Siklus, Jenis, dan Pemanfaatan Batuan Litosfer
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the Earth's lithosphere and the rock cycle, explaining the formation and movement of tectonic plates and how continents shift over time. It introduces the concept of continental drift, detailing the historical separation of the Gondwana and Laurasia supercontinents. The video also covers the three main types of rocks: igneous (formed from solidified magma), sedimentary (formed through deposition), and metamorphic (formed under pressure and heat). It concludes by discussing the various uses of rocks in construction, art, and other industries, making complex geological processes accessible to all viewers.
Takeaways
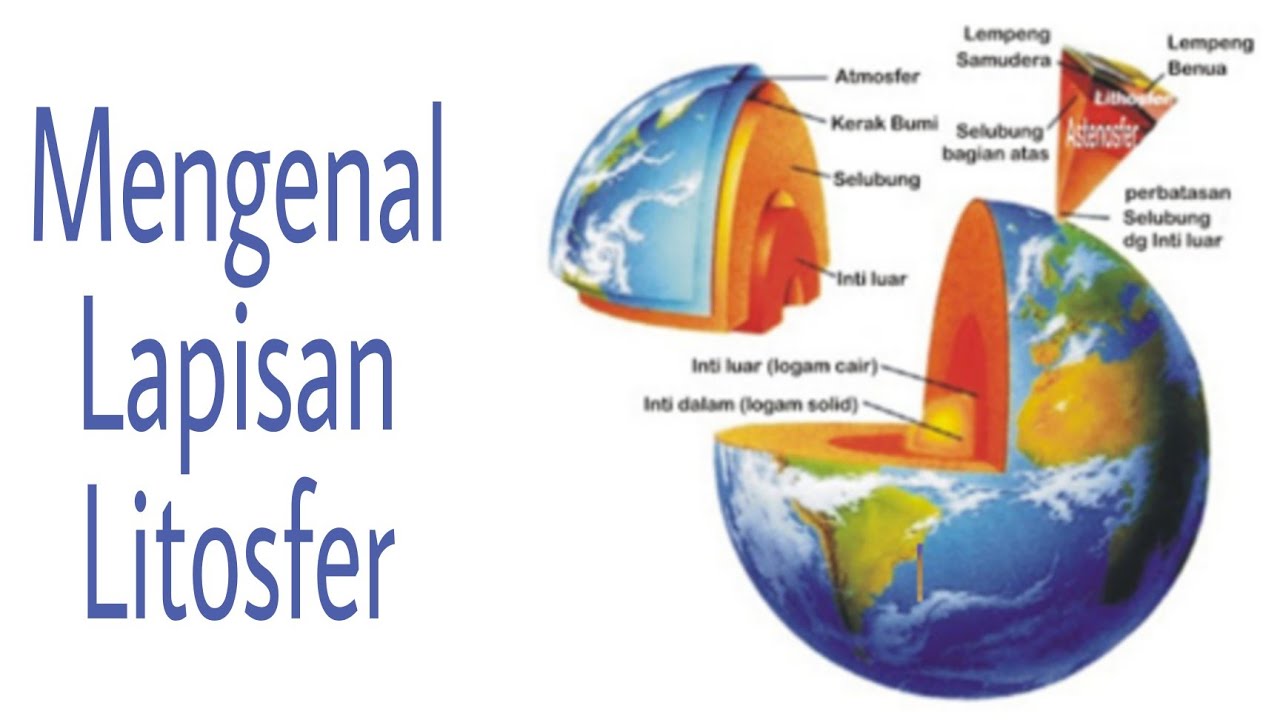
- 😀 The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, made up of rocks, and is divided into oceanic and continental plates.
- 😀 The Earth consists of multiple layers: the core (outer and inner), the mantle, and the crust (lithosphere).
- 😀 Continental plates are made of silicon and aluminum, while oceanic plates are composed of silicon and magnesium.
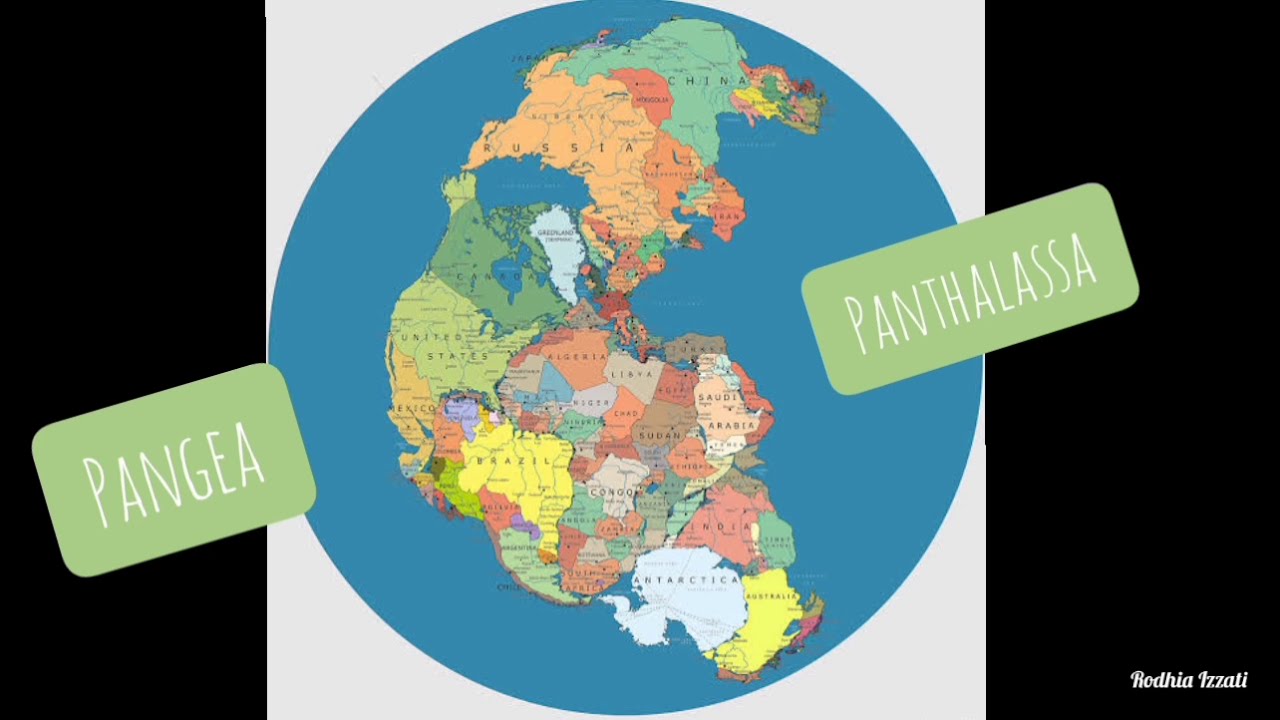
- 😀 According to the Gondwana-Laureasia theory, Earth's continents were once unified but separated due to plate movement.
- 😀 Plate movement continues today and is expected to persist for millions of years, gradually reshaping the Earth's continents.
- 😀 The rock cycle involves the transformation of rocks: from magma to solid rocks, into sedimentary rocks, and then to metamorphic rocks.
- 😀 Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, and there are three main types: intrusive, extrusive, and pegmatitic.
- 😀 Sedimentary rocks form through processes like erosion, sedimentation, and compaction. They are classified based on their origin and formation.
- 😀 Metamorphic rocks are formed from the alteration of pre-existing rocks due to high pressure and temperature, and they come in several types, including contact, dynamic, and pneumatolitic metamorphic rocks.
- 😀 Rocks have various uses, including as foundations for buildings, sculptures, and decorative items, as well as for producing cement and other materials.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, composed of rocks. It is divided into two main types: oceanic and continental plates.
What is the main difference between oceanic and continental plates?
-Oceanic plates are made up of silicon and magnesium, whereas continental plates are made up of silicon and aluminum.
What is the significance of the Gondwana and Laurasia theory?
-According to the Gondwana-Laursia theory, Earth’s continents were once joined together as two large supercontinents, Gondwana and Laurasia. Over time, these plates moved apart to form the continents we have today.
How do tectonic plates move?
-Tectonic plates move continuously, driven by the heat from the Earth's interior. These movements cause the continents and ocean floors to shift position over time.
What is the rock cycle, and how does it work?
-The rock cycle describes the transformation of rocks through various stages. It starts with magma, which cools and solidifies to form igneous rocks. These rocks then undergo weathering to become sedimentary rocks. Under heat and pressure, sedimentary rocks can turn into metamorphic rocks, which may melt back into magma.
What are the three main types of rocks formed in the Earth?
-The three main types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks.
What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks?
-Intrusive igneous rocks, such as granite, form below the Earth's surface, while extrusive igneous rocks, like basalt, form when magma cools quickly on the surface.
What are sedimentary rocks, and how are they classified?
-Sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation and compression of materials over time. They are classified based on their deposition environment (terrestrial, marine, or glacial), the way they are deposited (clastic, chemical, or organic), and the energy used in their deposition (aqueous, aeolian, or glacial).
What are metamorphic rocks, and how do they form?
-Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks (either igneous or sedimentary) undergo high pressure and temperature conditions, causing them to transform chemically or structurally. Examples include marble (from limestone) and schist.
What are some practical uses of rocks?
-Rocks are used for a variety of purposes, including as building foundations, in sculpture, for making cement, in decorative items like jewelry, and as materials for roads and infrastructure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)