SC4 Penjelasan Blynk dan projek simple
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Gaza Kani explains the process of setting up a simple Blink project using a mobile device. He demonstrates how to download the Blink app, register an account, and create a new project with a DHT11 sensor and an LED. He highlights the steps for connecting the project to Wi-Fi, obtaining a template ID and token, and controlling the LED through the app. The video also shows how to configure the sensor for monitoring temperature and humidity. Despite technical issues with USB connectivity, Gaza provides an insightful overview of the process and offers troubleshooting tips.
Takeaways
- 😀 The presenter introduces themselves as Gaza Kani and begins by explaining a project related to the Blink platform.
- 😀 The presenter apologizes for not being able to connect a USB device and uses a simulation instead for demonstration.
- 😀 The tutorial focuses on how to use the Blink application, which can be downloaded from the Play Store or App Store.
- 😀 After downloading the Blink app, users must register an account and create a new project template for their device.
- 😀 The DHT 11 sensor and LED are used in the project, and users are guided to select and connect devices via the app.
- 😀 The project involves connecting the devices to Wi-Fi, after which a template ID and name are used in the code to link the devices.
- 😀 A token is generated to make the program run correctly. The presenter shows how to obtain the token in the app.
- 😀 The configuration steps are explained for monitoring and controlling devices, such as turning on/off an LED via the app.
- 😀 The presenter demonstrates how to monitor temperature and humidity through the app and shows example values (e.g., 30°C, 80% humidity).
- 😀 A demonstration is provided where an LED is controlled from the Blink dashboard, illustrating the app's interface and controls.
- 😀 The circuit setup includes an ESP32, DHT 11 sensor, and LED, with safety measures like a 220-ohm resistor to prevent damage to components.
- 😀 The presenter emphasizes that the project can only be done via simulation due to issues connecting the USB device to the SP32.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the Blink application mentioned in the video?
-The Blink application is used to create and manage IoT projects, allowing users to control devices like LEDs and monitor sensors through a mobile phone interface. It requires downloading from either the Play Store or App Store and registering an account to create new projects.
What are the first steps to begin using the Blink application?
-The first steps involve downloading the Blink application from either the Play Store or App Store, registering for an account, and then creating a new project using the available templates.
What is the significance of the template ID and template name in the Blink application?
-The template ID and template name are important as they need to be copied and pasted into the code to connect the Blink application to the project. This allows the program to function properly and enables communication between the app and the hardware.
Why does the presenter use a simulation instead of connecting the USB to the SP32?
-The presenter uses a simulation because their USB cannot connect to the SP32 device, which prevents them from demonstrating the actual hardware connection. They clarify that it's just a simulation for the sake of the explanation.
How does the Blink application control the LED and what happens when it is turned on or off?
-The Blink application controls the LED through a simple switch in the app interface. When the user turns it on, the LED lights up, and when it is turned off, the LED will go dark. This is an example of controlling an actuator through the application.
What are the two main sensors mentioned in the project and what do they measure?
-The two main sensors mentioned are the DHT11 sensor, which measures temperature and humidity. The presenter shows how to interact with these sensors, displaying the temperature and humidity values in the Blink app.
What is the significance of the WiFi connection in the Blink project?
-The WiFi connection allows the Blink app to communicate with the SP32, enabling remote control and monitoring of the connected devices and sensors. This wireless connectivity is essential for the project to function.
What is the role of the resistor in the SP32 circuit setup?
-The resistor (220 ohms) is used to protect the circuit by limiting the current flow to the LED, preventing damage from excessive current. It is connected between the ground and the LED to ensure safe operation.
Why does the presenter apologize at the beginning and end of the video?
-The presenter apologizes because the USB device could not be connected to the SP32 for the demonstration, which led to the use of a simulation instead. They also apologize for any inconvenience this might cause during the explanation.
What kind of ESP32 device is used in the project?
-The presenter uses the ESP32 DevKit V1, which is a development board designed for building IoT projects. It has various features including WiFi capability, which is crucial for connecting to the Blink application.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cara membuat game MIT App Inventor
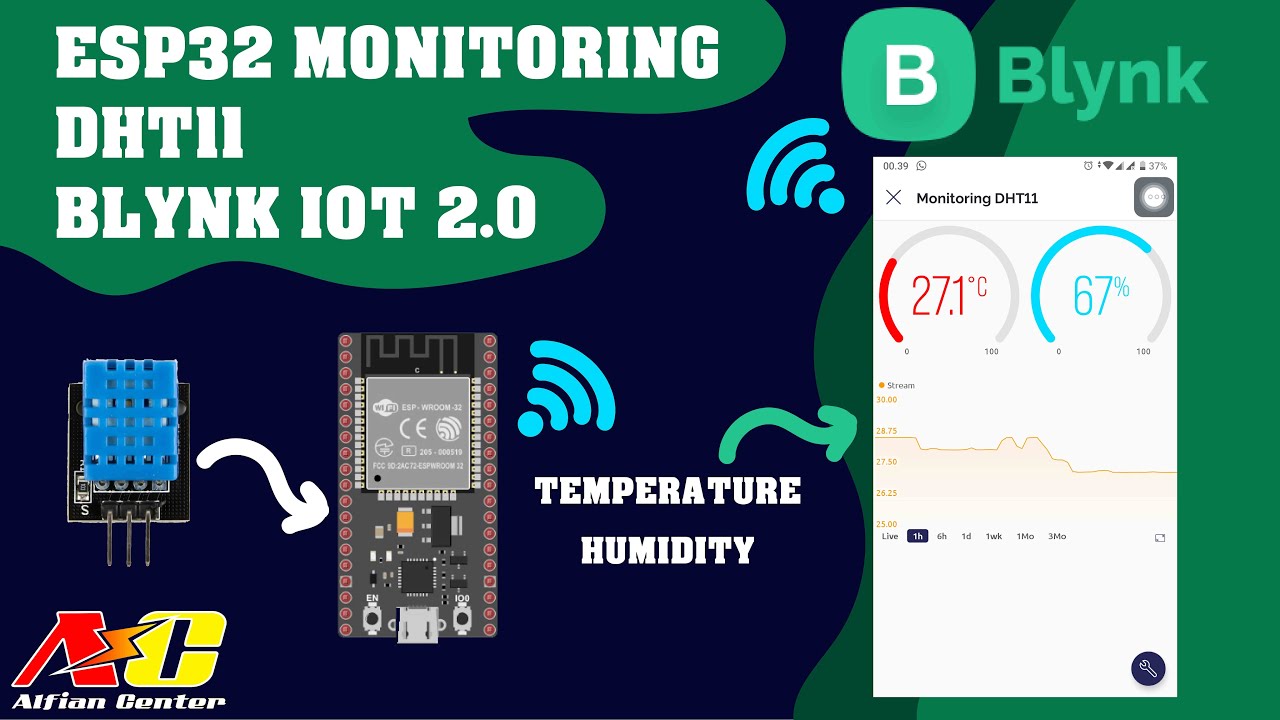
Monitoring Data Suhu dan Kelembapan Sensor DHT11 Menggunakan ESP32 dan BLYNK IOT 2.0

Control Water Pump From Mobile | IOT Projects | Home Automation
KKN UNY 2021 - Tutorial Membuat Aplikasi Ebook Menggunakan MIT App Inventor

Cara Cepat Seting Internet dan Wireless Mikrotik hAP Lite RB941-2nd

Simulasi LED Berkedip pada Proteus
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)