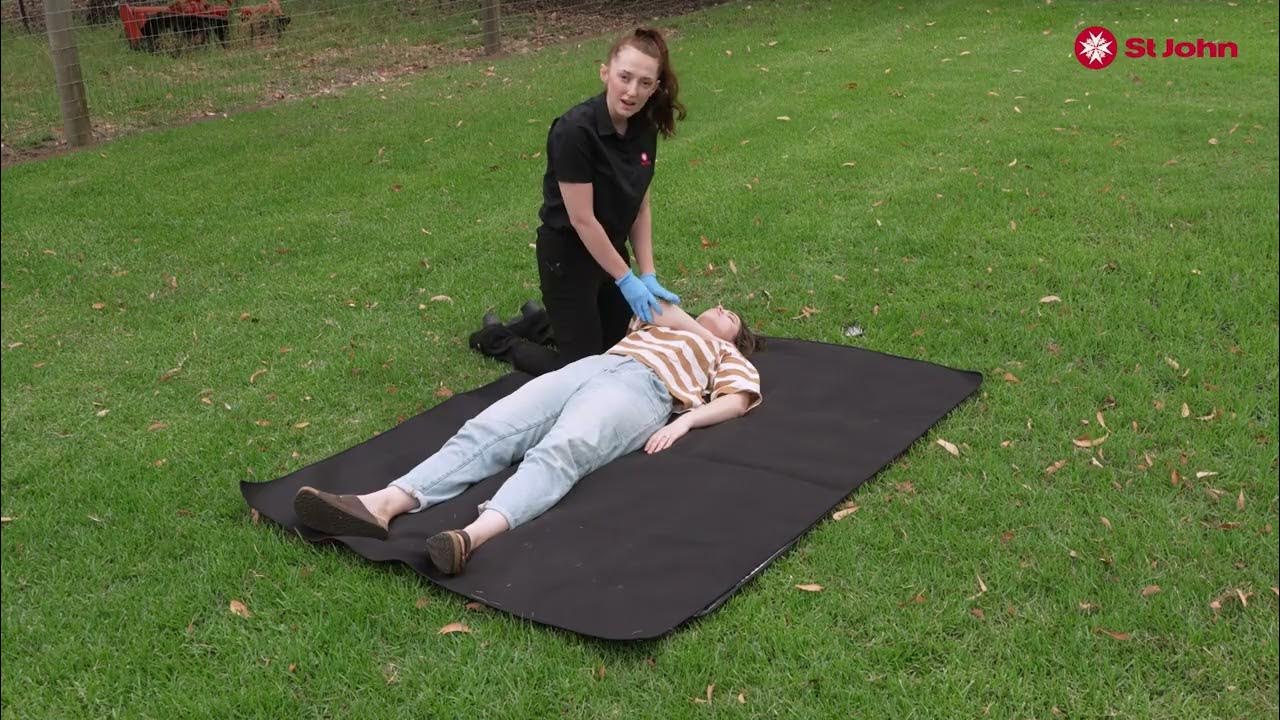
Bag Valve Mask: Apneic Patient
Summary
TLDRThis video script details the procedure for handling an unresponsive patient with weak pulse and no breathing. The responder follows a methodical approach, starting with ensuring scene safety, checking responsiveness, and performing a pulse and breathing assessment. The script highlights key steps such as suctioning the patient's airway, inserting an OPA, and administering ventilations with a bag-valve-mask (BVM) while ensuring adequate chest rise. It also emphasizes the importance of using oxygen, ventilating effectively, and monitoring the patient's condition to maintain proper care throughout the process.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ensure the scene is safe before approaching the patient.
- 😀 Check for responsiveness by tapping and shouting at the patient.
- 😀 If unresponsive, perform a trap squeeze to confirm lack of response.
- 😀 Call for ALS and request an AED if the patient is unresponsive.
- 😀 Check pulse and breathing for 5-10 seconds using the carotid artery.
- 😀 If no breathing but a weak pulse is detected, prepare for airway management.
- 😀 Clear the mouth of any vomitus using suction, making sure to suction for no longer than 15 seconds.
- 😀 Use the head-tilt, chin-lift technique to open the airway.
- 😀 Measure and insert an OPA (oropharyngeal airway) using the cross-finger technique.
- 😀 Perform ventilations using a BVM, ensuring adequate chest rise with each breath every 5-6 seconds.
Q & A
What are the first steps in assessing a patient in an emergency situation?
-The first steps are ensuring that the scene is safe and then attempting to gain a response from the patient by tapping and shouting. If the patient does not respond, proceed to check for a pulse and breathing.
How do you check the pulse of an unresponsive patient?
-To check the pulse, place two fingers lateral to the thyroid cartilage and inferior to the angle of the jaw, at the carotid artery. Check for pulse and breathing for 5 to 10 seconds.
What should you do if the patient has a weak pulse but no breathing?
-If the patient has a weak pulse but is not breathing, proceed with airway management by performing a head tilt-chin lift, followed by suctioning any vomitus or obstructions from the mouth and oral pharynx.
How do you suction the patient's airway effectively?
-To suction the airway, connect the suction catheter to the tubing and turn on the suction. Insert the catheter into the mouth, no further than the base of the tongue, and suction for no longer than 15 seconds while moving the catheter side to side or in a circular motion.
What is the purpose of the OPA (oropharyngeal airway) and how is it used?
-The OPA is used to maintain an open airway by preventing the tongue from obstructing it. To use it, measure from the front teeth to the angle of the jaw, insert the OPA inverted, and rotate it 180 degrees upon encountering resistance, ensuring the flange rests on the teeth or lips.
How do you perform positive pressure ventilation with a BVM (bag-valve-mask)?
-To perform positive pressure ventilation, place the BVM mask over the patient's face, securing it with the non-dominant hand while squeezing the bag with the dominant hand. Deliver one breath every 5 to 6 seconds, ensuring adequate chest rise with each breath.
How do you know that the ventilation with a BVM is effective?
-You can confirm effective ventilation by observing appropriate chest rise with each squeeze of the BVM, ensuring that each ventilation is delivered over one second.
What should you do if the patient continues to have a weak pulse and no breathing after two minutes of ventilation?
-If the patient still has a weak pulse and no breathing after two minutes, reassess the patient and continue ventilations, ensuring to monitor for any changes or improvements.
How is supplemental oxygen administered during BVM ventilation?
-Supplemental oxygen is administered by connecting the BVM to an oxygen source, adjusting the flow rate to 15 liters per minute, and continuing to deliver ventilations with the oxygen source attached.
What should be monitored during the entire resuscitation process?
-During the resuscitation process, continuously monitor for signs of adequate chest rise with each ventilation, pulse strength, and any changes in the patient's condition.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)