Kelas Fisika_Kalor_Part 3
Summary
TLDRIn this physics lesson, the teacher explains the mechanisms of heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation. Using examples like a heated metal rod and experiments with different materials such as aluminum, copper, and steel, the teacher illustrates how heat moves through substances. The lesson also covers the effects of fluid types on heat transfer, demonstrated through water and air experiments. The concept of radiation is explored with a focus on emissivity, and the teacher highlights how factors like surface area and temperature influence heat transfer rates in all three methods. The lesson concludes with a review of key formulas for each type of heat transfer.
Takeaways
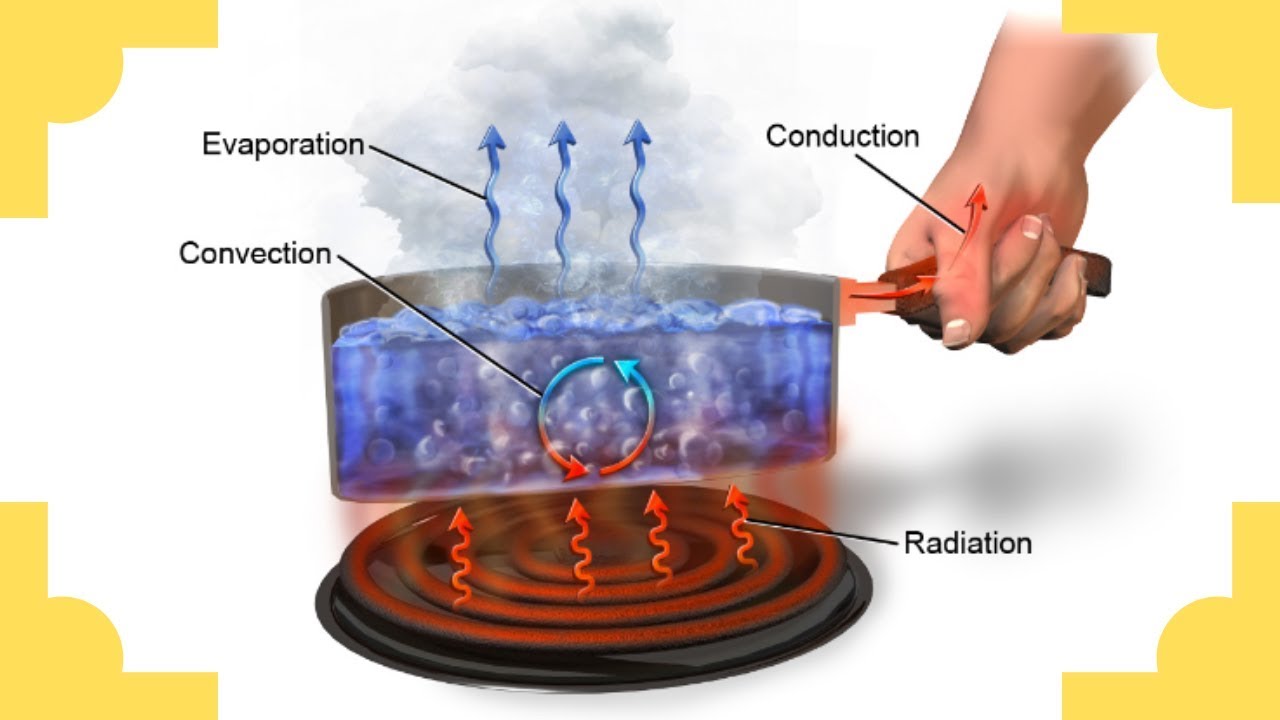
- 😀 Heat can transfer in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- 😀 In conduction, when one end of a metal rod is heated, the molecules vibrate faster and transfer heat to neighboring molecules.
- 😀 The rate of heat transfer by conduction depends on factors like thermal conductivity, cross-sectional area, temperature difference, and the length of the material.
- 😀 Aluminum has the highest thermal conductivity among metals, as demonstrated by a candle melting faster on aluminum compared to other metals.
- 😀 The heat transfer rate in conduction is governed by the equation Q/T = K * A * (ΔT / L), where Q/T is the rate of heat transfer, K is thermal conductivity, A is cross-sectional area, ΔT is temperature difference, and L is the length of the material.
- 😀 Convection occurs when heat is transferred through fluid motion, such as when water is heated and the colored dye moves upwards with the rising warmer water.
- 😀 The rate of heat transfer by convection depends on the convection coefficient, which varies based on the type of fluid (air, water, etc.).
- 😀 In convection, warmer fluids become lighter and rise, while cooler fluids sink, creating a circulation pattern.
- 😀 In radiation, heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves, as seen with the sun's energy reaching Earth through empty space.
- 😀 The rate of heat transfer by radiation depends on factors like emissivity, surface area, temperature, and the Stefan-Boltzmann constant.
- 😀 A black container absorbs heat faster than a white container, as demonstrated by the experiment where black water heats up more quickly under the sun and cools down faster when removed.
Q & A
What are the three mechanisms of heat transfer discussed in the video?
-The three mechanisms of heat transfer discussed are conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does heat transfer through conduction in a metal rod?
-When a metal rod is heated at one end, the molecules at that end vibrate faster and transfer this vibration to adjacent molecules through collisions. This process spreads the heat along the rod.
What factors affect the rate of heat transfer by conduction?
-The rate of heat transfer by conduction depends on several factors, including the material's thermal conductivity, the cross-sectional area, temperature difference, and the length of the object.
Why does aluminum have the fastest heat transfer in the experiment with different metals?
-Aluminum has the highest thermal conductivity compared to the other materials, which allows it to transfer heat more quickly, as demonstrated by the faster melting of wax on aluminum.
What role does temperature difference play in conduction?
-A greater temperature difference between the two ends of the material increases the rate of heat transfer, as heat moves from the hotter to the cooler area.
How does convection heat transfer occur in liquids or gases?
-In convection, the heated fluid (like water) becomes less dense and rises, while the cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a circulating flow that transfers heat. This process is demonstrated in the experiment with colored water.
What factors influence the rate of convection?
-The rate of convection is influenced by factors such as the convection coefficient, the type of fluid, and the temperature gradient between the fluid's hot and cold regions.
Why does air heat up faster than water in the convection experiment?
-Air has a lower specific heat capacity compared to water, meaning it heats up more quickly in response to the same heat input, as observed in the experiment.
What is the relationship between emissivity and radiation?
-Emissivity refers to a material's ability to absorb or emit radiation. A material with high emissivity, like the black container in the experiment, absorbs and radiates heat more effectively than a material with low emissivity.
What were the results of the experiment with black and white containers under sunlight?
-The black container absorbed more heat and showed a faster temperature increase compared to the white container. When removed from the sunlight, the black container also cooled down faster, demonstrating the effect of higher emissivity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Propagação de calor - CONDUÇÃO, CONVECÇÃO E IRRADIAÇÃO

The Physics of Heat: Crash Course Physics #22

La propagazione del calore: conduzione, convezione, irraggiamento

SCIENCE 11-Earth's Internal Heat by Teacher Salvictorino Reguya
Conduction -Convection- Radiation-Heat Transfer

FISIKA KELAS XI | SUHU DAN KALOR (PART 5) - PERPINDAHAN KALOR Konduksi, Konveksi, dan Radiasi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)