Exploring Production Methods: Job, Batch, and Flow Production Explained | ThinkIGCSE.com
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the three key production methods used in businesses: job production, batch production, and flow production. It explains job production's focus on customization, batch production's balance between flexibility and efficiency, and flow production's ability to mass-produce at scale. Each method's strengths and limitations are discussed, helping businesses choose the right approach based on product type, target market, and resources. Whether crafting bespoke items, producing in limited runs, or manufacturing in bulk, the video guides viewers in making informed production decisions for their business needs.
Takeaways
- 😀 Job production is all about creating a single, customized product from start to finish.
- 😀 Job production is labor-intensive and time-consuming, making it less suited for mass production.
- 😀 Batch production allows businesses to produce multiple units of the same product together in batches, balancing customization with efficiency.
- 😀 One limitation of batch production is potential downtime between batches, which can reduce overall efficiency.
- 😀 Maintaining quality consistency across batches can be challenging in batch production.
- 😀 Flow production is characterized by continuous production of large volumes of identical products.
- 😀 Flow production is highly efficient and cost-effective for mass production, such as in industries like automotive and beverage manufacturing.
- 😀 Flow production requires significant initial investment in machinery and setup, making it less flexible for smaller-scale operations.
- 😀 Businesses choose production methods based on product nature, target market, and available resources.
- 😀 A bespoke jeweler would lean towards job production, a craft brewery might choose batch production, and a car manufacturer would likely opt for flow production.
- 😀 Understanding the strengths and limitations of each production method is crucial for making strategic business decisions.
Q & A
What are the three key production methods discussed in the video?
-The three key production methods discussed are job production, batch production, and flow production.
What is the main characteristic of job production?
-The main characteristic of job production is the creation of a single tailormade product, which is highly customized and unique.
What are the advantages of job production?
-The advantages of job production include high levels of customization, quality, and uniqueness, making it appealing to consumers seeking a personalized product.
What are the limitations of job production?
-The limitations of job production include being labor-intensive, time-consuming, and less suitable for businesses aiming for mass production.
How does batch production work?
-Batch production involves producing multiple units of the same product together in a batch. It strikes a balance between customization and efficiency, offering more flexibility than job production.
What are the challenges of batch production?
-Challenges of batch production include potential downtime between batches and the difficulty of maintaining consistent quality across different batches.
What is the key feature of flow production?
-The key feature of flow production is the continuous movement of products through a highly structured production line, allowing for large-scale efficiency and mass production.
What are the benefits of flow production?
-Flow production excels in large-scale efficiency, enabling businesses to produce large volumes of identical products quickly and cost-effectively.
What are the limitations of flow production?
-The limitations of flow production include inflexibility and the need for significant initial investment in machinery and setup.
How should a business choose the right production method?
-The choice of production method depends on factors like the nature of the product, the target market, and available resources. For example, a bespoke jeweler may choose job production, a craft brewery might opt for batch production, and a multinational car manufacturer would likely use flow production.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Job, batch, flow and mass customization methods - Business Management - Teacher RK

Understanding Production Volume & Plant Layout: Job, Batch, and Mass Production Explained!
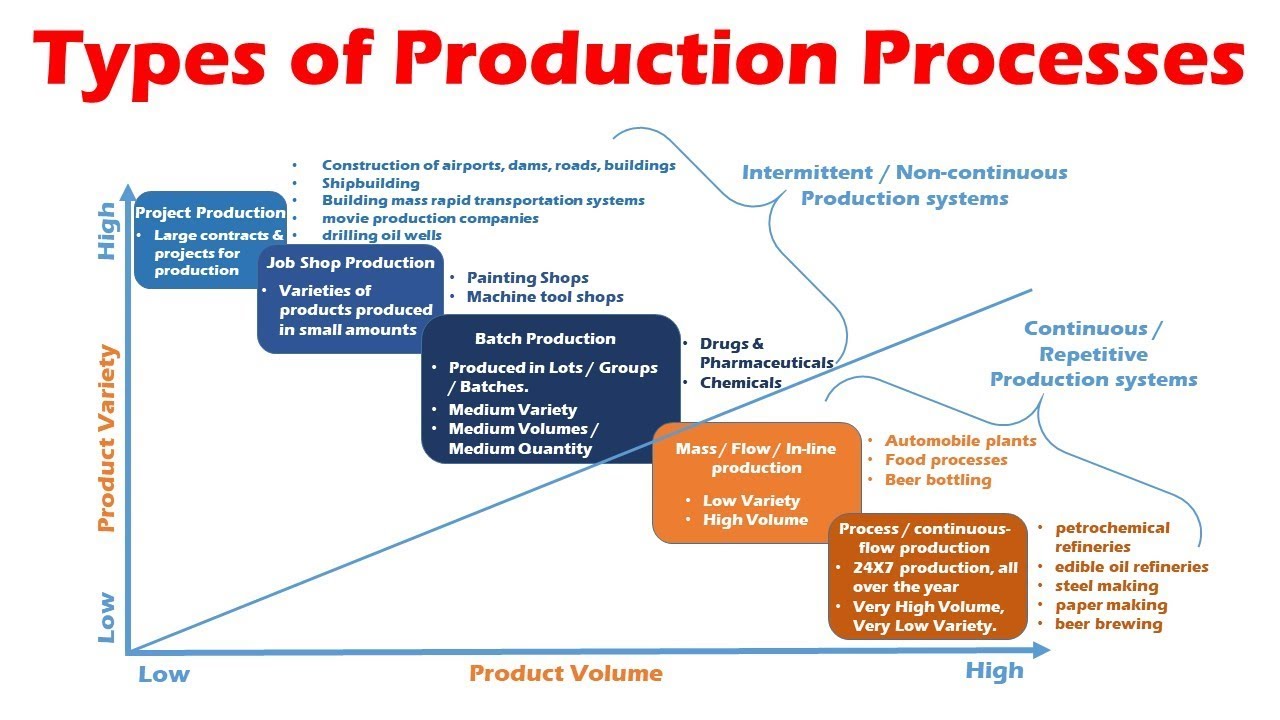
Types of Production Systems (Process, Mass, Flow, Batch, Job Shop & Project Production Systems)
What is Production? Types of Production, Factors of Production

Process Selection - A Review of Continuous Flow, Assembly Line, Batch Flow and Job Shop

Scales of Production
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)