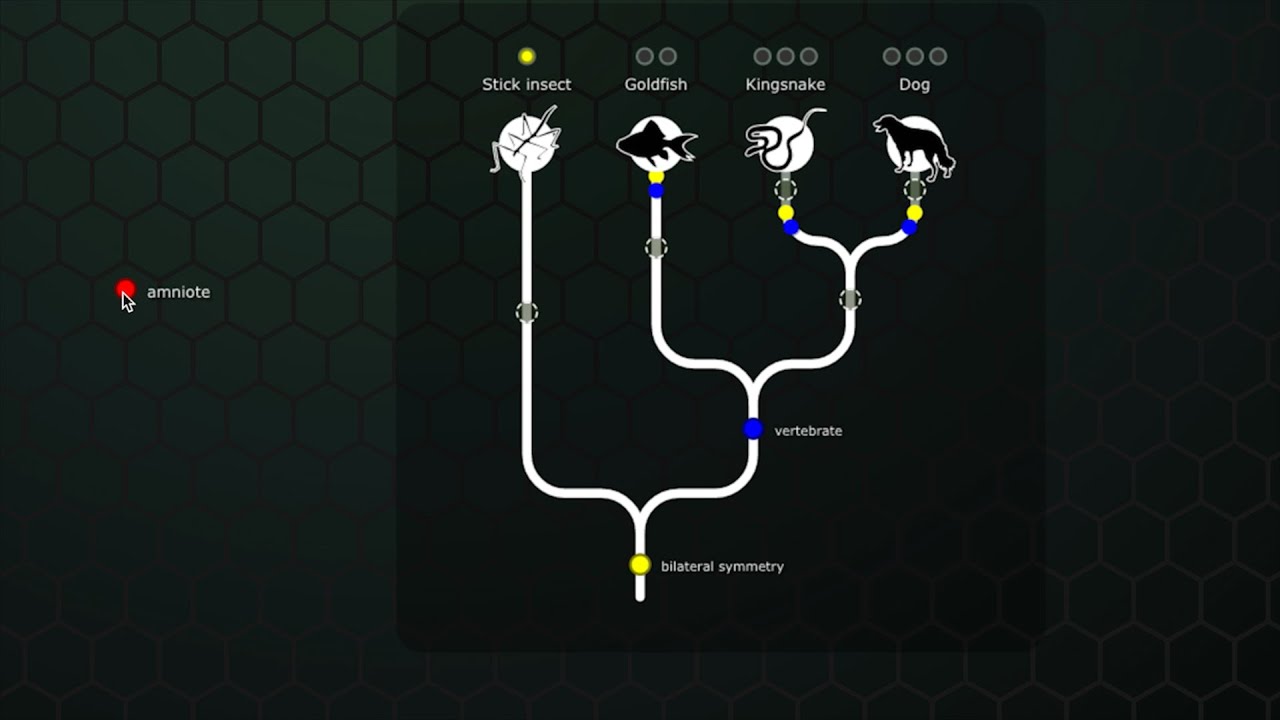
Taxonomy | Classification of Living Organisms
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating science of classification, explaining how scientists organize millions of species into groups based on shared traits. It introduces Carl Linnaeus's binomial nomenclature system, which names species with a two-part Latin or Greek term, helping avoid confusion caused by common names. The video explores the hierarchy of classification, from domains and kingdoms down to species, and emphasizes how genetic discoveries continue to shape our understanding of life. Viewers are invited to learn about the classifications of organisms like the bush baby, bridging the gap between observation and scientific naming.
Takeaways
- 😀 Taxonomy is the science of classifying and naming species to understand relationships between living things.
- 😀 Carl Linnaeus developed a formal classification system that groups organisms based on shared characteristics, such as genus and species.
- 😀 The classification system works like organizing toys into groups based on similarity, but it’s far more complicated because scientists need to agree on how to organize organisms.
- 😀 The classification system is hierarchical, with categories that go from least specific (domain) to most specific (species).
- 😀 There are three main domains of life: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya, each with distinct characteristics and structures.
- 😀 Organisms in the domain Bacteria are simple, unicellular, and lack a nucleus, while Archaea are also unicellular but with significant differences in DNA and structure.
- 😀 Eukarya includes complex organisms with membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
- 😀 The five main kingdoms of life are: Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, Protista, and Bacteria.
- 😀 The kingdom Protista is incredibly diverse, including plant-like, animal-like, and fungi-like organisms that don’t quite fit into those categories.
- 😀 Scientific names, like the two-part name for the bush baby (Galago senegalensis), help avoid confusion caused by local common names and ensure consistency across different regions.
- 😀 The scientific classification continues with levels such as phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species, which help organize organisms in more specific ways as you move down the hierarchy.
Q & A
What is taxonomy?
-Taxonomy is the science of classifying and naming species to better understand the relationships between living things.
What was Carl Linnaeus's contribution to classification?
-Carl Linnaeus developed a formal classification system, grouping organisms into larger categories based on shared characteristics and introducing the binomial nomenclature system for naming species.
How does the classification system resemble organizing toys in a playroom?
-The classification system is compared to organizing toys in a playroom because, like sorting toys by similarities, scientists must organize living things into groups, but they also have to agree on the method of classification, which can be challenging.
What are the three main domains of life?
-The three main domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What is the difference between the domains Bacteria and Archaea?
-Both Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes, meaning they lack a nucleus, but Archaea have unique DNA and structural differences, allowing them to thrive in extreme environments like high heat or high salinity.
What characteristics define organisms in the Eukarya domain?
-Organisms in the Eukarya domain are eukaryotes, meaning they have complex cell structures, including membrane-bound organelles and DNA contained within a nucleus.
How is the Kingdom Fungi different from the Kingdom Plantae?
-Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain energy by consuming other organisms, while plants are autotrophs, making their own food through photosynthesis. Fungi also have cell walls made of chitin, whereas plants have cellulose in their cell walls.
What makes the Kingdom Protista so unique?
-The Kingdom Protista is extremely diverse, containing both plant-like, animal-like, and fungi-like organisms. Many protists are unicellular, but some can also be multicellular.
Why are scientific names used in classification instead of common names?
-Scientific names are used because they provide a universal, standardized way to identify organisms, avoiding confusion from the varying common names used in different regions or languages.
How does the scientific name of a species work?
-The scientific name follows a two-part system called binomial nomenclature. The first part is the genus name, and the second part identifies the specific species within that genus. For example, the scientific name for the bush baby is 'Galago senegalensis,' with 'Galago' being the genus and 'senegalensis' the species.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)