Market Maker Models Remastered - Introduction (Part 1)
Summary
TLDRThis video series dives into the Market Maker Models, focusing on swing points instead of traditional PDRs. It explains the key components like daily candles, time frames, and entry/confirmation tools such as change in state, blocks, and fair value gaps. The process is broken down into stages: from smart money reversals to distribution and accumulation phases. The video emphasizes the remastered approach, detailing the buy and sell models, along with real-world examples and time frame alignment. The goal is to offer traders a more effective framework for identifying and executing swing trades in the market.
Takeaways
- 😀 Market Maker Models Workshop focuses on swing points rather than PDs for market analysis and trade strategies.
- 😀 The time frame alignment involves using a high time frame daily swing point and refining it down to hourly, 15-minute, and even 5-minute entries for precision.
- 😀 The market maker buy model in this workshop differs from the classic model by emphasizing swing points rather than points of interest (PDRs).
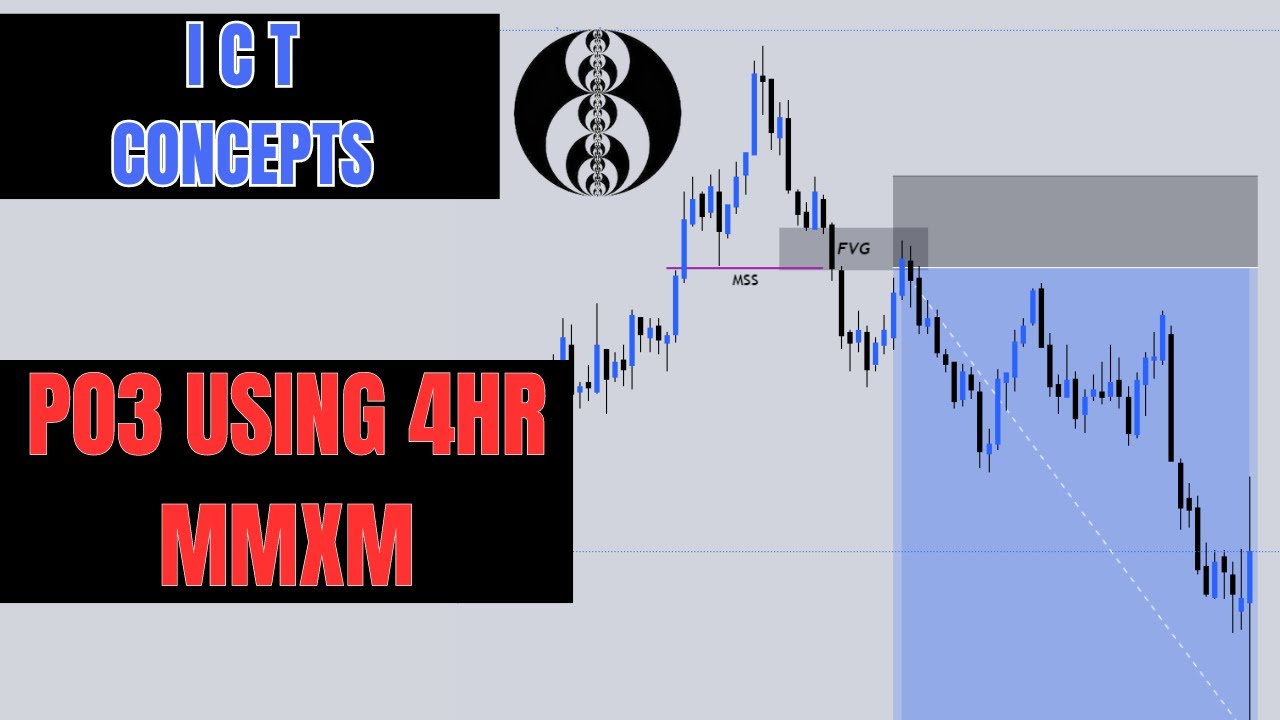
- 😀 The stages of the market maker model include sell side of the curve (candle one), smart money reversal (candle two), and the buy side of the curve (candle three), which is often the expansion candle.
- 😀 The buy side of the curve is characterized by the third candle being an open low-high-close candle, signaling entry points for swing trades.
- 😀 Market maker sell models follow a similar structure, with the first candle representing the buy side, the second confirming the smart money reversal, and the third signaling distribution to the downside.
- 😀 SMT (Smart Money Divergence) is an important concept, indicating when there is a divergence between two correlated assets (e.g., NQ and ES) to signal potential reversals.
- 😀 The workshop emphasizes understanding the change in state of delivery, which is a key factor in confirming market shifts and entry points.
- 😀 Market maker entries can be refined by moving to lower time frames, like 30-minute, hourly, and 5-minute charts, to catch precise entry points with better risk/reward ratios.
- 😀 The approach presented in this workshop is a remastered version of the classic market maker model, focusing on swing points and high time frame alignment for more accurate trading signals.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the 'Market Maker Models' Workshop?
-The 'Market Maker Models' Workshop focuses on explaining the market maker models with an emphasis on swing points, rather than using Points of Interest (PDRs) for entries and analysis.
How do time frames play a role in the Market Maker Models?
-Time frames are crucial for refining market models. A high time frame, such as the daily swing point, can be used for swing trades, and traders can refine these signals down to smaller time frames like hourly, 15-minute, or even 5-minute charts for more precise entries.
What is the difference between the classic Market Maker model and the remastered version?
-The classic Market Maker model focuses on Points of Interest (PDRs) to catch reversals. In contrast, the remastered version focuses on swing points, identifying key price levels based on the direction and structure of daily candles rather than just PDRs.
What are the stages of the Market Maker model?
-The stages include the sell side of the curve, smart money reversal, change in the state of delivery, accumulation, distribution stages, and the silver bullet phase, which represents the fastest stage of the market model.
What is the 'smart money reversal' and how is it used in the strategy?
-The smart money reversal occurs when the market shifts direction after a period of consolidation. It is used to confirm a change in the market’s structure and to signal when to move from a sell to a buy phase or vice versa.
What is an 'open low high close' candle and how does it fit into the strategy?
-An 'open low high close' candle represents a price action pattern that confirms the entry for a swing trade. It helps to identify key points where price expansion happens after a market reversal.
Why is it important to focus on the 'swing point' in the remastered Market Maker model?
-Focusing on the swing point in the remastered model allows traders to identify price levels where the market is likely to reverse or expand, providing more reliable entries based on actual price action rather than just pre-defined areas of interest.
What role does the 'change in state of delivery' play in the strategy?
-The 'change in state of delivery' signals a shift in market structure, indicating that the previous trend or consolidation phase has ended. This helps traders identify the right moment to enter a trade after the market confirms a direction change.
What is an example of how a market maker buy model can be applied in practice?
-In a practical scenario, a trader would wait for the price to manipulate a consolidation range, look for a smart money reversal, and then enter on a third expansion candle. The trader may also refine the entry by looking for a fair value gap or using a lower time frame for better accuracy.
How can a trader confirm their entry when using the 'market maker sell model'?
-A trader can confirm their entry by looking for a reversal at the buy side of the curve, followed by the smart money reversal and change in state of delivery. They would then trade the third candle, often characterized as an 'open high low close' candle, to enter the sell position.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)