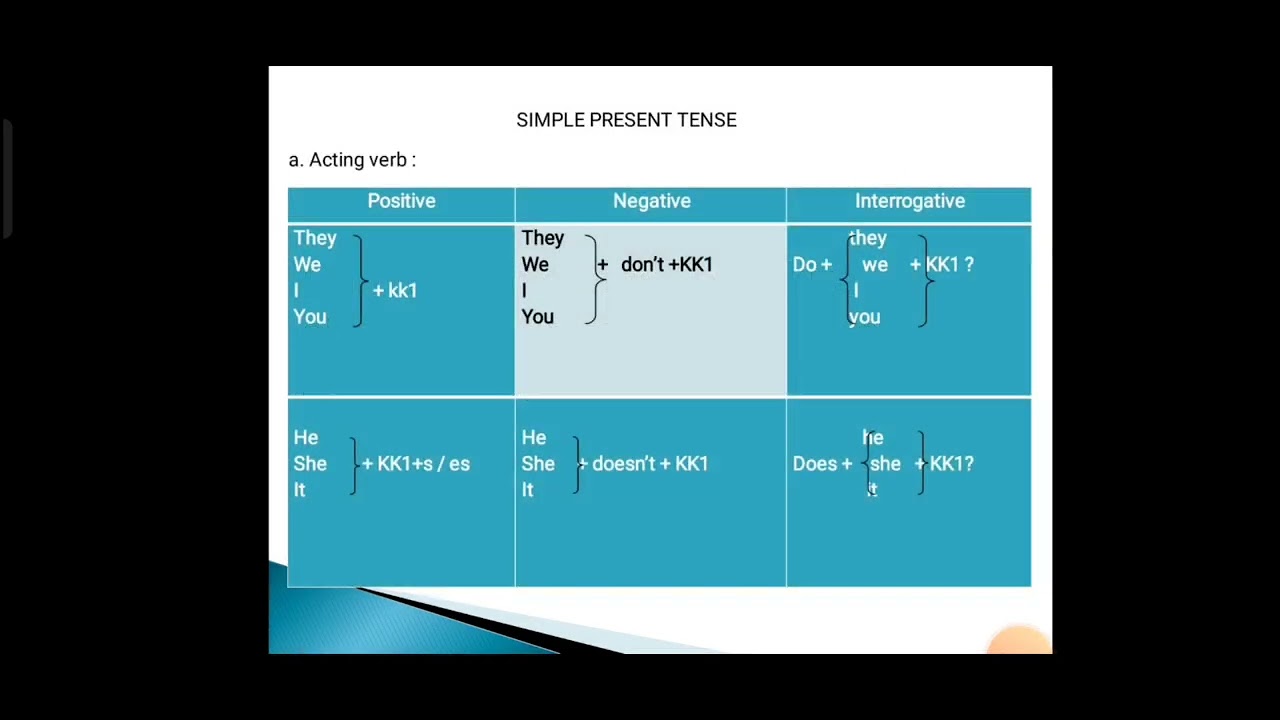
- 😀 Positive sentences follow the structure: Subject + Verb 1 + Object/Complement.
- 😀 Some verbs are intransitive and do not require an object in the sentence.
- 😀 Negative sentences use 'do not' for plural subjects and 'does not' for singular subjects, followed by Verb 1 + Object/Complement.
- 😀 Interrogative sentences use 'Do' for plural subjects and 'Does' for singular subjects at the beginning of the sentence.
- 😀 When using 'does' in questions or negatives, the main verb does not receive an additional 's' or 'es'.
- 😀 Verbs ending in most letters add '-s' in third person singular, but verbs ending in consonant + 'y' change 'y' to 'i' and add '-es'.
- 😀 Verbs ending in 's', 'z', 'x', 'ch', 'sh', or 'o' add '-es' in third person singular.
- 😀 Examples of simple present tense include: 'I wake up at 5 in the morning', 'She waters the flowers twice a day', and 'The Earth revolves around the Sun'.
- 😀 Translating from Indonesian to English involves applying the simple present tense rules: e.g., 'Rani mencuci bajunya' → 'Rani washes her clothes'.
- 😀 The simple present tense is essential for expressing daily activities, repeated actions, general facts, and scheduled events correctly.
Q & A
What is the Simple Present Tense used for?
-The Simple Present Tense is used to describe habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed plans or schedules.
How is a positive sentence in the Simple Present Tense structured?
-A positive sentence in the Simple Present Tense follows the structure: Subject + Verb1 + Object/Complement. For example, 'I drink milk every morning.'
What is the formula for forming negative sentences in the Simple Present Tense?
-The formula for negative sentences is: Subject + do/does + not + Verb1 + Object/Complement. For example, 'I do not drink milk every morning.'
What is the difference between using 'do' and 'does' in negative sentences?
-'Do' is used for plural subjects or with 'I' and 'you'. 'Does' is used for singular third-person subjects (he, she, it).
How do we form an interrogative sentence in the Simple Present Tense?
-In interrogative sentences, we use: Do/Does + Subject + Verb1 + Object/Complement. For example, 'Do you drink milk every morning?' or 'Does he go to the market on Sunday?'
How does subject-verb agreement work with third-person singular subjects in the Simple Present Tense?
-For third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), the verb typically takes an 's' or 'es' ending. For example, 'She runs,' or 'He plays.'
What happens when a verb ends in a consonant + 'y' in the Simple Present Tense?
-When a verb ends in a consonant + 'y,' the 'y' is changed to 'i' and 'es' is added. For example, 'fly' becomes 'flies,' and 'cry' becomes 'cries.'
What happens when a verb ends in 'sh', 'ch', 'x', or 'o' in the Simple Present Tense?
-For verbs ending in 'sh', 'ch', 'x', or 'o', we add 'es' to form the third-person singular. For example, 'fix' becomes 'fixes' and 'go' becomes 'goes.'
How do you form a sentence in the Simple Present Tense using the verb 'to be'?
-The verb 'to be' is irregular in the Simple Present Tense. For singular subjects, 'am,' 'is,' or 'are' are used: 'I am,' 'She is,' 'They are.' For example, 'He is a teacher.'
Can a Simple Present Tense sentence exist without an object or complement?
-Yes, sentences can exist without an object or complement when they use intransitive verbs. For example, 'He sleeps,' or 'She sings.'
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE (Part 1) ~ Video Pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris

Simple Present Tense
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE,SOAL & KUNCI JAWAB (Revised Edition) (@fxsurana9258)

The Usages of Present Simple Tense

Simple Present Tense | Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 | Verbal dan Nominal

Simple Present ❗ O Tempo Verbal mais Utilizado no Inglês❗ | Teacher Elza
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)