Identifying Minerals -- Earth Rocks!
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the identification and significance of minerals in rock formation. It highlights the importance of minerals in understanding geologic processes and the conditions under which rocks form. Through various distinguishing characteristics, including luster, streak, crystal form, cleavage, hardness, and density, viewers learn to identify key rock-forming minerals like quartz, feldspar, calcite, and garnet. The video also emphasizes how these minerals provide clues about the temperature, pressure, and chemical environment during rock formation, offering a deeper understanding of Earth's geology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Minerals are the building blocks of rocks, and understanding them is key to studying Earth's geologic history.
- 😀 Identifying minerals in rocks helps uncover information about the temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions during rock formation.
- 😀 There are over 300 different minerals, but a few dozen are the most common rock-forming minerals.
- 😀 Color is not a reliable characteristic for identifying minerals due to the wide variety of colors in common minerals like quartz and feldspar.
- 😀 Luster (how light reflects from a mineral) is a key distinguishing feature, with minerals categorized as metallic or non-metallic.
- 😀 Streak tests, where minerals are scraped on a streak plate, help differentiate minerals, as their streak color often differs from their surface color.
- 😀 Hardness is a critical property in mineral identification, with softer minerals being scratched by nails or other objects.
- 😀 Cleavage refers to how minerals break along flat planes, while fracture refers to irregular breakage patterns.
- 😀 Density, or specific gravity, can be used to distinguish minerals, with some minerals being much denser than others.
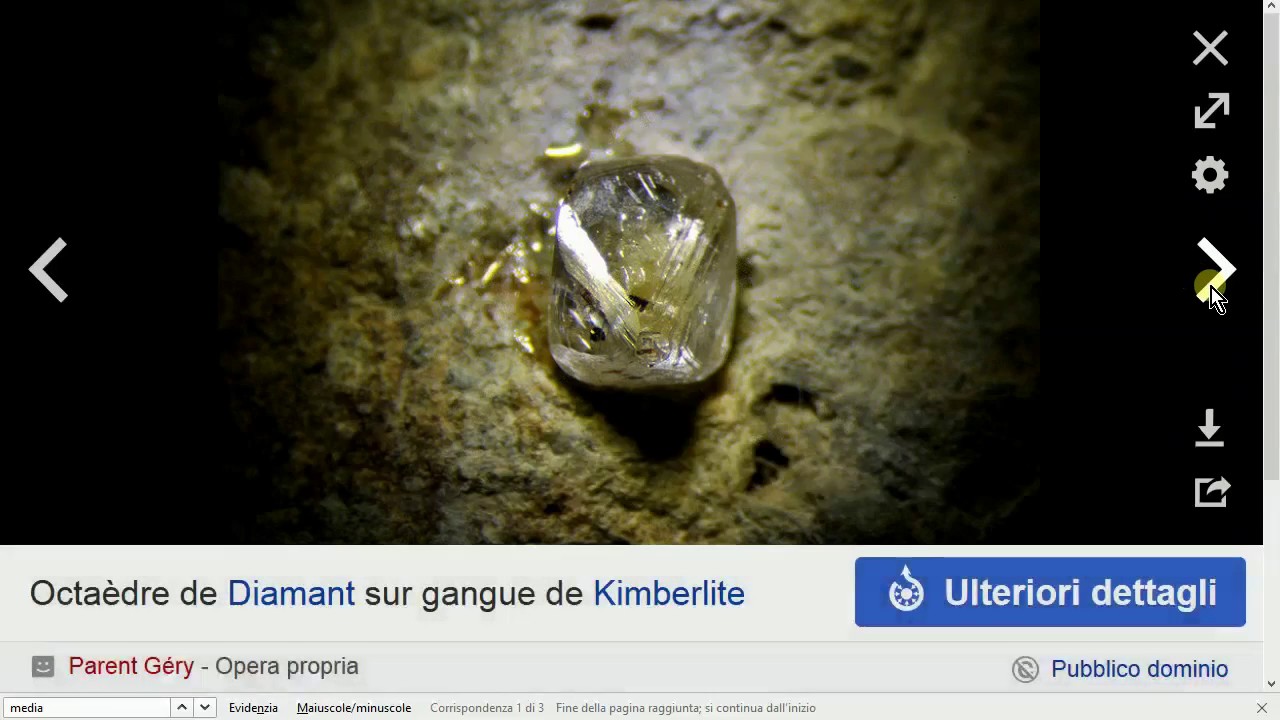
- 😀 Crystal form reveals a mineral's internal structure and can be used for identification, though natural weathering often hides perfect crystals.
Q & A
Why is studying minerals important in geology?
-Studying minerals is crucial because all rocks on Earth are composed of minerals, and understanding the minerals within rocks can reveal information about the conditions and processes that formed them, including temperature, pressure, and chemical environments.
How many minerals are known in the world, and how many are common rock-forming minerals?
-There are over 300 known minerals in the world, but only a few dozen represent the core of common rock-forming minerals.
What are some basic methods to identify minerals without advanced technology?
-Basic methods for mineral identification include using sensory traits such as color, luster, hardness, streak, touch, and even taste in some cases. These traits can help distinguish minerals without the need for expensive technology like mass spectrometers or electron microscopes.
What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic luster in minerals?
-Metallic luster means that light reflects off the mineral's surface similarly to how it reflects off metals, making the mineral appear shiny. Non-metallic luster can vary, including categories like greasy, glassy, dull, pearly, and resinous, among others.
What is a mineral's streak, and how does it help in identification?
-A mineral's streak is the color of the powder it leaves behind when scraped across a streak plate. This can be particularly useful for identifying minerals with similar colors, as their streak color may differ.
What role does crystal form play in identifying minerals?
-Crystal form reflects a mineral's internal crystalline structure and is a key identifying feature. Minerals may grow in perfect crystals, but more often they form massive shapes due to space limitations. Even if the crystals are broken, their form can still provide valuable identification clues.
What is the significance of cleavage in mineral identification?
-Cleavage refers to how a mineral breaks along smooth planes. Minerals can display perfect cleavage (breaks along regular planes) or fracture (breaks irregularly). The pattern and number of cleavage planes can help distinguish between minerals with similar appearance.
How does density (specific gravity) help in mineral identification?
-Density, or specific gravity, is a measure of how heavy a mineral is for its size. Minerals with high density, like galena (lead sulfide), are significantly heavier than others, providing a useful characteristic for identification.
Why is the mineral halite associated with evaporative environments?
-Halite, also known as rock salt, forms when salty water evaporates in hot, dry climates. Its presence in a rock suggests the rock formed in an evaporative environment, such as salt flats or evaporating ponds.
What is the identifying feature of the feldspar family of minerals?
-Feldspar minerals are identified by their hardness, opacity, and two cleavage planes at right angles. Some feldspar varieties, like plagioclase feldspar, show a distinctive feature called twinning, which appears as parallel grooves on the mineral surface.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)