Accounting Cycle - Definition, Example, 9 Steps of Accounting Cycle
Summary
TLDRIn this video, WallStreetmojo explains the key steps of the accounting cycle, from data collection and analysis of transactions to preparing financial statements and closing the books. The cycle includes steps like journalizing transactions, posting to ledger accounts, adjusting trial balances, and creating income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Understanding these steps helps businesses track their financial transactions effectively, and for investors, it offers insight into a company’s financial health. This knowledge is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The accounting cycle is a series of steps every company follows to record, analyze, and close financial transactions.
- 😀 Understanding the accounting cycle is essential for making informed financial decisions about a company.
- 😀 The cycle starts with the collection and analysis of transaction data to ensure accurate financial reporting.
- 😀 Journalizing is the next step, where accountants record transactions into the journal, detailing debits and credits.
- 😀 Posting to the ledger comes after journalizing, organizing transactions by accounts like cash and capital.
- 😀 The unadjusted trial balance is prepared to check if the total debits and credits match, indicating correct entries.
- 😀 Adjusting entries are made to account for accruals, depreciation, and other adjustments needed for accuracy.
- 😀 After adjustments, the adjusted trial balance is created, which reflects all changes and is used to prepare financial statements.
- 😀 Financial statements—such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement—are derived from the adjusted trial balance.
- 😀 Closing the books involves resetting temporary accounts (like revenues and expenses) to prepare for the next period, followed by the post-closing trial balance to ensure all entries are accurate.
Q & A
What is the accounting cycle, and why is it important?
-The accounting cycle is a systematic process that includes collecting, analyzing, recording, and reporting financial transactions. It is important because it helps maintain accurate and reliable financial records, essential for decision-making, financial reporting, and business operations.
What is the first step in the accounting cycle?
-The first step in the accounting cycle is the collection and analysis of transaction data. Accountants gather transaction details, analyze why they occurred, and ensure they are classified correctly under the right accounts.
Why is the journalizing process critical in the accounting cycle?
-Journalizing, or making journal entries, is crucial because it records transactions in the first books of accounts. Each entry must be accurate, as errors in this stage will carry over to later stages, affecting the financial statements.
What role do ledger accounts play in the accounting cycle?
-Ledger accounts summarize the balances from journal entries. After transactions are journalized, they are posted to the respective ledger accounts (e.g., cash, capital). This helps in preparing a trial balance and eventually the financial statements.
What is an unadjusted trial balance, and why is it prepared?
-An unadjusted trial balance is prepared after posting transactions to the ledger accounts. It helps ensure that total debits equal total credits, which is essential for maintaining balance in the books before any adjustments are made.
What are adjusting entries, and when are they necessary?
-Adjusting entries are necessary to correct discrepancies and reflect accruals, depreciation, and amortization. They are made after the unadjusted trial balance is prepared and ensure that the financial statements reflect accurate financial data for the period.
How does the adjusted trial balance differ from the unadjusted trial balance?
-The adjusted trial balance is prepared after adjusting entries are recorded, whereas the unadjusted trial balance is compiled before any adjustments. The adjusted trial balance is used to create financial statements and provides more accurate financial data.
What are the four primary financial statements created from the adjusted trial balance?
-The four primary financial statements are: 1) Income Statement (shows profit/loss), 2) Balance Sheet (lists assets, liabilities, and equity), 3) Cash Flow Statement (tracks cash flow), and 4) Notes (additional disclosures).
What is the purpose of closing the books in the accounting cycle?
-Closing the books ensures that all financial data for the period is accurately recorded. This process allows for the preparation of the financial statements and resets the books for the next accounting period.
What is a post-closing trial balance, and why is it important?
-A post-closing trial balance is prepared after the books are closed to ensure that all transactions have been recorded accurately. It confirms that debit balances equal credit balances and ensures the integrity of the financial data before starting a new accounting period.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Accounting Cycle Step 1: Analyze Transactions
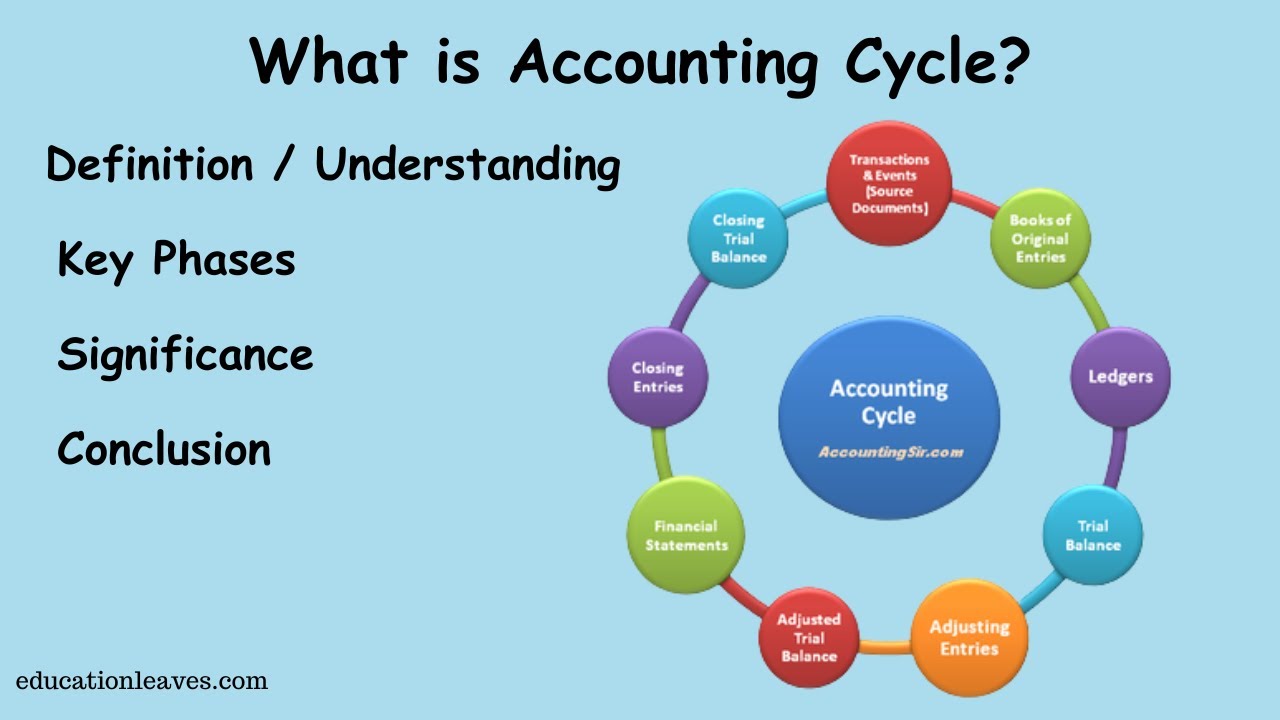
What is Accounting cycle? | Key phase, Significance of Accounting cycle

"CARA MUDAH MEMAHAMI SIKLUS AKUNTANSI PERUSAHAAN DAGANG "
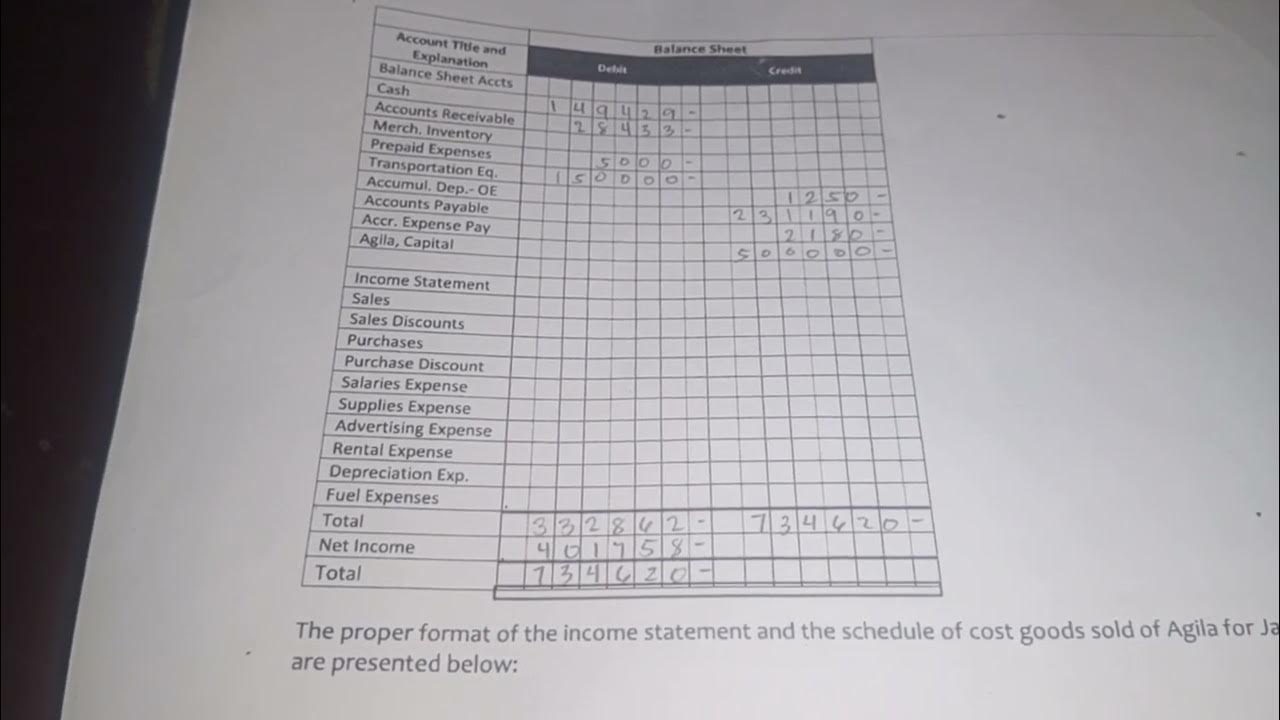
November 15, 2024

Financial Analysis in Arabic - 04 1080p

Seri Pengantar Akuntansi Pemerintahan Soal dan Pembahasan SIklus Akuntansi Pemerintahan (1)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)