Pharmacology Introduction in Hindi || Basic terms || Nursing || Pharmacy || 2nd year
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the basics of pharmacology, covering its definition and two main branches: pharmacodynamics (how drugs affect the body) and pharmacokinetics (what the body does to drugs). It explains essential pharmacology terms like drug, dose, potency, and efficacy, as well as concepts like drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. The video also highlights the roles of agonists, antagonists, side effects, toxicity, and contraindications in medicine, emphasizing the importance of proper drug administration for safe and effective treatment. Ideal for those new to pharmacology or seeking a refresher on key concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Pharmacology is a branch of medicine and biology that studies the effects of drugs, chemicals, and other substances on living organisms.
- 😀 Pharmacodynamics focuses on what drugs do to the body, including their mechanisms of interaction with cells, tissues, and organs to produce therapeutic effects.
- 😀 Pharmacokinetics examines what the body does to the drug, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
- 😀 The therapeutic index is a ratio that compares the dose required to produce a toxic effect with the dose required for therapeutic effect, ensuring drug safety.
- 😀 Half-life refers to the time it takes for a drug’s plasma concentration to reduce by half, helping determine the drug’s duration of effect.
- 😀 Agonists are substances that fully activate receptors, producing biological responses, while antagonists block receptors, preventing activation by agonists.
- 😀 Side effects are unintended effects of a drug, which can occur alongside the intended therapeutic effects.
- 😀 Toxicity is the harmful effects a drug can have on the body, often resulting from an overdose.
- 😀 Contraindications refer to specific situations where a drug or procedure should not be used, as it may harm the patient.
- 😀 Potency refers to the amount of a drug needed to produce a certain level of effect, helping determine appropriate doses for patients.
Q & A
What is pharmacology?
-Pharmacology is a branch of medicine and biology that studies the effects of drugs, chemicals, and other substances on living organisms. It involves understanding how these substances interact with biological systems and impact the body.
What are the two main branches of pharmacology?
-The two main branches of pharmacology are pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics explores what drugs do to the body, while pharmacokinetics examines what the body does to the drug.
What does pharmacodynamics study?
-Pharmacodynamics studies what drugs do to the body, including how they interact with cells, tissues, and organs, and how they produce therapeutic effects. It also looks at the mechanisms of drug action.
What is pharmacokinetics?
-Pharmacokinetics focuses on how the body processes a drug, examining the processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME), and how these processes determine drug concentration in the body over time.
What does the term 'ADME' stand for in pharmacokinetics?
-ADME stands for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion. It refers to the processes through which a drug is absorbed into the body, distributed, metabolized, and eventually excreted.
What is the therapeutic index?
-The therapeutic index is the ratio of the drug dose required to produce a therapeutic effect to the dose that could cause a toxic effect. It helps assess the safety of a drug.
What does half-life mean in pharmacology?
-Half-life refers to the time it takes for the concentration of a drug in the plasma to decrease by 50%. It is an important factor in determining how often a drug should be administered.
What is the difference between an agonist and an antagonist?
-An agonist is a substance that fully activates a receptor, leading to a biological response. In contrast, an antagonist binds to a receptor but does not activate it, blocking the action of an agonist.
What are side effects in pharmacology?
-Side effects are unintended effects that occur alongside the intended therapeutic effect of a drug. These effects are not the primary purpose of the medication but can still impact the patient.
What is potency in pharmacology?
-Potency refers to the amount of a drug needed to produce a certain level of effect. It is a measure of how much drug is required to achieve a specific therapeutic outcome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

INTRODUÇÃO A FARMACOLOGIA E TERMINOLOGIAS - FARMACOLOGIA 1

Introduction to PHARMACOLOGY | Pharmacology Quick and Easy | Flavonoide

Farmakologi Dasar : Pendahuluan
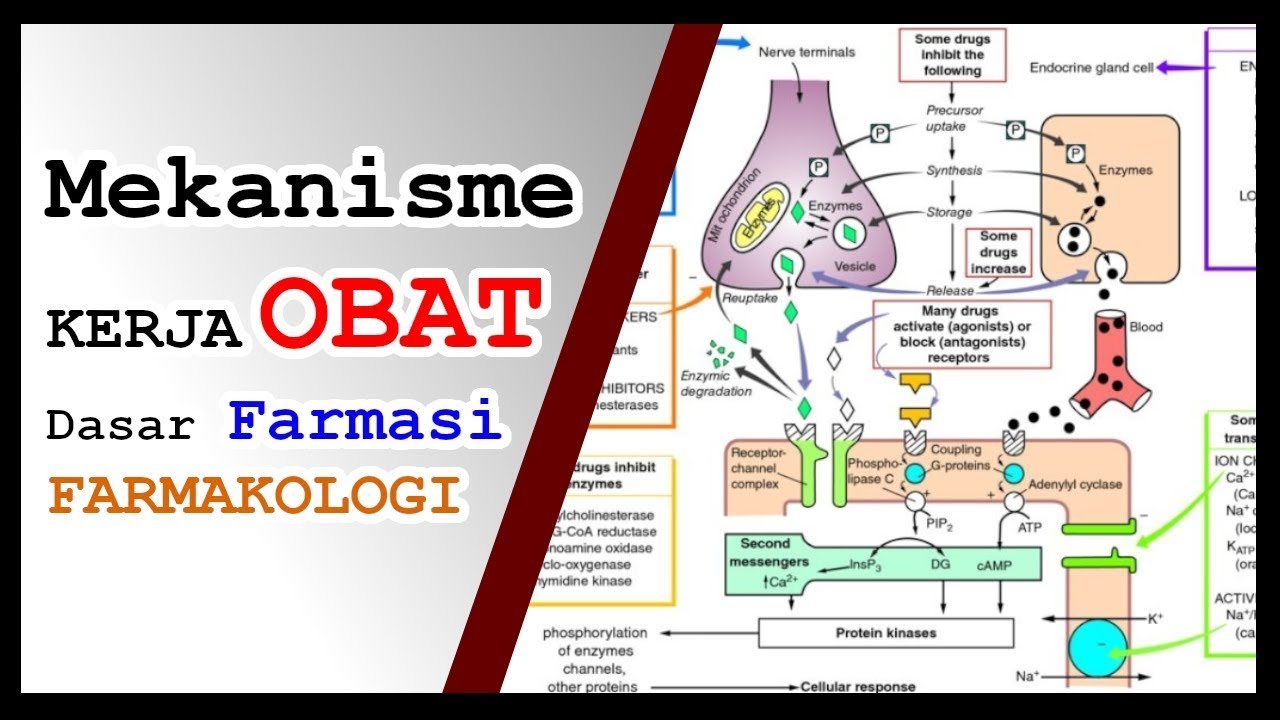
Farmakologi Medis - Mekanisme Kerja Obat Dasar Farmasi (1/5)

Pengantar Farmakologi Dasar - Part 1 I Sejarah dan Konsep Farmakologi I Cabang Ilmu Farmakologi

Pharmacology MADE EASY (Drugs and Receptors) - Perfect for beginners
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)