Superposition Theorem (with example)(Unit 1 DC circuits) BEE
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the Superposition Theorem, a fundamental concept in solving electrical circuits. The theorem is explained in the context of determining current flow through a resistor when multiple energy sources (voltage or current sources) are present. The presenter demonstrates how to deactivate and activate energy sources to calculate the current using superposition. Various practical examples are provided, including how to deactivate voltage sources by short-circuiting and current sources by open-circuiting. The video concludes with a hands-on numerical problem to solidify the understanding of the theorem and its application in solving circuits.
Takeaways
- 😀 Superposition Theorem is used to solve electrical circuits with multiple energy sources like voltage or current sources.
- 😀 The Superposition Theorem can only be applied when there are at least two energy sources in a circuit.
- 😀 Energy sources can be either voltage sources or current sources, and both types can be combined in a circuit for the application of this theorem.
- 😀 To apply the Superposition Theorem, deactivate all sources except for one at a time and calculate the resulting current or voltage in the circuit.
- 😀 Deactivating a voltage source involves short-circuiting it, while deactivating a current source involves open-circuiting it.
- 😀 Once the current or voltage is calculated with one active source, repeat the process with the other sources to find their contribution.
- 😀 The total current or voltage is obtained by algebraically adding the individual contributions, considering the directions of the currents or voltages.
- 😀 The speaker explains the step-by-step procedure of deactivating sources and calculating their impact on the circuit in a detailed manner.
- 😀 Numerical examples are used to demonstrate the application of the Superposition Theorem and to provide a clearer understanding of the procedure.
- 😀 The final result for the current or voltage in a circuit is derived using formulas like the current division rule and considering the equivalent resistances of different branches.
Q & A
What is the Superposition Theorem used for in electrical circuits?
-The Superposition Theorem is used to solve electrical circuits with multiple energy sources, such as voltage and current sources. It helps in calculating the current or voltage in a specific branch of the circuit by considering the effects of each source independently.
When can we apply the Superposition Theorem to a circuit?
-The Superposition Theorem can be applied to circuits that contain two or more independent energy sources, either voltage sources or current sources.
What is the first step in applying the Superposition Theorem to a circuit?
-The first step is to identify all the energy sources in the circuit. Then, deactivate all but one source. If it's a voltage source, deactivate it by short-circuiting it. If it's a current source, deactivate it by open-circuiting it.
How do you deactivate a voltage source in a circuit when applying the Superposition Theorem?
-To deactivate a voltage source, short-circuit it, which means connecting a wire across the voltage source to bypass it.
How do you deactivate a current source in a circuit when applying the Superposition Theorem?
-To deactivate a current source, open-circuit it, meaning disconnecting it from the circuit so that no current can flow through that branch.
What happens after you deactivate all but one energy source in the circuit?
-After deactivating all but one energy source, you analyze the circuit with the active source and calculate the resulting current or voltage in the branches of the circuit.
Once the effects of each source have been calculated, what should you do next?
-Once the individual effects of each source are calculated, you sum the effects algebraically. If the currents are in the same direction, add them; if they are in opposite directions, subtract them.
What is the final step after adding or subtracting the currents?
-The final step is to find the total current or voltage in the branch by adding or subtracting the contributions from each energy source, based on their directions.
Can you explain how to apply the Superposition Theorem with a numerical example?
-In the given example, you deactivate one energy source at a time. For instance, if you have a 9V voltage source and a 2A current source, you first deactivate the current source by open-circuiting it, then calculate the current caused by the voltage source. Next, deactivate the voltage source by short-circuiting it, and calculate the current caused by the current source. Finally, add or subtract the results depending on the direction of the currents.
What should you do if you have multiple energy sources in the circuit with different directions of current flow?
-If there are multiple energy sources and the currents flow in opposite directions, subtract the currents. If the currents flow in the same direction, add them. This algebraic process will give the total current flowing through the resistor or branch.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Basic Electrical Engineering | Module 1 | Superposition Theorem (Lecture 06)
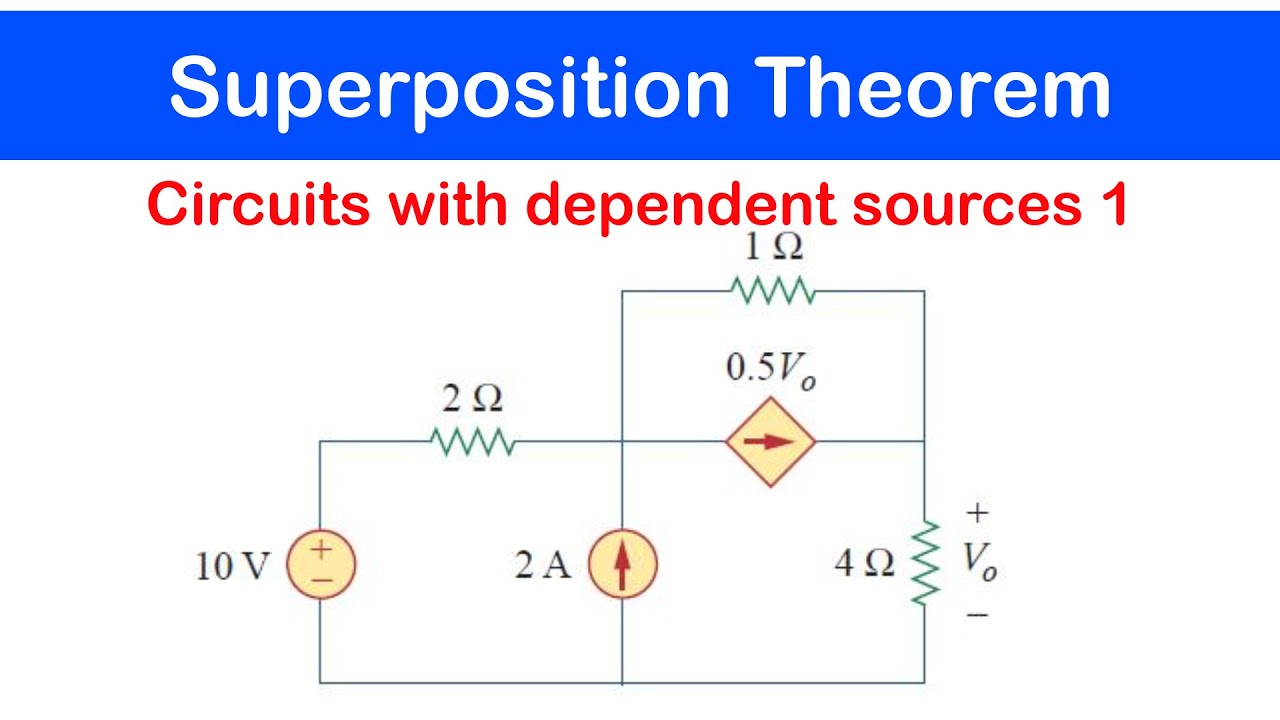
☑️19 - Superposition Theorem: Circuits with Dependent Sources 1

La legge di Ohm - Tutorial di elettronica - #2

Video Pembelajaran Modul 2 & 3 Praktikum Rangkaian Listrik 2024/2025 (DK)

Teorema Thevenin

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Rangkaian Arus Searah | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)