SISTEM PENGISIAN PADA SAAT KECEPATAN RENDAH DAN SEDANG PART 2 NEW
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how the vehicle's charging system works at low and medium speeds, focusing on the alternator, voltage regulator, and related components. At these speeds, the rotor coil generates a magnetic field that induces voltage in the stator coil, which is then regulated by the voltage regulator. The system charges the battery, but at a reduced rate due to the lower power output from the alternator. The voltage relay controls the current to the rotor coil, ensuring the magnetic field and voltage are adjusted as needed, maintaining optimal performance for the vehicle's electrical system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The alternator and regulator are key components in controlling the electrical system of the vehicle.
- 😀 At low and moderate speeds, the rotor coil generates a magnetic field, which is captured by the stator coil to produce voltage.
- 😀 The voltage produced in the stator coil is transferred to the regulator, then to the voltage relay, and eventually to ground.
- 😀 The voltage relay creates a magnetic field that activates a switch to turn off the charging light when the system is functioning correctly.
- 😀 The alternator produces AC voltage, which is then rectified to DC voltage before being sent to the battery and other electrical components.
- 😀 The regulator controls the voltage by adjusting the magnetic field in the rotor coil, preventing overcharging or undercharging.
- 😀 The voltage regulator adjusts the voltage by controlling the current flow, ensuring that the battery gets charged correctly.
- 😀 The voltage relay regulates the current entering the rotor coil, ensuring it doesn't exceed required levels, which adjusts the magnetic field accordingly.
- 😀 During low and moderate speeds, battery charging occurs, but the process is not maximized due to limited current supply from the alternator.
- 😀 The overall electrical system requires careful regulation of voltage and current to maintain battery health and efficient operation.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this video script?
-The primary focus of the video script is explaining how the alternator and voltage regulator work during low and medium speed operations to manage battery charging and electrical supply.
What is the role of the alternator in the system described in the script?
-The alternator generates electricity by using the magnetic field produced by the rotor coil. This electricity is then captured by the stator coil and delivered to the system for charging the battery and powering electrical components.
What happens when the motor's speed is low or medium?
-At low and medium speeds, the rotor coil's magnetic field increases, which is captured by the stator coil to produce voltage. This voltage then flows through various components, such as the regulator and relay, to manage the charging of the battery.
How does the voltage regulator function in this system?
-The voltage regulator controls the voltage entering the rotor coil by adjusting the position of the voltage relay's contacts (PL0 and PL1), thus regulating the magnetic field and the amount of electricity produced by the alternator.
What is the purpose of the voltage relay in the system?
-The voltage relay's purpose is to regulate the current flowing into the rotor coil. It creates a magnetic field that influences the movement of the contacts to control the voltage output and maintain stable battery charging.
What is the role of the rectifier or diode in the alternator system?
-The rectifier or diode converts the alternating current (AC) generated by the stator coil into direct current (DC) before it is sent to the battery and other components, ensuring proper electrical flow.
What happens when the charging light turns off?
-When the charging light turns off, it indicates that the voltage relay has successfully closed the contacts, allowing the current to flow and properly regulate the charging process.
Why does the alternator not provide maximum charging at low and medium speeds?
-At low and medium speeds, the alternator and rotor coil are not supplying maximum current to the system. This results in less than full charging of the battery, though some power is still being supplied.
What happens to the current when the voltage relay pulls the contacts (PL0 and PL1) apart?
-When the voltage relay pulls the contacts apart, it decreases the current entering the rotor coil, reducing the magnetic field strength and therefore the voltage generated, thus helping to manage the overall electrical supply.
What is the significance of the magnetic field in the alternator system?
-The magnetic field generated by the rotor coil is crucial for inducing voltage in the stator coil. The strength of this magnetic field directly affects the amount of electrical power produced and the efficiency of the charging system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
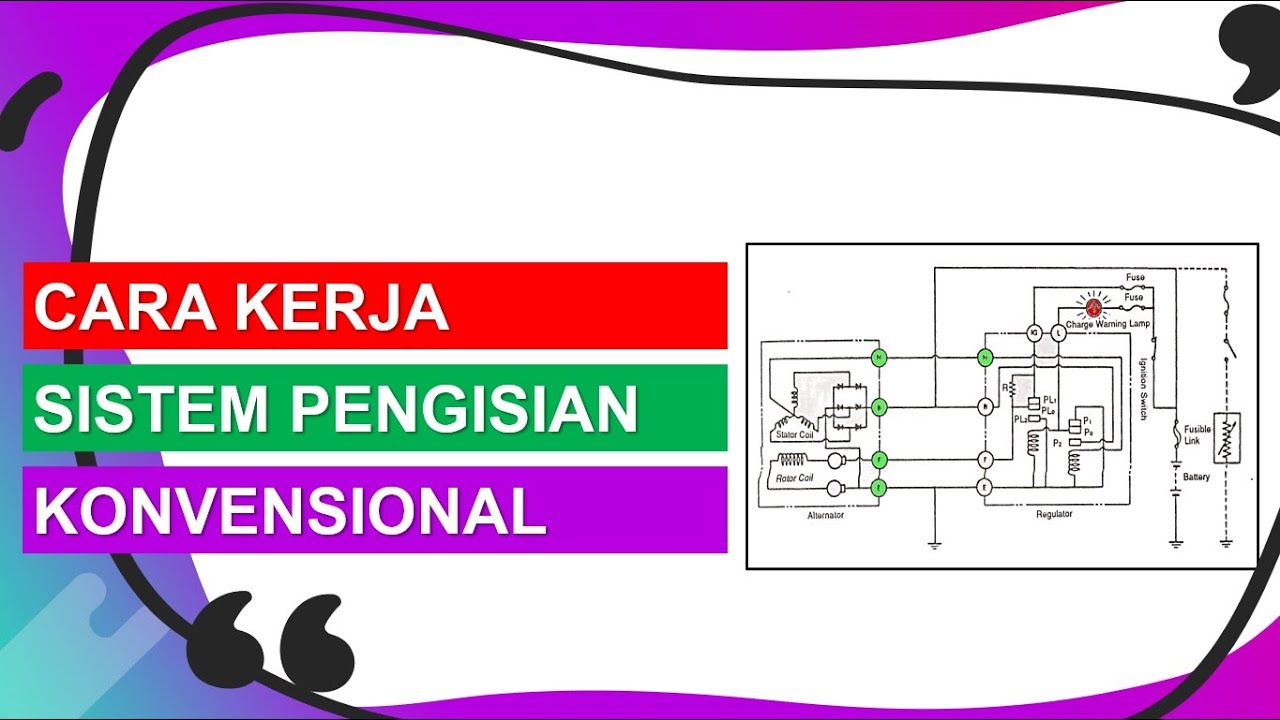
CARA KERJA SISTEM PENGISIAN KONVENSIONAL

JARANG YANG TAHU!!! Ternyata inilah Prinsip Kerja Generator Brushless PMG Excitation

Automotive Electrical System Basics - EricTheCarGuy

Prinsip kerja sistem pengisian IC regulator
How Alternators Work - Automotive Electricity Generator
Doosan Portable Power How A Generator Works
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)