Major Pharmacokinetic Processes animation
Summary
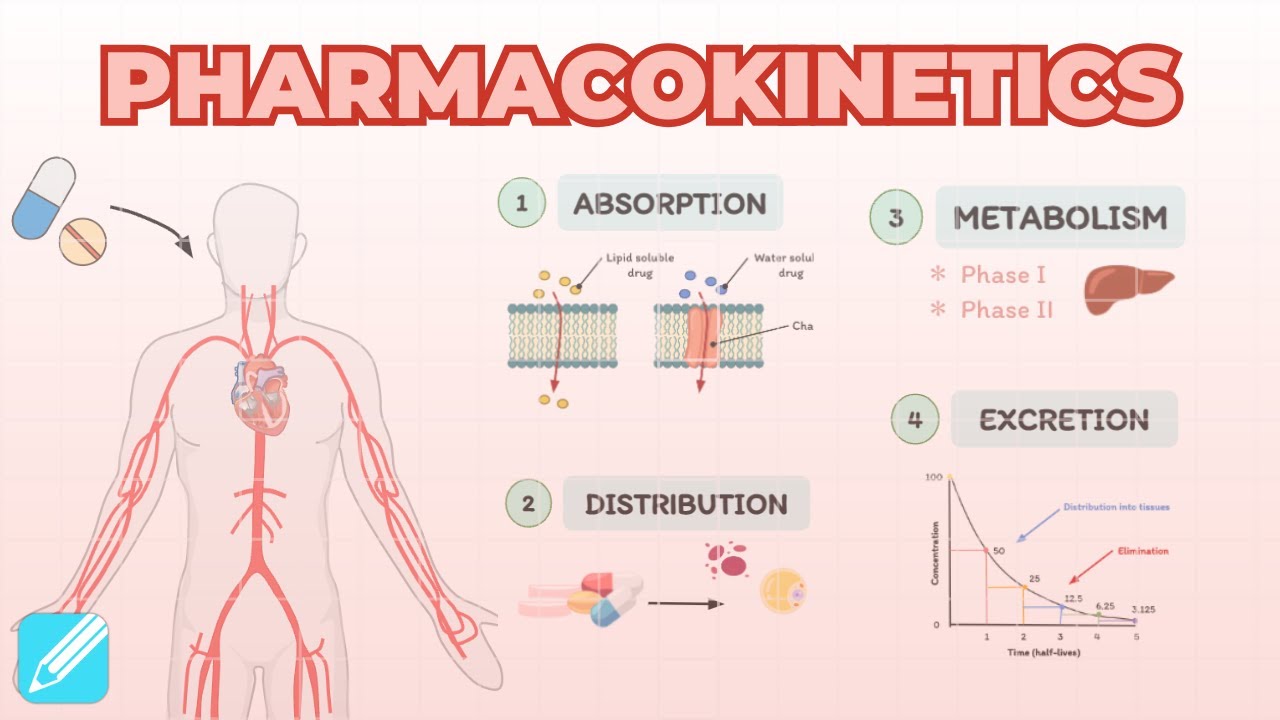
TLDRThis video explains the four major pharmacokinetic processes that a drug undergoes in the body. The first process is absorption, where the drug moves from the site of administration to the bloodstream. The second process, metabolism, involves the liver breaking down the drug, which can either activate or deactivate it. The third process is distribution, where the drug is transported through the bloodstream to tissues, where it has its effects. The final process is elimination, mainly through the kidneys, ensuring the drug and its metabolites do not accumulate in the body.
Takeaways
- 😀 Absorption is the process of transporting a drug from the administration site into the bloodstream.
- 😀 The metabolism of a drug primarily occurs in the liver, where it is chemically altered.
- 😀 After metabolism, drugs may either become more active or, more commonly, less active.
- 😀 Distribution refers to the movement of the drug from the bloodstream into body tissues where it exerts its effects.
- 😀 Elimination is crucial to prevent drug accumulation and potential toxicity in the body.
- 😀 The kidneys are the main organ responsible for eliminating drugs from the body.
- 😀 Some drugs are eliminated through bile ducts into the gastrointestinal tract or via the lungs.
- 😀 The pharmacokinetic journey ensures drugs reach their intended site of action and are safely cleared.
- 😀 Each drug undergoes these four processes in a sequential order during its time in the body.
- 😀 The four key pharmacokinetic processes are absorption, metabolism, distribution, and elimination.
- 😀 Metabolism can either activate a drug or make it less active, influencing its therapeutic effect.
Q & A
What are the four major pharmacokinetic processes a drug goes through in the body?
-The four major pharmacokinetic processes are absorption, metabolism, distribution, and elimination.
What does the absorption process refer to in pharmacokinetics?
-Absorption refers to the transport of a drug from the site of administration to the systemic circulation.
Where does the main metabolism of drugs occur in the body?
-The main site of drug metabolism is the liver.
What happens to drugs after they are metabolized?
-After metabolism, drugs may either become activated or, more commonly, become less active.
What is the definition of the distribution process in pharmacokinetics?
-Distribution is the movement of drugs from the blood vessels into the extravascular spaces and body tissues where they exert their biological effects.
How does drug elimination prevent harm to the body?
-Elimination prevents the accumulation of drugs and their toxic metabolites in the body.
Which organ is primarily responsible for drug elimination?
-The primary organ responsible for drug elimination is the kidney.
Are all drugs eliminated by the kidneys?
-No, some drugs are eliminated through the bile ducts into the gastrointestinal tract or through the lungs.
What role do kidneys play in drug pharmacokinetics?
-The kidneys are mainly responsible for the elimination of drugs and their metabolites, ensuring they do not accumulate to toxic levels.
Why is the metabolism process important for drug effectiveness?
-The metabolism process is important because it determines whether a drug is activated or deactivated, impacting its therapeutic effects and duration of action.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Farmacologia - Farmacocinética de forma FÁCIL│ Medicina Resumida

FARMAKOLOGI - Prinsip Farmakokinetika Distribusi Metabolisme
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism & Excretion

Pharmacokinetics | Drug Distribution

Pharmacokinetics: Drug absorption and distribution

Lecture 1 Two compartment models
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)