Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
Summary
TLDRProfessor Dave explains the evolutionary history of life on Earth, beginning with the concept of natural selection and speciation. He describes the tree of life, showing how organisms are classified based on common ancestry, from the single-celled common ancestor at the base to diverse species today. The transcript covers key moments in life’s history, including the origin of life, the Cambrian explosion, and the rise of multicellular organisms. It delves into the classification system, from domains down to species, and emphasizes the connection between all living things. The discussion ends with a brief mention of biotechnology’s role in modern science.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Tree of Life is a diagram that illustrates the evolutionary relationships between all living organisms, tracing everything back to a single-celled ancestor.
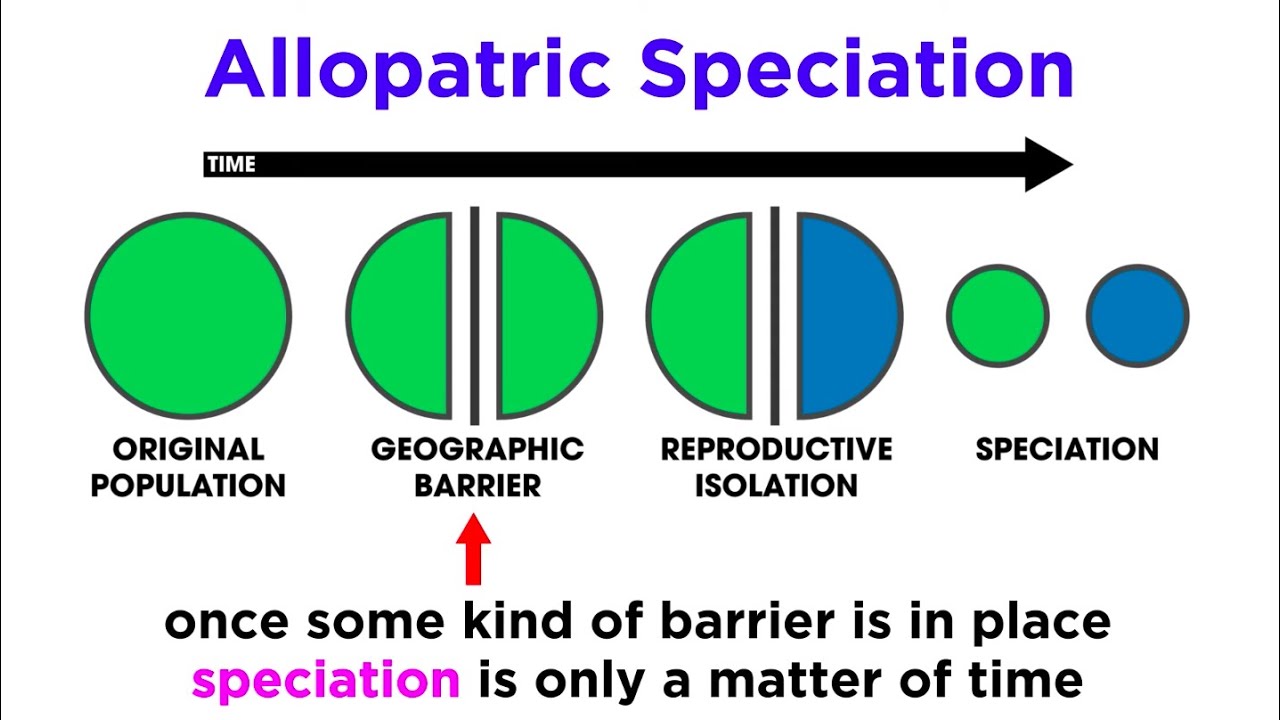
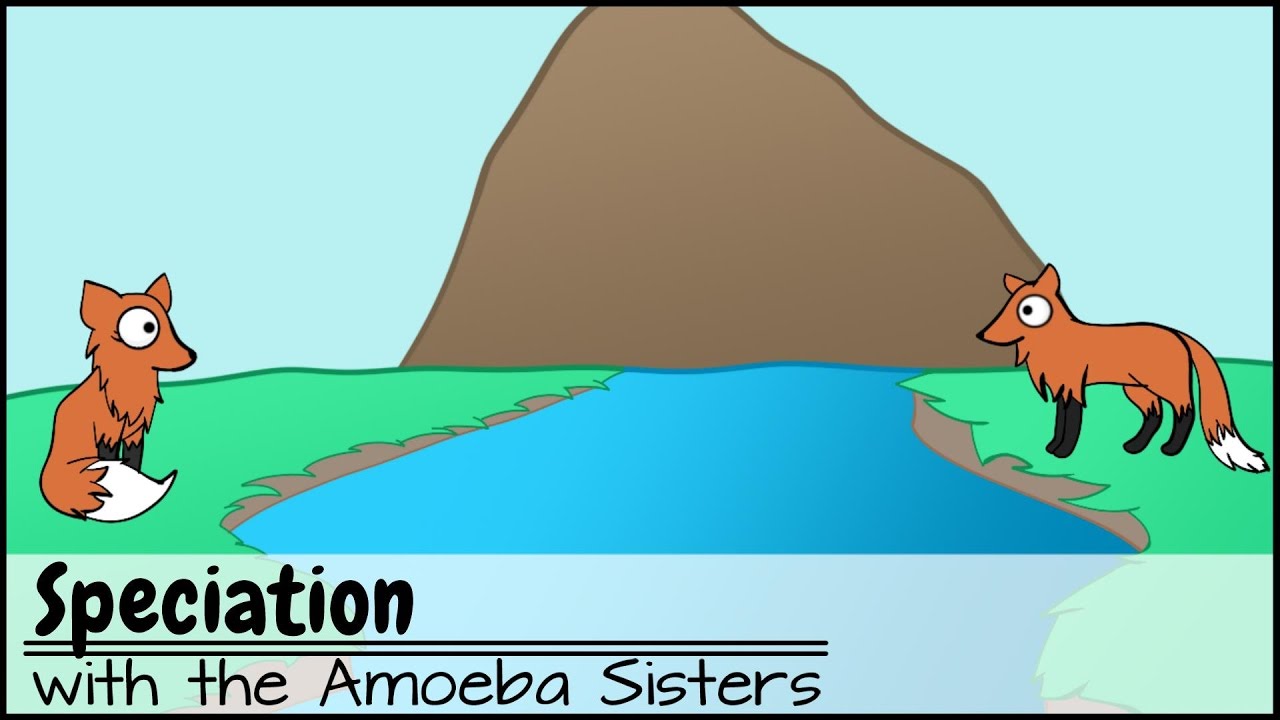
- 😀 Speciation is the process by which new species are formed, bridging microevolution (small genetic changes) and macroevolution (major evolutionary changes).
- 😀 Organisms are classified into a hierarchical system that includes domains, kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species, helping to organize evolutionary history.
- 😀 The three domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya, with Eukarya encompassing all multicellular life and unicellular protists.
- 😀 Humans belong to the genus *Homo*, the family *Hominidae*, the order *Primates*, and the class *Mammalia*, with our species being *Homo sapiens*.
- 😀 The Earth’s history is divided into eons and eras, with the Phanerozoic eon marking the time when animals appeared, followed by major extinction events that are visible in the fossil record.
- 😀 The evolutionary history of life can be traced using fossils, which provide critical insights into how species evolved over billions of years.
- 😀 The concept of homology is used to identify evolutionary relationships by comparing similarities in organisms’ genetic or physical traits.
- 😀 Major extinction events, like the Cambrian explosion, played a key role in shaping the development of life on Earth and are marked in the fossil record.
- 😀 Modern techniques, such as ribosomal RNA sequencing, help scientists analyze genetic relationships between species, offering a deeper understanding of common ancestry.
Q & A
What is the 'tree of life' and why is it important in biology?
-The tree of life is a way of organizing and visualizing the evolutionary relationships between all living organisms. It represents how different species are related through common ancestors, with branches that diverge as species evolve over time. It helps biologists track the ancestry and connections between different forms of life on Earth.
How does speciation relate to microevolution and macroevolution?
-Speciation is the process by which one species splits into two or more distinct species. It serves as the bridge between microevolution, which involves small genetic changes within a population, and macroevolution, which involves large-scale changes that result in new species or major evolutionary patterns over long periods.
What are the three main domains of life, and what types of organisms do they include?
-The three main domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Bacteria and Archaea are unicellular prokaryotes, while Eukarya includes all eukaryotic organisms, ranging from unicellular protists to all multicellular life forms such as plants, animals, and fungi.
How are species classified in the context of the tree of life?
-Species are classified through a hierarchical system that includes domains, kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species. This system reflects evolutionary relationships, with organisms grouped based on shared characteristics and common ancestry.
What does the term 'phylogeny' refer to in biology?
-Phylogeny refers to the evolutionary history or ancestry of a species or group of organisms. It shows how different species are related through common ancestors, and it helps in understanding the evolutionary pathways that led to the diversity of life on Earth.
What was the significance of the Miller-Urey experiment in understanding the origin of life?
-The Miller-Urey experiment demonstrated that amino acids and other organic compounds could form under conditions similar to those on early Earth. This provided important evidence for the possibility of life emerging from simple chemical building blocks, supporting the idea that life could have originated spontaneously.
What were some key events in the early history of life on Earth?
-Key events in early life history include the formation of amino acids and nucleic acids, the development of self-replicating molecules, the origin of prokaryotic life, the rise of oxygen due to photosynthesis, and the evolution of multicellular eukaryotes through processes like endosymbiosis.
What is the significance of the Cambrian Explosion in evolutionary history?
-The Cambrian Explosion, which occurred around 540 million years ago, marks a period of rapid diversification of life forms. During this time, many of the major groups of animals first appeared, setting the stage for the complex ecosystems we see today.
How is the concept of homology used to trace evolutionary relationships?
-Homology refers to the similarities between organisms' structures, genes, or other biological features due to shared ancestry. By comparing homologous traits, scientists can infer evolutionary relationships between species, with the assumption that similar traits often indicate common origins.
Why is the genus Homo significant in the context of human evolution?
-The genus Homo is significant because it includes humans and our closest extinct relatives. The species within this genus, such as Homo sapiens, Homo erectus, and Homo habilis, represent different stages in human evolution, with Homo sapiens being the only surviving species.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)