PENYETARAAN REAKSI REDOKS
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial covers the process of balancing redox reactions using two primary methods: the oxidation number method and the half-reaction method. It begins with an introduction to redox reactions, explaining the concepts of oxidation and reduction. The video then demonstrates step-by-step techniques for balancing redox reactions, focusing on balancing atoms, charges, and electrons. Detailed examples, including the reaction of Cr₂O₇²⁻, are provided to illustrate how to apply these methods effectively. The tutorial aims to help viewers understand the principles of redox reactions and how to approach their balanced equations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Redox reactions involve both oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons), and they always occur together.
- 😀 The oxidation number of an element changes during a redox reaction, which helps identify whether a substance is oxidized or reduced.
- 😀 In a redox reaction, if one element's oxidation state increases, it's oxidized, and if it decreases, it's reduced.
- 😀 A reaction with both oxidation and reduction processes is called a redox reaction, such as the combustion of sulfur dioxide.
- 😀 The two main methods for balancing redox reactions are the oxidation number method and the half-reaction method.
- 😀 The oxidation number method balances reactions by tracking changes in oxidation states and adjusting for electron loss or gain.
- 😀 The half-reaction method splits the redox reaction into two parts: one for oxidation and one for reduction, making it easier to balance.
- 😀 Balancing redox reactions requires ensuring the number of atoms, charges, and electrons are equal on both sides of the equation.
- 😀 In balancing reactions, atoms can be balanced by adjusting coefficients, while charges are balanced by adding electrons or ions like H⁺.
- 😀 Example: The reaction of Cr₂O₇²⁻ with SO₂ shows how to apply both methods by adjusting atoms, charges, and adding electrons to balance the equation.
Q & A
What is a redox reaction?
-A redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction involves both oxidation and reduction processes, where one species loses electrons (oxidation) and another gains electrons (reduction).
How can we identify a redox reaction?
-A redox reaction can be identified by a change in oxidation numbers of elements involved in the reaction. Oxidation involves an increase in oxidation number, while reduction involves a decrease.
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction in redox reactions?
-Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, leading to an increase in oxidation number, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in oxidation number.
How do you balance redox reactions using the oxidation number method?
-In the oxidation number method, first balance the atoms involved in the redox process. Then, balance the charges by adding electrons. Lastly, balance oxygen and hydrogen atoms by adding water and H+ ions, respectively.
What are the steps involved in the half-reaction method for balancing redox reactions?
-The half-reaction method involves breaking the reaction into two half-reactions: one for oxidation and one for reduction. Each half-reaction is balanced separately, with oxygen balanced using water, hydrogen using H+ ions, and charges using electrons.
What is the purpose of adding H2O in redox reactions during balancing?
-H2O is added to balance the number of oxygen atoms in the reaction. It is added to the side where oxygen is lacking.
What is the role of H+ ions in balancing redox reactions?
-H+ ions are used to balance the number of hydrogen atoms in the reaction, particularly in acidic conditions where the medium is not neutral.
What are the key steps in balancing redox reactions using the oxidation number method?
-The key steps include: balancing the number of atoms involved in the redox reaction, balancing the number of electrons, balancing the charges by adding H+ or H2O, and ensuring the overall number of atoms and charges are equal on both sides of the equation.
In the provided example, how is the number of electrons equalized during the balancing process?
-The number of electrons is equalized by adjusting the coefficients of the compounds in the half-reactions. In this case, the number of electrons lost during oxidation is matched by the number of electrons gained during reduction.
Why is it necessary to add electrons during the balancing of redox reactions?
-Electrons are added to ensure that the charges on both sides of the equation are equal. This step helps to satisfy the law of conservation of charge in a redox reaction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PENYETARAAN REAKSI REDOKS | CARA SETENGAH REAKSI DAN BILANGAN OKSIDASI

Module 2 - Balancing Redox - Oxidation Number Method - 1

19.2 Balancing Redox Equations
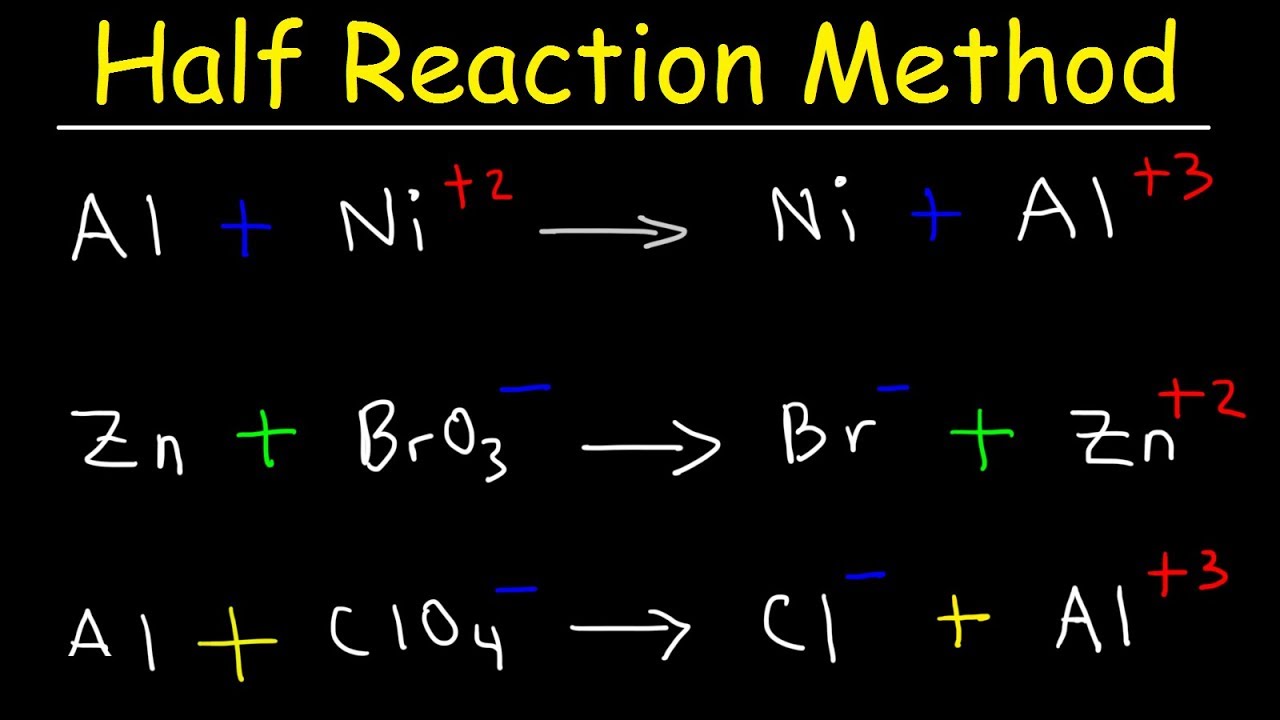
Half Reaction Method, Balancing Redox Reactions In Basic & Acidic Solution, Chemistry

Trick for Balancing Redox Reactions in Acidic Medium

Penyetaraan Reaksi Redoks Metode Perubahan Bilangan Oksidasi | Kimia Kelas 12
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)