Kelenjar Tiroid 2 : Regulasi dan Efek Hormon Tiroid
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the role of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in the body, explaining their lipophilic nature and their ability to regulate metabolism, heat production, and growth. The thyroid hormones enhance the body’s response to catecholamines, improving cardiovascular function and growth processes. It also outlines the feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid, ensuring the balance of hormone production. This regulatory system helps maintain body temperature and metabolic rate, crucial for overall health. The content highlights both the physiological effects and regulatory processes of thyroid hormones.
Takeaways
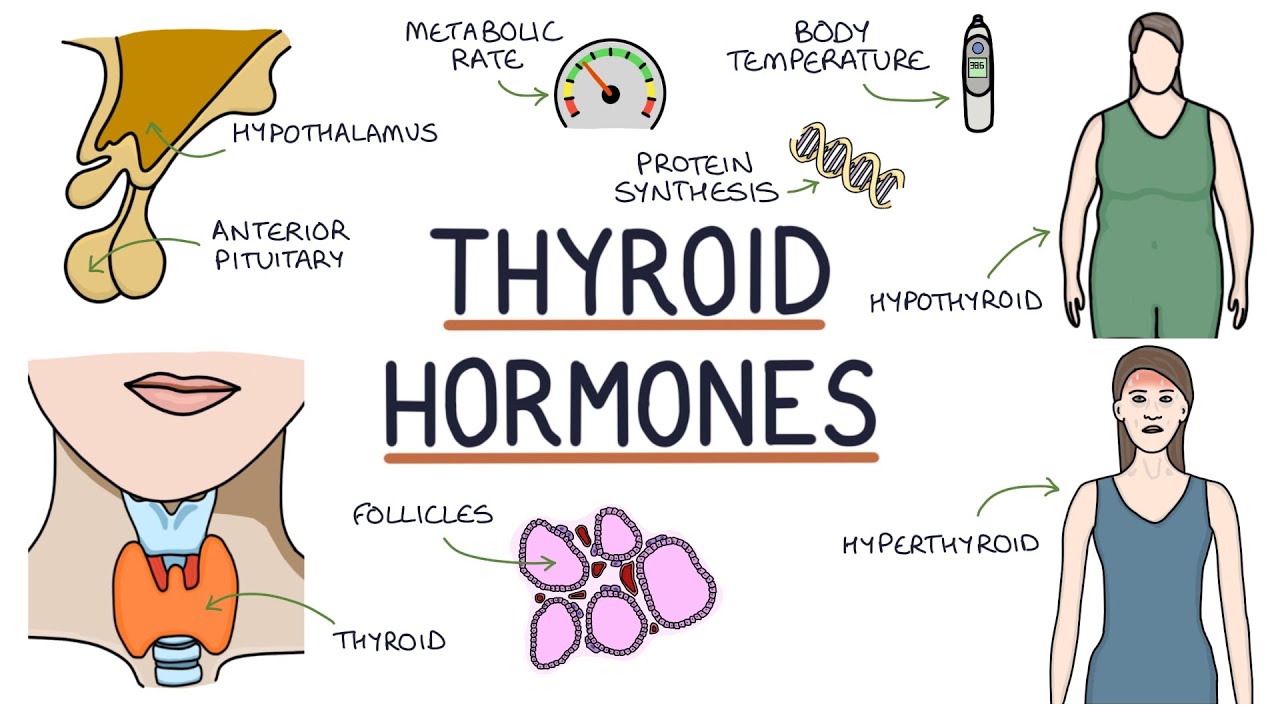
- 😀 Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are lipophilic and can easily cross the cell membrane to bind to intracellular receptors.
- 😀 Once inside the cell, thyroid hormones influence mRNA transcription in the nucleus, leading to specific protein synthesis.
- 😀 One of the primary effects of thyroid hormones is the increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR), which in turn raises body temperature.
- 😀 Thyroid hormones also have a sympathomimetic effect, meaning they enhance the responsiveness of cells to catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine.
- 😀 The effect of thyroid hormones on catecholamines is termed 'permissive,' where thyroid hormones help cells respond better to other hormones.
- 😀 In the cardiovascular system, thyroid hormones increase heart rate and cardiac output by enhancing the heart's responsiveness to catecholamines.
- 😀 Thyroid hormones do not have specific target cells but affect all cells in the body due to their role in regulating metabolism.
- 😀 Thyroid hormones stimulate growth hormone production and play a role in the growth and development of the nervous system.
- 😀 The regulation of thyroid hormone secretion involves a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland.
- 😀 Cold exposure in infants stimulates the hypothalamus to release TRH, which then prompts the pituitary to secrete TSH, activating thyroid hormone production to increase metabolism and warmth in the body.
Q & A
What are thyroid hormones, and what are their key types?
-Thyroid hormones are crucial for regulating metabolism and growth in the body. The key types of thyroid hormones are T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), both of which are lipophilic, meaning they are fat-soluble and can pass through cell membranes easily.
Where are the receptors for thyroid hormones located?
-The receptors for thyroid hormones are located intracellularly, inside the cell. These receptors are specifically found within the cytoplasm or nucleus of the target cells.
How do thyroid hormones affect the cell’s gene expression?
-Thyroid hormones bind to intracellular receptors, which then influence the transcription of specific mRNA within the nucleus. This results in the synthesis of proteins, with varying effects depending on the specific hormonal stimulation.
What is the primary effect of thyroid hormones on metabolism?
-The primary effect of thyroid hormones is to increase the basal metabolic rate (BMR), which results in higher energy consumption and heat production. This process helps maintain body temperature and supports various metabolic activities.
What is the role of thyroid hormones in the sympathetic nervous system?
-Thyroid hormones have a sympathomimetic effect, meaning they enhance the body's response to catecholamines (such as epinephrine and norepinephrine). This is done by increasing the number of receptors for these hormones on target cells, thereby improving the body’s response to stress.
How do thyroid hormones affect the cardiovascular system?
-Thyroid hormones influence the cardiovascular system by increasing the heart rate and cardiac output. This is a result of their sympathomimetic effect, where thyroid hormones improve the heart’s responsiveness to catecholamines.
What are the general target cells of thyroid hormones?
-Thyroid hormones do not have a specific target cell. Instead, they affect virtually all cells in the body, as their main function is to regulate the metabolic processes across the entire body.
How do thyroid hormones contribute to growth and development?
-Thyroid hormones stimulate the release of growth hormone and influence the liver to promote growth. Additionally, they play a crucial role in the development of the nervous system.
What is the regulatory mechanism that controls the secretion of thyroid hormones?
-The secretion of thyroid hormones is regulated by a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. When thyroid hormone levels are sufficient, they inhibit the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), a process known as negative feedback.
Can thyroid hormones regulate body temperature, and if so, how?
-Yes, thyroid hormones regulate body temperature by increasing the basal metabolic rate, which generates heat. This mechanism is particularly important in cold conditions, such as in infants, where thyroid hormone secretion helps to raise body temperature.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)