Hukum Coulomb Kelas 12
Summary
TLDRThis video explains Coulomb's Law for Physics Class 12, focusing on the attraction and repulsion between two charges based on their type and magnitude. It demonstrates how the force between charged objects depends on both the product of the charges and the square of the distance between them. Through multiple examples, including scenarios with different charge magnitudes and distances, the video illustrates the direct and inverse relationships outlined in Coulomb's Law. Additionally, the video explores more complex situations involving multiple charges and two-dimensional force calculations, helping viewers understand the practical application of these concepts in physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Kulom's Law explains the relationship between the force of attraction/repulsion and the charges and distance between two charged objects.
- 😀 There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative. Objects with opposite charges attract each other, while objects with the same charge repel each other.
- 😀 Kulom's Law states that the force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
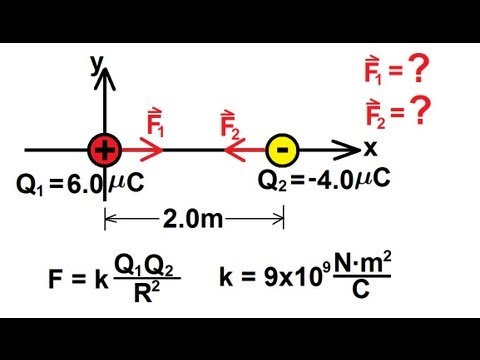
- 😀 The formula for Kulom's Law is: F = k * Q1 * Q2 / r², where k is the electric constant (9 x 10⁹ N·m²/C²), Q1 and Q2 are the charges, and r is the distance between the charges.
- 😀 Example 1 shows how increasing the charge of Q2 results in a stronger force on Q1, illustrating that force is directly proportional to the charge.
- 😀 The second statement of Kulom's Law shows that as the distance between two charges increases, the force between them decreases, proving an inverse relationship with distance.
- 😀 In example 2, the force decreases as the distance between the charges increases, confirming that force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
- 😀 In the case of multiple charges, the total force felt by a charge is the vector sum of the forces exerted by the other charges. This involves both attraction and repulsion forces.
- 😀 Example 3 discusses a scenario with three charges arranged in parallel. The total force on Q1 is the result of the forces from Q2 (repulsion) and Q3 (attraction), which are calculated and then combined.
- 😀 In the case of charges arranged in a triangle (Example 4), the total force on Q1 is found by calculating forces on the x and y axes and then combining them using the Pythagorean theorem to find the resultant force.
- 😀 The direction of the total force can be determined by using trigonometry. For example, the angle of the force relative to the x-axis can be calculated using the arctangent function.
Q & A
What is Coulomb's Law, and how does it describe the interaction between two charges?
-Coulomb's Law states that the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The mathematical form of this law is F = k * Q1 * Q2 / r^2, where F is the force, k is the electric constant, Q1 and Q2 are the charges, and r is the distance between them.
What are the two key relationships described by Coulomb's Law?
-The two key relationships in Coulomb's Law are: 1) The force is directly proportional to the product of the charges (Q1 * Q2), meaning the greater the charges, the greater the force. 2) The force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r^2), meaning the greater the distance between the charges, the smaller the force.
What happens when two objects with different charges interact according to Coulomb's Law?
-When two objects with different charges interact, they will attract each other with a force, F. The force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, with a positive charge attracting a negative charge.
What happens when two objects with the same charge interact according to Coulomb's Law?
-When two objects with the same charge (both positive or both negative) interact, they will repel each other with a force, F. The force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
In the given example, what is the magnitude of the force when Q1 = -1 * 10^-6 C, Q2 = 2 * 10^-6 C, and r = 0.15 m?
-Using Coulomb's Law, F = (9 * 10^9) * (-1 * 10^-6) * (2 * 10^-6) / (0.15)^2, the magnitude of the force is calculated to be 0.8 N.
How does the force change when Q2 is increased from 2 * 10^-6 C to 5 * 10^-6 C in the given example?
-When Q2 is increased to 5 * 10^-6 C, the magnitude of the force increases to 2 N, as the force is directly proportional to the product of the charges.
What happens to the force when the distance between two charges is increased?
-As the distance between two charges increases, the force between them decreases. This is because the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r^2). For example, when the distance is increased from 0.15 m to 0.45 m, the force decreases significantly.
What does the negative sign indicate in the total force calculation for three charges arranged in parallel?
-The negative sign indicates that the force on charge Q1 is directed to the left, meaning Q1 is being repelled by Q2 more strongly than it is being attracted by Q3.
How is the total force on Q1 calculated when three charges are arranged in a parallel configuration?
-The total force on Q1 is calculated by considering the forces from Q2 and Q3 separately, then subtracting the force from Q2 (repulsion) from the force from Q3 (attraction). The formula is F_total = F3 - F2.
What is the magnitude of the total force acting on Q1 when the charges form a right triangle?
-When the charges form a right triangle, the total force on Q1 is found by calculating the forces along the x-axis and y-axis separately, then using the Pythagorean theorem to find the resultant force. In the given example, the total force is 6.03 N.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Coulomb's Law | Electrostatics | Electrical engineering | Khan Academy
Physics 35 Coulomb's Law (1 of 8)

[NEW VERSION!]GAYA COULOMB | Listrik Statis - Fisika Kelas 12

01. Conceptos Básicos de la Electrostática (Introducción)

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Hukum Coulomb & Medan Listrik | GIA Academy

Listrik Statis Kelas 9 SMP (Part-2) Gaya Coulomb
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)