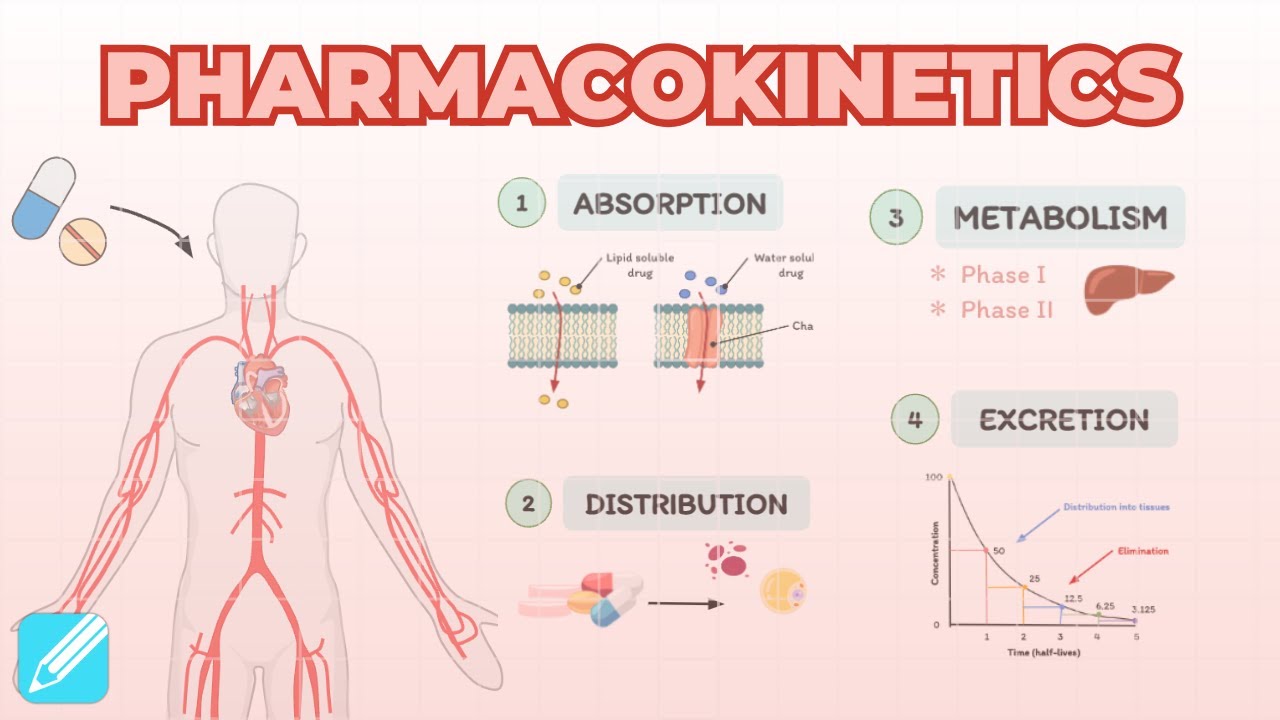
FARMAKOLOGI - Prinsip Farmakokinetika Distribusi Metabolisme
Summary
TLDRThis video covers key concepts in pharmacokinetics, focusing on the processes of drug distribution, metabolism, and excretion. The distribution of drugs in the body is influenced by factors such as solubility and protein binding, with different body areas experiencing fast or slow distribution. Metabolism, primarily occurring in the liver, converts drugs into metabolites for easier elimination. The video also discusses pharmacokinetic parameters like volume of distribution, clearance, half-life, and bioavailability, concluding with the excretion process, where drugs are eliminated from the body, primarily through the kidneys.
Takeaways
- 😀 Distribution is the process of transporting drugs in the body through the blood to the target action site, influenced by protein binding and solubility (water or fat soluble).
- 😀 Fast distribution areas in the body include the liver, heart, kidneys, and brain, while slower distribution occurs in the muscles, skin, and fat tissue.
- 😀 The volume of drug distribution is influenced by body fluids, with plasma being the smallest compartment, interstitial fluid being moderate, and intracellular fluid being the largest.
- 😀 Serum concentration decreases during the elimination phase of a drug, which is important for understanding drug removal over time.
- 😀 Metabolism involves the biological transformation of drugs into metabolites that are more soluble or active, primarily occurring in the liver but also in kidneys, lungs, and mucosa.
- 😀 Phase 1 of metabolism involves modifying drugs to become more polar (hydrophilic), making them easier to eliminate, while Phase 2 involves conjugation with acids or amino acids.
- 😀 The first-pass effect refers to the metabolism of a drug in the liver before it reaches the systemic circulation, affecting drug potency and delivery to target tissues.
- 😀 Enzymes like cytochrome P450 play a key role in drug metabolism, converting lipophilic drugs into more water-soluble forms for easier elimination.
- 😀 Metabolites, like those from acetaminophen, can be hepatotoxic (damaging to the liver), highlighting the risks associated with drug metabolism.
- 😀 Excretion is the process of eliminating drugs from the body, primarily through urine via the kidneys, though drugs can also be excreted through sweat, eyes, or the digestive tract.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video focuses on explaining the principles of pharmacokinetics, covering the processes of drug distribution, metabolism, and excretion, as well as key pharmacokinetic parameters.
What factors influence the distribution of a drug in the body?
-The distribution of a drug is influenced by its solubility (water or fat-soluble), plasma protein binding, and the ability of the drug to pass through biological barriers such as the blood-brain barrier.
What are the differences between fast and slow distribution areas in the body?
-Fast distribution areas include organs with high blood flow such as the liver, heart, kidneys, and brain. Slow distribution areas include tissues like muscles, skin, and fat, where drugs take longer to reach.
What is the 'first-pass effect' in drug metabolism?
-The first-pass effect refers to the initial metabolism of a drug in the liver after being absorbed from the intestines, which may reduce the drug's effectiveness before it reaches the bloodstream.
What is the role of phase 1 and phase 2 in drug metabolism?
-Phase 1 involves the transformation of drugs into more polar, water-soluble compounds, while Phase 2 involves conjugation with substances like glucuronic acid to further facilitate elimination from the body.
Why are the liver and kidneys important in drug metabolism?
-The liver is the primary site for drug metabolism, where Phase 1 and Phase 2 reactions occur. The kidneys play a role in eliminating drug metabolites and the excretion of drugs through urine.
What is the main purpose of metabolism in pharmacokinetics?
-The main purpose of metabolism is to transform drugs into metabolites that are easier to eliminate from the body, usually through the kidneys or other excretion routes.
What are pharmacokinetic parameters and why are they important?
-Pharmacokinetic parameters, such as volume of distribution, clearance, half-life, and bioavailability, are crucial for understanding how a drug behaves in the body, including its absorption, distribution, elimination, and overall effectiveness.
What is the significance of the volume of distribution (Vd) in drug pharmacokinetics?
-The volume of distribution (Vd) indicates how widely a drug is distributed throughout the body. A larger volume suggests the drug is more widely distributed, while a smaller volume suggests it remains in the bloodstream or specific tissues.
How is drug clearance measured and why is it important?
-Drug clearance measures the body's ability to eliminate a drug, mainly through the kidneys. It is important for determining the dosage and frequency of drug administration to maintain therapeutic levels.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)