¿Qué son las potencias Activa, Reactiva y Aparente? ⚡ Triángulo de Potencias
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of electrical power, focusing on the distinctions between active, reactive, and apparent power. Active power is useful for generating work, while reactive power, though not directly useful, is linked to devices like motors and generators that involve coils. The video uses the analogy of beer and foam to differentiate active power from reactive power. It introduces the power triangle, illustrating how apparent power combines both active and reactive power. Lastly, it touches on the importance of the power factor, defined by the cosine of an angle, in understanding the efficiency of power use.
Takeaways
- 😀 Power is defined as the amount of energy used in a specific time, measured in joules per second (watts).
- 😀 In direct current (DC) circuits, power is calculated as the product of voltage and current intensity.
- 😀 In alternating current (AC) circuits, more phenomena come into play, requiring a distinction between active power and reactive power.
- 😀 Active power is the power consumed to perform useful work, like heating or generating motion.
- 😀 Reactive power does not perform useful work but is essential for the operation of devices with coils, such as motors and transformers.
- 😀 An analogy of beer and foam is used to explain that active power is the 'beer' (useful), while reactive power is the 'foam' (not directly useful).
- 😀 Although reactive power is not directly useful, it affects the capacity of transmission lines by taking up space and reducing the ability to carry active power.
- 😀 Coils in motors and generators create reactive power, which can oppose the power created by capacitors, leading to the need for capacitor banks in substations.
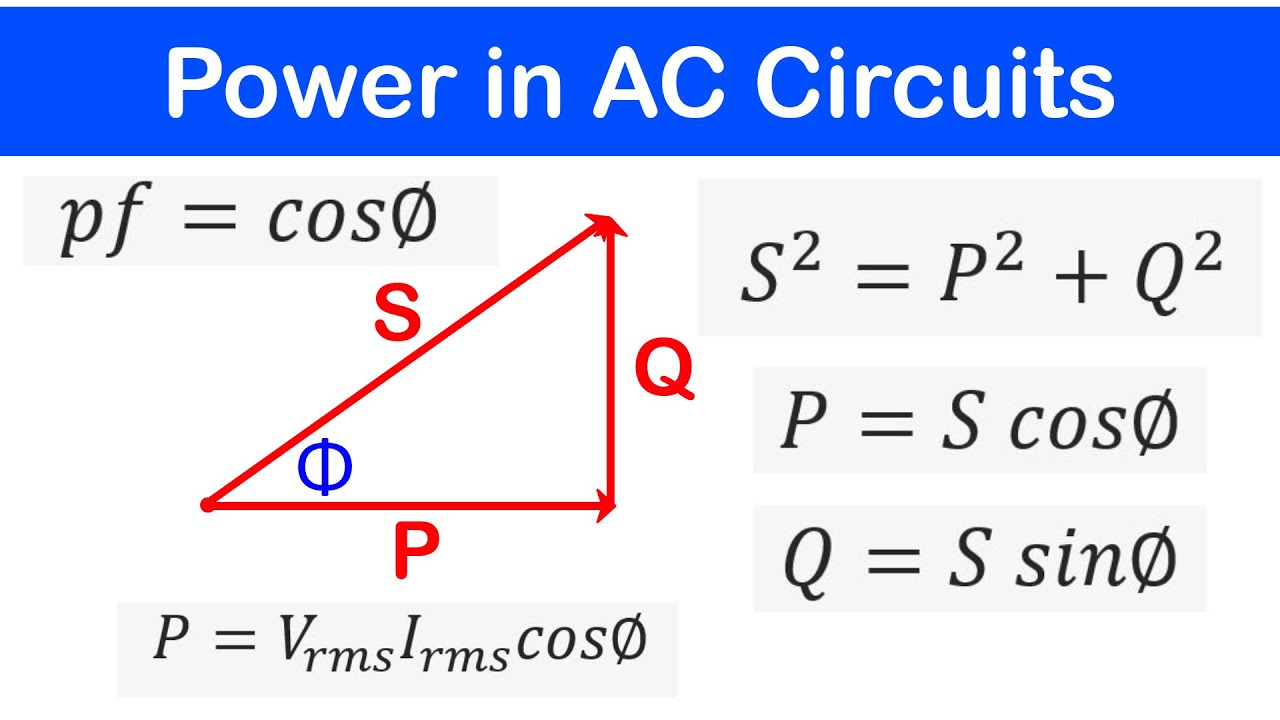
- 😀 The power triangle is a key concept for understanding how active power, reactive power, and apparent power relate to each other in AC circuits.
- 😀 Apparent power is the vector sum of active and reactive power, and is represented by the hypotenuse of the power triangle.
- 😀 All forms of power are measured in the same units (watts), even though they are differentiated by terms such as reactive and apparent power, which refer to the type of power involved.
- 😀 The power factor, which is the cosine of the angle in the power triangle, helps determine the proportion of useful active power in the total apparent power circulating in the system.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video is explaining electrical power, particularly the division into active, reactive, and apparent power, and how they relate to each other through the power triangle.
Why is the concept of power important for engineers?
-The concept of power is crucial for engineers as it helps quantify the amount of energy used over time and is essential in understanding and managing electrical systems, particularly in terms of voltage and current intensity.
What is the difference between active and reactive power?
-Active power is the power that is consumed and performs useful work, such as generating heat or mechanical energy. Reactive power, on the other hand, does not perform any useful work but is necessary for the functioning of devices like motors and transformers.
How is active power calculated in direct current circuits?
-In direct current circuits, active power is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current intensity, represented as P = V x I, where P is the power, V is the voltage, and I is the current.
What role do coils play in generating reactive power?
-Coils, typically found in devices like motors and transformers, generate reactive power through the magnetic fields they create. This reactive power is essential for the operation of such devices, even though it doesn’t perform useful work like active power.
Why is reactive power transported through high-voltage lines if it's not useful?
-Although reactive power doesn't do useful work, it is transported through high-voltage lines because it is necessary to support the magnetic fields in devices like motors and transformers. Without it, the system wouldn't function properly.
What is the power triangle and how does it relate to active, reactive, and apparent power?
-The power triangle is a graphical representation where the apparent power is the vector sum of active power and reactive power. Active power is represented on the horizontal axis, reactive power on the vertical axis, and the hypotenuse represents the apparent power.
What does apparent power represent in the power triangle?
-Apparent power represents the total power circulating in the system, combining both active and reactive power. It is the hypotenuse of the power triangle, and its magnitude is determined by the active and reactive power components.
How are the units of active power, reactive power, and apparent power related?
-All three types of power are measured in similar units: watts (joules per second). Active power is measured in watts, reactive power in volt-amperes reactive (which is conceptually similar to watts), and apparent power in volt-amperes.
What is the power factor and how is it calculated?
-The power factor is the cosine of the angle between the active power and apparent power in the power triangle. It indicates how much of the total apparent power is being used as active power and is a key factor in determining the efficiency of power use in a system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Fator de Potência / Correção do FP
44 - Power in AC Circuits 1 | Power Triangle - Apparent, Real and Reactive Power

Circuitos Trifásicos Equilibrados e Ligação Estrela e Triângulo (#65)

Complex Power || Apparent Power || Real || Example 11.11 || Practice Problem 11.11 || ENA 11.6(E)

Power factor explained | Active Reactive Apparent Power correction

What is Apparent Power ? || Example & Practice11.9 || Example & Practice 11.10 || ENA 11.5(English)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)