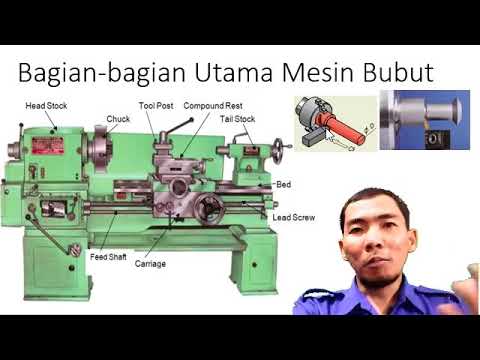
bagian bagian mesin bubut
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of the main parts of a lathe machine. The speaker discusses key components such as the headstock, tailstock, support elements, and bed. Each part’s function is outlined, including the main spindle, speed transmission, and tool movement mechanisms. Emphasis is placed on the importance of maintaining precision in the machine's bed and other parts. The video serves as an informative guide to understanding the fundamental components of a lathe machine and their respective roles in the machining process.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lathe machine has three main parts: headstock, tailstock, and support components.
- 😀 The headstock is where the main spindle and workpiece are mounted, and it houses the speed control levers and transmission system.
- 😀 The tailstock is used to support long workpieces and can be equipped with a rotary center for stability.
- 😀 The headstock functions as the central control for the lathe, managing the spindle's rotation and speed adjustments.
- 😀 The tailstock also serves as a drilling unit, where drills or clamps can be mounted for specific operations.
- 😀 The support components include the toolp (tool post), top slide, cross slide, and saddle, all contributing to the precise movement of the cutting tool.
- 😀 The top slide moves the cutting tool at an angle, while the cross slide allows for sideways movement of the tool.
- 😀 The saddle acts as the base for supporting the tool and helps move the chisel in a sideways direction during operation.
- 😀 The machine bed (or base) is essential for the lathe's precision and serves as the track for the saddle’s movement.
- 😀 Maintaining the cleanliness and precision of the machine bed is critical to ensure the lathe functions accurately over time.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe machine?
-The headstock primarily holds the main spindle, where the workpiece is mounted. It also contains speed control levers, a replacement gear, and serves as the main control center for the lathe.
How does the tailstock support the lathe's functionality?
-The tailstock supports long workpieces by installing a rotary center and can be used for drilling by holding a drill clamp or drill chuck. It ensures stability during operations such as turning and drilling.
What is the purpose of the tool post in the lathe machine?
-The tool post serves as the housing for the cutting tools (chisels), allowing them to be securely mounted and adjusted during the machining process.
What are the key components of the carriage system in a lathe machine?
-The carriage system consists of the tool post, top slide, cross slide, and saddle. These components move and adjust the tool in various directions to perform precise cutting and shaping.
What function does the top slide serve in the carriage system?
-The top slide allows the tool to move at specific angles, enabling more intricate or angled cuts during the lathe operation.
What does the cross slide do in a lathe machine?
-The cross slide moves the tool in the transverse direction, allowing for cutting in a horizontal or lateral plane.
Can you explain the role of the saddle in the lathe machine?
-The saddle is the base that supports the carriage system and moves the tool sideways. It provides the stability and precision required for the machining process.
What is the difference between the upper and lower carriages in the lathe machine?
-The upper carriage, also known as the LED screw, moves the saddle for automatic lathe threading. The lower carriage (Feedsaf) moves the saddle for flat lathe operations, facilitating automatic tool movement.
Why is the machine bed important in a lathe machine?
-The machine bed acts as a rail or track for the saddle to move sideways. It is crucial for maintaining the lathe's precision and requires regular maintenance to ensure accurate operations.
What are some of the additional components found in a lathe machine?
-Additional components include the machine feet for stability, a coolant hose for lubrication, an engine brake for safety, and a barrier or guard to protect operators from moving parts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)