PERSAMAAN GAS IDEAL | Teori Kinetik Gas dan Termodinamika #2 - Fisika Kelas 11
Summary
TLDRThis educational video, delivered in Indonesian, covers the ideal gas law and its applications in physics. The presenter explains key concepts such as pressure, volume, temperature, and the use of constants like the universal gas constant (R) and Boltzmann constant (k). Through practical examples, including the behavior of helium and argon gases, students learn to calculate gas properties using equations like PV = nRT and PV = NkT. The video also emphasizes unit conversions and provides step-by-step problem-solving techniques for gas-related calculations in real-world contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on the ideal gas equation and its applications in physics for 11th-grade students, following the Merdeka curriculum.
- 😀 The key equation discussed is PV = NRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, N is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
- 😀 The value of the gas constant (R) is typically 8.31 J/mol·K, though it may vary slightly (8.315 or 8.32) depending on the context of the problem.
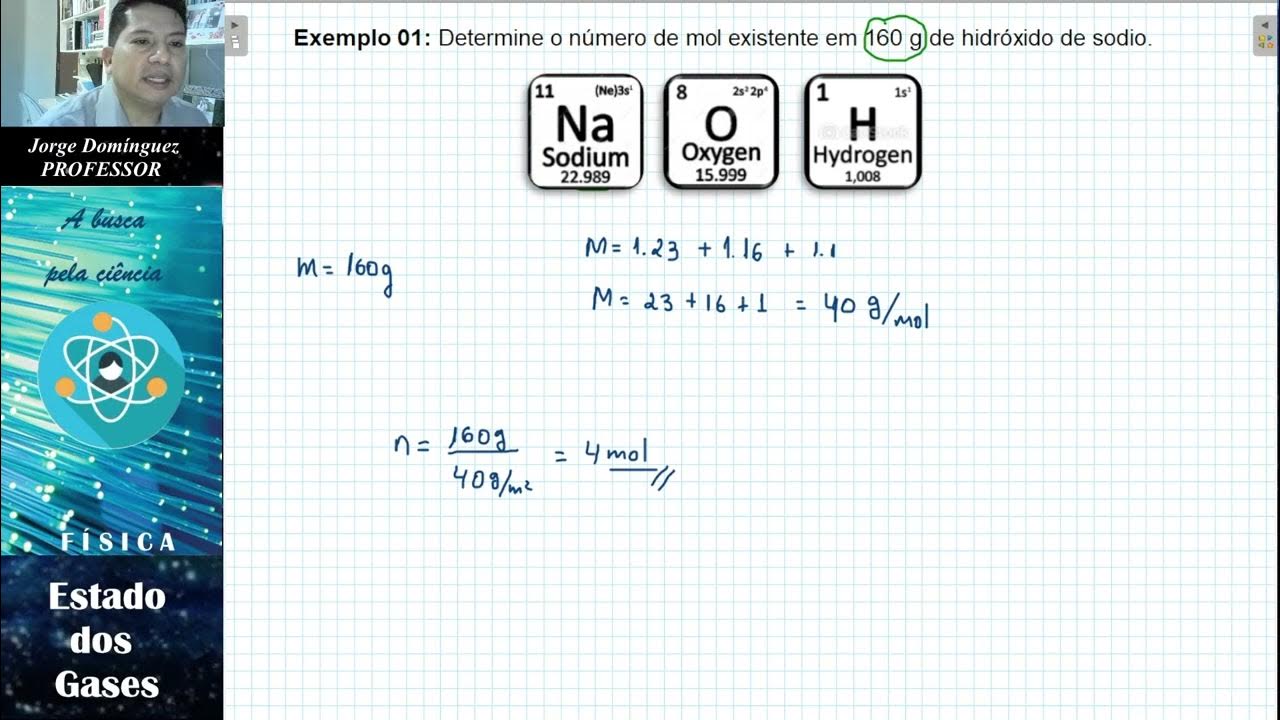
- 😀 The number of moles (n) can be determined using the formula m/mr, where m is the mass of the gas and mr is the molar mass of the gas.
- 😀 Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10^23 particles per mole) is used to find the number of gas molecules in a given amount of substance.
- 😀 When the ideal gas equation is manipulated, it leads to the concept of Boltzmann's constant (k = 1.38 × 10^-23 J/K), used when working with smaller numbers of particles.
- 😀 The lesson explains how to convert Celsius temperatures to Kelvin (add 273) when using them in gas law equations.
- 😀 Example problems are provided to demonstrate how to use the ideal gas law and Boltzmann’s constant for real-life calculations, including pressure, volume, and temperature.
- 😀 The importance of using the correct units is emphasized, such as converting volumes to cubic meters (1 liter = 10^-3 m³) and pressures to Pascals (1 atmosphere = 10^5 Pascals).
- 😀 The script presents multiple example problems, demonstrating step-by-step how to apply both PV = NRT and the Boltzmann constant equation (PV = kNT), including converting values and calculating results.
Q & A
What is the ideal gas law equation and how is it derived from the kinetic theory of gases?
-The ideal gas law is represented as PV = nRT. It is derived from the kinetic theory of gases, where the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and the number of moles (n) of the gas is defined. The constant R is the universal gas constant, and it represents the proportionality factor.
What is the significance of the gas constant R in the ideal gas law?
-The gas constant R is a fundamental constant in the ideal gas law equation and has a value of 8.31 J/mol·K. It links the energy, temperature, and quantity of gas in a mathematical relation. It can sometimes be approximated as 8.31 or even rounded to 8.3 in certain problems for simplicity.
How is the number of moles (n) of gas related to its mass?
-The number of moles (n) of a gas can be calculated using the formula n = m / M, where m is the mass of the gas and M is the molar mass (molecular weight) of the gas. This formula is essential when calculating the amount of substance in a given sample.
What is Avogadro’s number, and how is it used in the ideal gas law?
-Avogadro’s number (6.022 x 10^23 particles/mol) defines the number of particles (atoms or molecules) in one mole of a substance. In the context of the ideal gas law, it is used to convert between the number of moles and the number of particles when required.
What is the difference between using the universal gas constant R and the Boltzmann constant k?
-The universal gas constant R is used when working with the ideal gas law in terms of moles (n), while the Boltzmann constant k (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K) is used in the formulation of the ideal gas law at the particle level, relating the energy of a single particle to its temperature.
How do you convert Celsius to Kelvin when using the ideal gas law?
-To convert Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273 to the Celsius temperature. This is necessary because the ideal gas law uses temperature in Kelvin units.
What is the significance of the equation PV = NkT?
-The equation PV = NkT is a form of the ideal gas law where N is the number of particles and k is the Boltzmann constant. This equation expresses the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of particles in a gas when dealing with individual particles instead of moles.
What does the constant k (Boltzmann constant) represent in gas equations?
-The Boltzmann constant k (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K) represents the energy per temperature increment for a single particle of gas. It is crucial in linking the macroscopic and microscopic descriptions of gases.
In the example of helium gas, why was the temperature converted to Kelvin?
-The temperature was converted to Kelvin because the ideal gas law requires temperature in Kelvin for the calculations. The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero (0 K), which is the lowest possible temperature, ensuring that all gas calculations are physically valid.
How can you calculate the pressure of a gas using the ideal gas law with given parameters?
-To calculate the pressure using the ideal gas law, use the equation PV = nRT, rearranging to P = nRT / V. By substituting the values of the number of moles (n), the gas constant (R), the temperature (T), and the volume (V), you can solve for the pressure (P) of the gas.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Gas Law Formulas and Equations - College Chemistry Study Guide

FISIKA KELAS XI | TEORI KINETIK GAS (PART 2) - Persamaan Gas Ideal

Teori Kinetik Gas | Contoh Soal Materi Teori Kinetik Gas | Fisika SMA

FISIKA KELAS XI | TEORI KINETIK GAS (PART 1) - Hukum-Hukum Gas Ideal
Estado dos Gases

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 4 Module 2 | Kinetic Molecular Theory, Avogadro's Law and Ideal Gas Law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)