PERISTIWA PENTING DI EROPA : RENAISANCE
Summary
TLDRThe video lesson explores the Renaissance period in Europe, highlighting its origins, key figures, and transformative impact on society. It explains how Europe transitioned from the stagnant Dark Ages to a vibrant era of cultural rebirth, fueled by economic growth, progressive rulers, the fall of Constantinople, and the invention of the printing press. The lesson introduces prominent Renaissance figures such as Donatello, Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael, emphasizing their contributions to art, literature, and humanist thought. The Renaissance encouraged freedom of thought, scientific and artistic innovation, weakened the Church's dominance, and laid the foundation for modern European exploration, society, and culture.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Renaissance was a period in Europe from the 14th to 17th century, peaking around 1510, marked by the revival of classical Greek and Roman culture.
- 😀 The term 'Renaissance' means 'rebirth,' referring to the revival of art, literature, and humanist thought after the Middle Ages.
- 😀 Europe before the Renaissance experienced the Dark Ages, with limited cultural and scientific progress due to the dominance of the Church.
- 😀 Political power in pre-Renaissance Europe was fragmented, with kings largely figureheads and real authority held by nobles.
- 😀 Social life in the Middle Ages focused on the afterlife, limiting individual freedom, self-expression, and personal development.
- 😀 The emergence of a prosperous middle class in cities like Florence, Genoa, and Venice fueled interest in classical learning and worldly achievements.
- 😀 Progressive rulers and nobles supported education, arts, and culture, which helped spread Renaissance ideas.
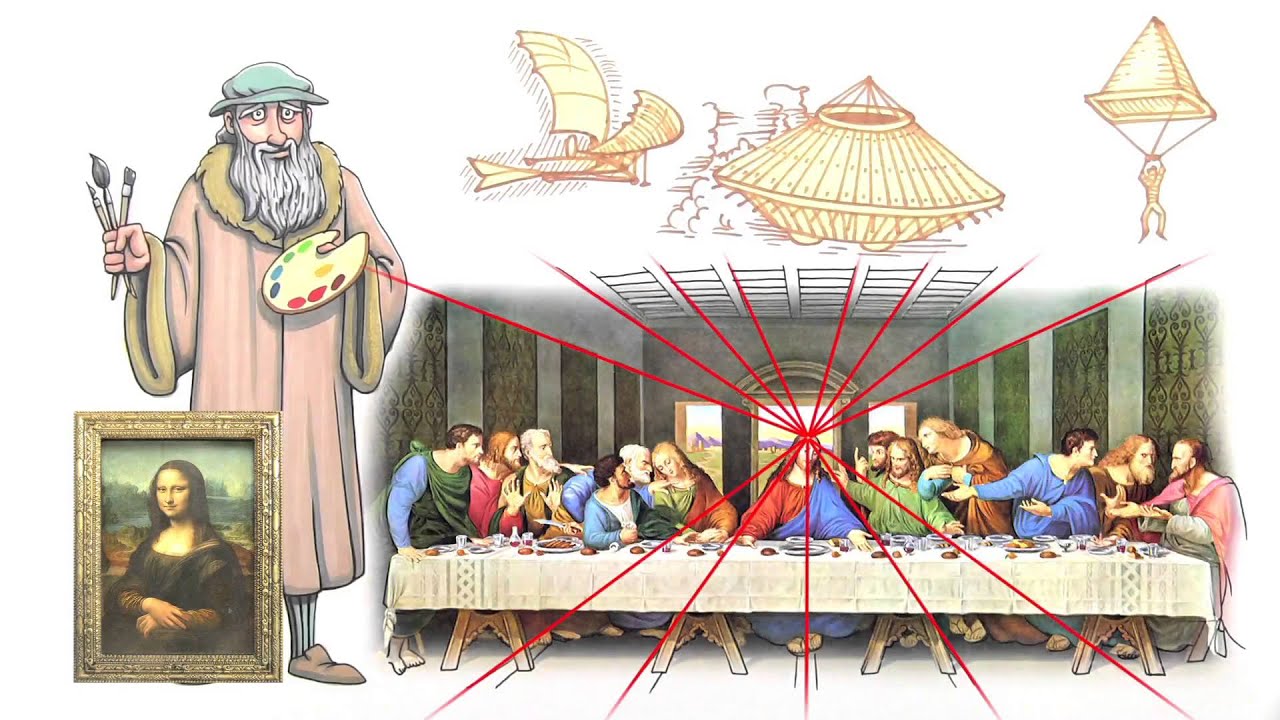
- 😀 Key Renaissance figures include Donatello (sculptor), Leonardo da Vinci (artist and inventor), Michelangelo (artist and poet), and Raphael (painter and architect).
- 😀 Major factors contributing to the Renaissance included the fall of Constantinople (1453), the invention of the printing press (1454), and harsh social and economic conditions of the Middle Ages.
- 😀 The Renaissance led to significant impacts: individual freedom and independence, development of science and art, decline of Church dominance, rise of entrepreneurs, pride in human achievement, and innovation in exploration and science.
Q & A
What does the term 'Renaissance' mean, and when did it occur?
-The term 'Renaissance' comes from the French word 'renaissance', meaning 'rebirth'. It refers to the revival of classical culture, especially Greek and Roman, and occurred from the 14th to the 17th century, peaking around 1510.
Why was Europe referred to as being in a 'Dark Age' before the Renaissance?
-Europe was in a 'Dark Age' because culture and science were stagnant, and the church dominated all aspects of life, restraining intellectual and artistic development.
What were the main social and cultural conditions in Europe before the Renaissance?
-People focused on the afterlife rather than the world, which limited personal freedom and self-esteem. Art was primarily religious, and scientific development was minimal since only the church's teachings were accepted as truth.
What political and economic factors contributed to the rise of the Renaissance?
-Politically, kings had limited real power while nobility held authority. Economically, prosperous cities like Florence, Genoa, and Venice created a new middle class that supported learning and arts, shifting focus toward worldly prosperity and happiness.
How did the fall of Constantinople in 1453 influence the Renaissance?
-The fall of Constantinople led Greek and Roman scholars to flee to Europe, bringing classical texts in literature, law, and art, which fueled interest in studying ancient Greek and Roman culture.
What role did the invention of the printing press play in the Renaissance?
-Invented in 1454 by Johannes Gutenberg, the printing press accelerated the spread of knowledge and ideas, supporting the development of humanism and Renaissance thinking.
Who were some of the most influential figures of the Renaissance and their contributions?
-Key figures include: Donatello (sculptor, known for bronze and marble works like the statue of David), Leonardo da Vinci (artist and inventor, famous for Mona Lisa and The Last Supper), Michelangelo (sculptor and painter, known for David and Sistine Chapel paintings), and Raphael (painter, known for School of Athens and Madonna paintings).
Did the Renaissance oppose religion?
-No, the Renaissance did not oppose religion. While it encouraged humanism and rational thinking, it often enhanced religious art and decorated places of worship.
What were the main impacts of the Renaissance on European society?
-Impacts included increased individual freedom, the development of science, art, and culture, decline of church dominance, strengthening of merchants and entrepreneurs, pride in human potential, and promotion of exploration and innovation.
What factors motivated Europeans to shift from a Middle Ages perspective to Renaissance thinking?
-Factors included the rise of a prosperous middle class, support from progressive rulers and nobles, harsh economic realities prompting reflection on life, exposure to classical knowledge from fleeing scholars, and access to widely distributed ideas through the printing press.
How did art and philosophy change during the Renaissance?
-Art became more realistic, human-centered, and idealized, often emphasizing muscular and idealized human figures. Philosophy shifted towards rational and humanist thinking, while still respecting religious beliefs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)