How I Would Build a Business in 2025 (If I Had to Start Over)
Summary
TLDRThis video provides valuable insights into business growth, focusing on the relationship between customer acquisition cost (CAC) and lifetime value (LTV). The speaker explains how scaling a business inevitably increases costs and introduces inefficiencies, such as the need for more team members. To stay profitable, businesses must improve their models by raising prices, reducing costs, and optimizing customer acquisition strategies. The importance of a strong business model versus relying on cheaper methods is emphasized, alongside strategies like upsells, cross-sells, and financing to enhance cash flow. Ultimately, it's about managing cash effectively to scale successfully.
Takeaways
- 😀 Customer acquisition costs (CAC) tend to increase as businesses scale, particularly when targeting colder markets or facing more competition.
- 😀 As you expand your business, inefficiencies arise due to the need to hire and train new employees, leading to a temporary decrease in profitability.
- 😀 The key to successful scaling is ensuring your business model can support the added costs of new hires and processes while maintaining profitability.
- 😀 The LTV (Lifetime Value) to CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) ratio is essential for business growth; businesses should aim to maximize this ratio for better returns.
- 😀 Businesses should focus on improving the customer experience through methods like upselling, downselling, cross-selling, and offering financing options.
- 😀 Raising prices, reducing operational costs, and optimizing payment collection methods are all strategies to increase revenue while scaling.
- 😀 The quality of customers is more important than the cost to acquire them; businesses should focus on acquiring high-value customers, not just cheap ones.
- 😀 Improving the offer, creative ads, and conversion rate optimization (CRO) can lower CAC and increase efficiency in customer acquisition.
- 😀 Companies need to balance the cost of customer acquisition with the return on investment to ensure long-term profitability.
- 😀 Scaling is not just about acquiring more customers but ensuring your business model can afford the inefficiencies that come with growth.
- 😀 Being willing to spend more on acquiring higher-quality customers, even if it means higher upfront costs, can lead to a more profitable business in the long run.
Q & A
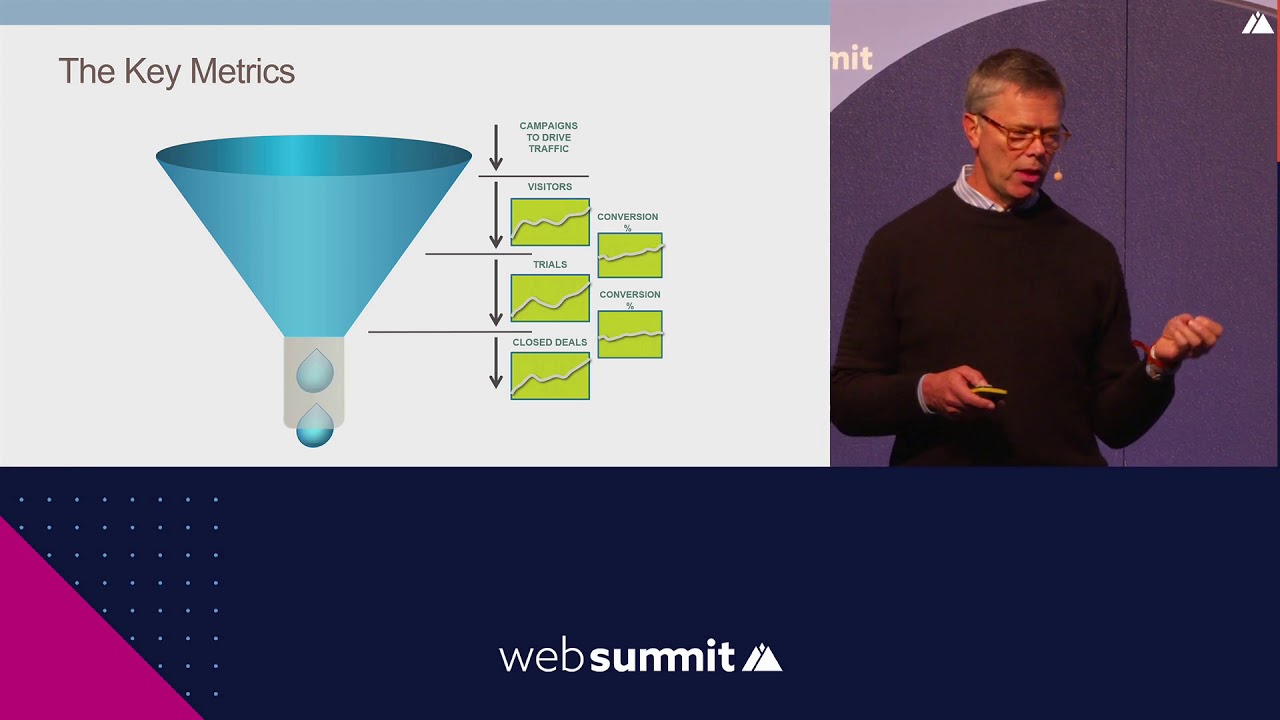
Why does the cost of acquiring customers typically increase over time?
-The cost of acquiring customers increases over time due to market saturation, more competitors entering the marketplace, and the algorithm reaching colder markets with less interested individuals. As a result, more resources are required to convert the same number of customers, driving up the customer acquisition cost (CAC).
How does scaling a business impact the internal infrastructure and costs?
-As a business scales, it requires additional infrastructure, such as management layers and new team members (e.g., sales, marketing, account reps). These additions introduce inefficiencies, as new employees may not be as productive initially, leading to higher operational costs and affecting profitability in the short term.
What is the significance of the LTV to CAC ratio when scaling a business?
-The LTV to CAC ratio is crucial because it determines whether a business is making a sustainable profit from acquiring customers. A higher ratio indicates that a business is generating more revenue from each customer relative to the cost of acquiring them. This ratio is a key metric in scaling, ensuring that the business can continue growing even as customer acquisition costs rise.
How can businesses immediately increase their revenue without acquiring new customers?
-Businesses can increase revenue through several strategies: raising prices, reducing costs, offering upsells (more expensive options), introducing downells (cheaper alternatives), adding financing options, or cross-selling additional products. These methods help boost the lifetime value (LTV) of existing customers.
What is the difference between an upsell and a downell?
-An upsell involves offering a more expensive version of a product or service, while a downell offers a cheaper alternative to a customer who might not be able to afford the original offering. Both strategies can increase revenue, but they need to be applied carefully to avoid reducing overall profitability.
Why is it important for businesses to focus on improving their business model rather than just seeking cheaper leads?
-Focusing solely on acquiring cheaper leads can be a short-term fix and may lead to low-quality customers. A better business model allows businesses to afford more expensive leads, leading to higher-quality customers. This strategic approach gives a competitive advantage over businesses relying on cheaper customer acquisition methods, which are easily replicated.
What does it mean for a business to 'pay to play' in terms of customer acquisition?
-'Paying to play' refers to the willingness to invest more money into acquiring high-quality customers, even if it means spending more upfront. The idea is that high-value customers can generate a much higher return over time, justifying the higher acquisition costs.
How can businesses balance between customer acquisition cost (CAC) and customer lifetime value (LTV)?
-Businesses should aim for a balanced approach where the CAC is optimized for the highest possible LTV. Rather than focusing solely on lowering CAC, they should seek customers who will provide a higher return in the long term. This ensures that the business can continue to grow sustainably while managing the upfront costs of acquisition.
What happens when a business scales and has to bring in new employees or systems?
-When a business scales, the addition of new employees or systems (e.g., salespeople, marketers, account reps) often leads to temporary inefficiencies. These new employees take time to become as productive as existing team members, and this lag can cause short-term decreases in performance and profitability, even though it’s necessary for long-term growth.
Why is it important for a business to have a cushion in terms of lifetime gross profit when scaling?
-A cushion in lifetime gross profit is essential to cover the additional costs of scaling, such as hiring new employees or increasing marketing efforts. This cushion ensures that the business can continue to operate smoothly even during periods of inefficiency and can afford the temporary dips in profitability that often occur during growth.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Business Owners: You NEED to Know This

How I Spent $40K on Ads and Quadrupled my $ ($30k/month SaaS App)

KPIs for Digital Marketing | How to Evaluate Your Marketing Performance
The SaaS business model & metrics: Understand the key drivers for success

This Will Make You More Profit Than 99% Of Businesses

How To Create a Marketing Budget (Proven Formula)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)