||NTPC| Unchahar Power Plant in Uttar Pradesh with reason.
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host discusses a catastrophic boiler explosion at NTPC's Unchahar thermal power plant in 2017, highlighting the events that led to the disaster. The explosion occurred due to a buildup of clinkers in the boiler, which caused pressure to rise. Despite the risk, NTPC officials bypassed safety measures to keep the boiler running, leading to unstable conditions and eventually an explosion. The video explores the technical failures, safety lapses, and hurried commissioning of the unit, which resulted in 37 deaths and numerous injuries. The incident raises critical questions about boiler safety protocols and operational oversight.
Takeaways
- 😀 A boiler explosion at the NTPC plant in Uttar Pradesh caused 37 deaths and over 80 injuries, highlighting serious safety concerns in power plant operations.
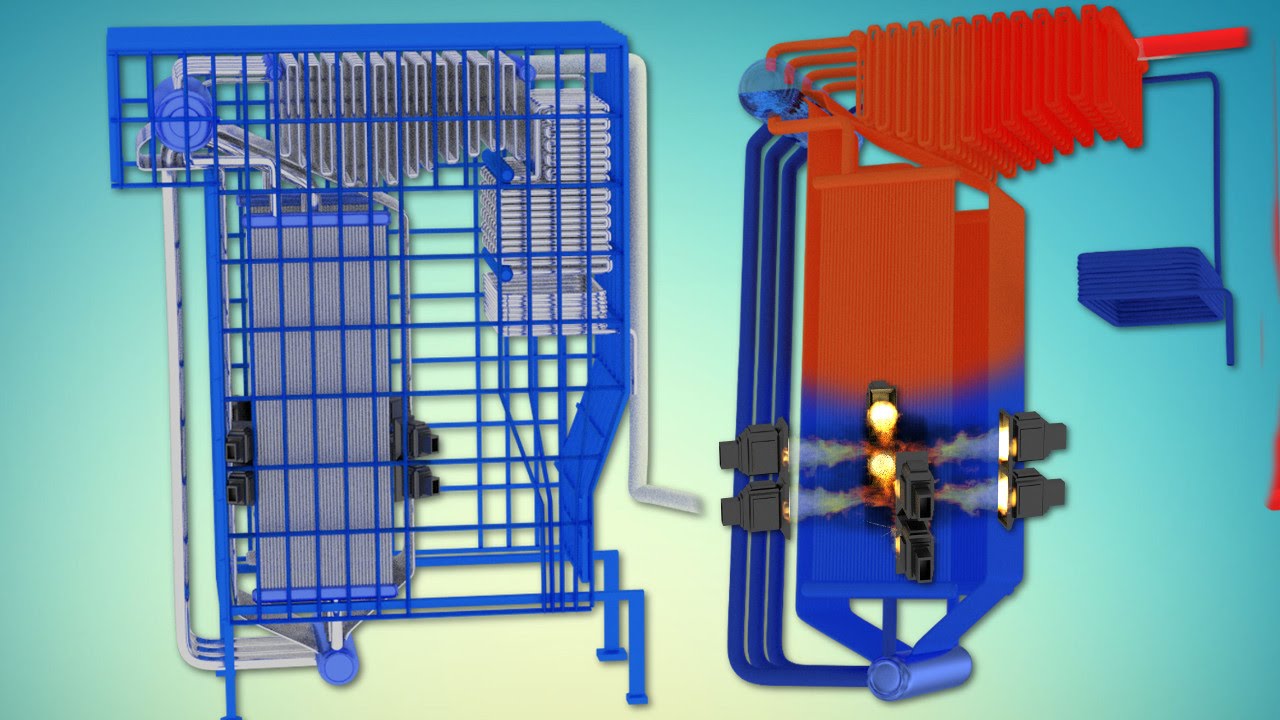
- 😀 The explosion occurred due to a build-up of clinkers (solidified ash) inside the boiler, which led to high pressure and unstable conditions.
- 😀 NTPC workers tried to manually remove clinkers using steel rods, a process known as 'double poke,' which led to further instability within the boiler.
- 😀 The boiler protection system was bypassed when NTPC officials disabled the master fuel relay trip to prevent shutting down the boiler, despite high pressure levels.
- 😀 The explosion occurred when unburned coal particles, carried into the rear path of the furnace, caught fire and triggered an explosion in the economizer.
- 😀 High-pressure fluctuations caused water wall cracks in the boiler, exacerbating the risk of explosion and endangering nearby workers.
- 😀 The NTPC plant was hurriedly put into commercial operation on September 30, 2017, despite incomplete trial operations, allegedly due to a scheduled visit by the Prime Minister.
- 😀 The rushed start of operations and lack of proper safety measures contributed to the severity of the explosion.
- 😀 The NTPC officials’ decision to bypass safety protocols and proceed with manual interventions inside the boiler was a key factor leading to the disaster.
- 😀 The explosion not only caused immediate harm to workers but also raised questions about the readiness of power plants and the importance of adhering to safety protocols before starting operations.
Q & A
What caused the NTPC boiler explosion at the Unchahar thermal power plant?
-The explosion was caused by a buildup of clinkers (solidified ash), which choked the bottom ash hopper. As a result, pressure inside the furnace increased. The NTPC officials attempted to remove the clinkers manually, bypassing the boiler protection system, which led to unstable conditions and an explosion in the furnace.
What is clinker and how did it contribute to the boiler explosion?
-Clinker is the solidified ash that forms almost like blocks of cement. In this case, the clinkers choked the bottom ash hopper, leading to a pressure buildup inside the boiler. This buildup of pressure caused the eventual explosion when the clinkers were dislodged manually.
Why did the NTPC officials bypass the boiler protection system?
-The NTPC officials bypassed the boiler protection system (specifically the master fuel relay trip) to keep the boiler running while attempting to remove the clinkers. They disabled the system to avoid shutting down the boiler despite the growing pressure.
What is the 'double poke' method mentioned in the video?
-The 'double poke' method refers to the process of manually removing clinkers by inserting steel rods through the manhole doors and bottom ash hopper. This method was used in an attempt to clear the buildup of clinkers inside the boiler.
What happened after the clinkers were removed during the 'double poke' process?
-After the clinkers were removed, a huge mass fell down, creating unstable conditions inside the boiler. This caused large pressure fluctuations, which cracked the water walls. Unburned coal particles were carried over to the rear path of the furnace, leading to an explosion.
Why did unburned coal particles contribute to the explosion?
-The unburned coal particles, after being carried over to the rear of the furnace, caught fire, which led to an explosion in the economizer. This was a direct result of the unstable conditions caused by the clinkers being removed and the bypassed protection system.
What role did the workers play in the explosion?
-Around 300 workers were in the vicinity of the boiler when the explosion occurred. Many of them suffered severe burns due to the release of hot flue gas, ash, and steam from the economizer area.
Why was the NTPC unit put into commercial operation despite being incomplete?
-The unit was hurriedly put into commercial operation on September 30, 2017, likely due to the impending visit of the Prime Minister, who was scheduled to inaugurate the unit on November 9, 2017. This rush may have led to the lack of proper testing and readiness of the unit.
What are the key safety concerns that were ignored during the incident?
-The key safety concerns included bypassing the boiler protection system, working in a high-pressure environment, and allowing workers to be in close proximity to the furnace when it was not fully operational. Additionally, the hurried commissioning of the unit contributed to the unsafe conditions.
What was the aftermath of the explosion in terms of casualties?
-The explosion resulted in 37 deaths and left more than 80 people seriously injured. The event became the largest accident in the history of NTPC.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)