2022 ICT Mentorship Episode 26 - Example Of Tape Reading Practice
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth walkthrough of trading using institutional order flow, focusing on liquidity analysis and trading against the daily bias. The trader explains how to identify sell-side and buy-side liquidity pools, fair value gaps, and order blocks to time entries and exits. Real-time annotations demonstrate pyramiding positions, dynamic stop-loss management, and partial profit-taking at key levels. Emphasis is placed on understanding market structure, retail psychology, and anticipating institutional moves rather than relying solely on trend-following. Viewers gain a clear framework for observing price behavior, reading order flow, and executing high-probability trades while managing risk effectively.
Takeaways
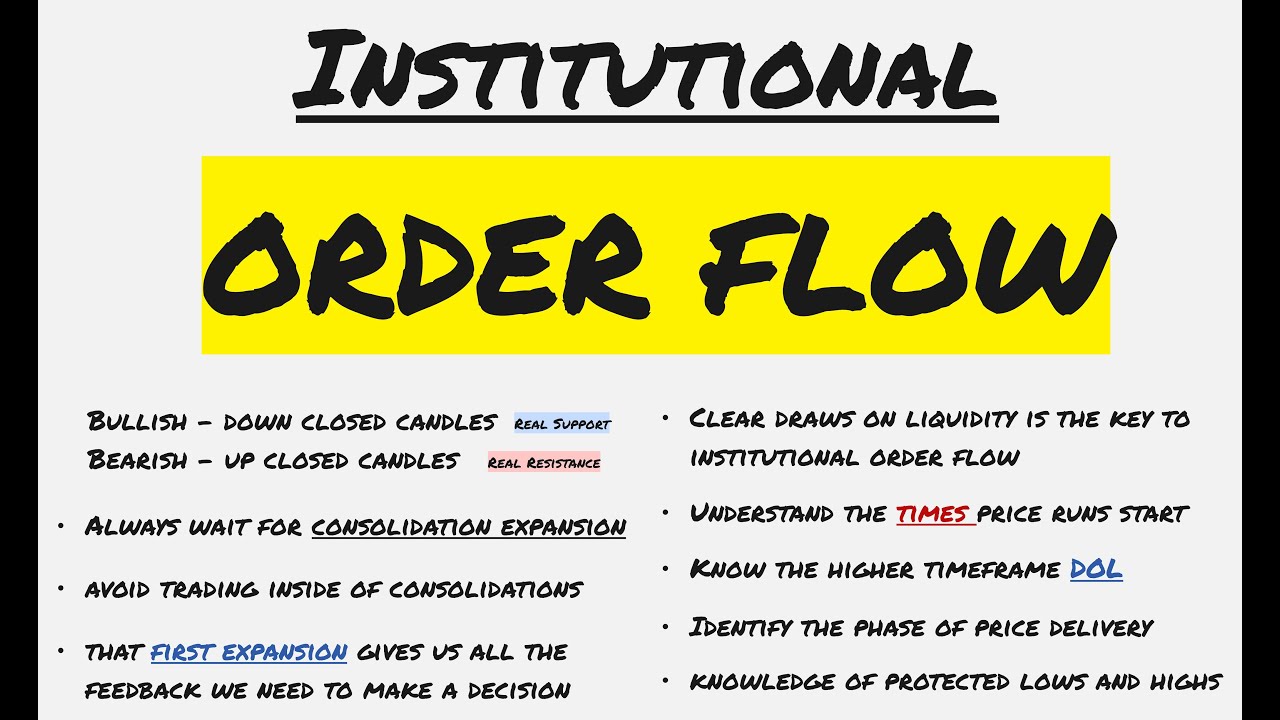
- 😀 Identify and annotate key liquidity areas, including buy-side and sell-side liquidity pools, before entering trades.
- 😀 Trade against the daily bias by observing intraday order flow and liquidity grabs.
- 😀 Use fair value gaps (FVG) and order blocks as critical reference points for entries and exits.
- 😀 Enter positions after liquidity has been taken, targeting potential expansion into buy-side liquidity.
- 😀 Pyramid positions gradually to manage risk and maximize favorable exposure.
- 😀 Place stop-loss orders below key levels, such as FVGs and previous short-term lows, and adjust as the trade progresses.
- 😀 Observe candle patterns, including down-close candles and large green 'caffeine bars,' to confirm trade direction.
- 😀 Take partial profits at significant liquidity levels while leaving some exposure for potential upside.
- 😀 Retail traders may misinterpret market moves as bear flags; trade logic should capitalize on these misconceptions.
- 😀 Real-time chart annotation and tracking of order blocks, FVGs, and liquidity pools enhances understanding and decision-making.
- 😀 Profit and loss numbers are secondary; focus primarily on reading price action and institutional order flow.
- 😀 Monitor market response to annotated levels and be prepared for variations in execution while adhering to the trading framework.
Q & A
What is the primary trading strategy discussed in the video?
-The primary strategy is trading against the daily bias using institutional order flow, focusing on capturing liquidity pools and trading off fair value gaps and order blocks.
What does the trader mean by 'sell-side liquidity being taken'?
-It refers to the market moving below relative equal lows, triggering sell stops, and clearing liquidity on the sell side, which signals an opportunity to enter long positions.
How does the trader identify buy-side and sell-side liquidity?
-The trader observes areas where stop-loss clusters exist or where price previously reversed. Buy-side liquidity is above the current price (highs), and sell-side liquidity is below (lows).
What is a 'fair value gap' and how is it used?
-A fair value gap (FVG) is an area on the chart where price moved too quickly, leaving a gap in liquidity. The trader uses it as a reference for potential entries or stop-loss placement.
Why does the trader pyramid positions, and how is it managed?
-Pyramiding allows adding to winning trades in stages to maximize potential gains while managing risk. Stop-losses are adjusted as positions are added to protect profits.
What role do bullish order blocks play in the strategy?
-Bullish order blocks are areas where institutions likely placed buy orders. The trader uses them as zones for entering long positions and anticipating upward momentum.
How does the trader decide where to place stop-loss orders?
-Stop-losses are placed under significant support areas such as the lower end of a fair value gap or a previous short-term high, ensuring risk is limited if the market moves against the trade.
Why does the trader trade against retail expectations?
-Retail traders often misinterpret liquidity moves (e.g., a drop as a bear flag), creating opportunities for contrarian trades that follow institutional liquidity flow.
What is meant by 'caffeine bar' in the video?
-A 'caffeine bar' is the trader's humorous term for a big green bullish candle, indicating strong upward momentum and confirming bullish signals.
How does the trader handle risk and partial profits?
-The trader takes partial profits at key liquidity levels, adjusts stop-losses to break-even or higher, and allows remaining positions to run if the market continues in their favor.
What is the importance of real-time chart annotations in this strategy?
-Annotations like order blocks, liquidity pools, and fair value gaps help the trader visualize key levels, structure trades, and follow institutional behavior effectively.
Does the strategy require the price to reach all target levels to be profitable?
-No, the trader emphasizes that capturing the bulk of the position at intermediate liquidity zones is sufficient, and reaching the higher targets is optional.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ICT Daily Bias Was Hard, Until I Understood This

The OTE Trader - Institutional Orderflow Educational Video - [Inner Circle Trader] Concepts
Real ICT Institutional Order Flow Explained

ICT Mentorship Core Content - Month 05 - Defining Open Float Liquidity Pools

ICT Institutional Order Flow Explained – Trade Like the Banks and Outsmart the Market

ICT Mentorship 2023 - Deep Dive Into Institutional Order Flow
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)