Sociology Series - [Week 11] - Sex, Gender, and Sexuality Definition (1)
Summary
TLDRThis transcript introduces a sociology lesson on gender, sex, and sexuality, focusing on the distinctions between biological sex and gender. It explains that sex refers to biological differences, while gender involves social behaviors and roles, which vary across cultures. The lecture explores how individuals may identify with gender roles different from their biological sex. It also discusses the Bugis culture's five gender identities and the concept of gender fluidity. The session touches on how cultural perceptions of gender and sexuality can influence social norms and understanding of human diversity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sex refers to the biological and physiological differences between males and females, such as reproductive organs and hormonal differences.
- 😀 Gender is a social and cultural construct related to the roles, behaviors, and traits associated with being male or female.
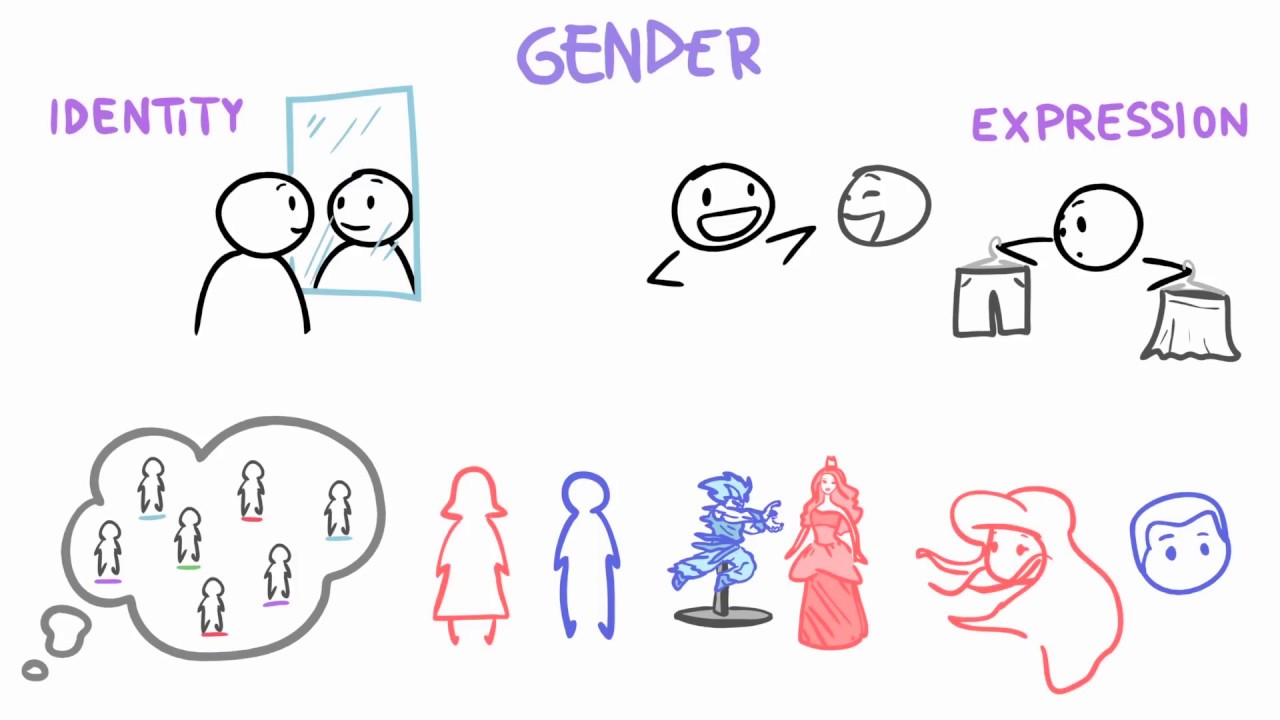
- 😀 There is a distinction between sex and gender, meaning someone may have a male biological sex but identify with a female gender, and vice versa.
- 😀 Gender identity is fluid and can encompass more than just masculine or feminine roles.
- 😀 Cultural differences influence gender perceptions, as seen in the example of skirts being masculine in Scotland but feminine in the U.S.
- 😀 In the Bugis culture of Indonesia, there are five recognized gender identities beyond the male-female binary.
- 😀 The Bugis gender identities include: 'Oroane' (biologically male with masculine roles), 'Makur Sori' (biologically female with feminine roles), 'Calabay' (biologically male performing feminine roles), 'Kalalai' (biologically female performing masculine roles), and 'Bisu' (a non-binary identity bridging the human and spiritual worlds).
- 😀 'Bisu' in Bugis culture is a transcendent identity that combines all gender elements and serves as a mediator between the human and spiritual realms.
- 😀 The understanding of gender is not universal and can vary significantly between cultures, as shown in both Western and Bugis cultural contexts.
- 😀 The upcoming discussion will focus on sexual orientation, its classifications, and its social implications.
Q & A
What is the difference between 'sex' and 'gender' as described in the script?
-The script explains that 'sex' refers to the biological or physiological differences between males and females, such as reproductive systems and physical traits. 'Gender', on the other hand, refers to the social roles, behaviors, and personalities associated with being male or female, which can vary across cultures and societies.
How does the script define 'sex' in terms of biological differences?
-'Sex' is described as the biological or physiological differences between males and females, such as the presence of reproductive organs, menstruation in females, and sperm production in males. These traits are largely universal and do not vary much across cultures.
What are some cultural variations mentioned in the script regarding gender roles?
-The script highlights the example of wearing a skirt: in the United States, wearing a skirt is often seen as feminine, whereas in Scotland, it is viewed as masculine. This demonstrates how gender roles and stereotypes can differ between cultures.
What does the script say about the fluidity of gender identity?
-The script emphasizes that gender identity is fluid and not strictly limited to masculine or feminine roles. A person may identify with a gender that differs from their biological sex, and there is a wide spectrum of gender identities beyond just male and female.
How does the script address gender roles in Native American cultures?
-The script mentions the concept of 'Two-Spirit' individuals in Native American cultures, where some people embody both male and female gender roles. This identity is accepted within certain Native American communities, showing a more inclusive view of gender roles.
What is the significance of the Bugis culture in relation to gender identity?
-The Bugis culture recognizes five gender identities, as outlined in their traditional understanding. These include male (oroane), female (makunai), and gender-nonconforming identities like calabay (biologically male but adopting feminine roles), kalalai (biologically female but adopting masculine roles), and bisu (a non-binary identity that blends all gender elements).
What does 'bisu' refer to in Bugis culture?
-'Bisu' refers to a non-binary or transcendent gender identity in Bugis culture. It is considered a combination of all gender elements and is seen as a mediator between the human and spiritual worlds.
What role does culture play in shaping gender identities, according to the script?
-The script highlights that culture plays a significant role in shaping gender identities. It discusses how different societies can have varying norms and expectations about gender roles, as seen in examples from Bugis culture and Native American traditions.
How does the script distinguish between the concepts of biological sex and gender identity?
-The script clarifies that biological sex refers to the physical, physiological traits that differentiate males and females, such as reproductive organs and physical strength. In contrast, gender identity is a social and personal understanding of oneself, which may not necessarily align with one's biological sex.
Why is it important to distinguish between sex, gender, and sexuality in sociological studies?
-Distinguishing between sex, gender, and sexuality is important because each concept represents a different aspect of human identity. Understanding these differences allows for a deeper comprehension of social roles, behaviors, and orientations, which is crucial for addressing issues related to equality, rights, and cultural diversity in sociology.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sex & Sexuality: Crash Course Sociology #31

Sex, Sexuality, Gender Relations | Prof. Mary Barby P. Badayos-Jover

DEFINIÇÃO SEXO/GÊNERO E IDENTIDADE/ ORIENTAÇÃO SEXUAL

Kenapa Jenis Kelamin ada 2? (Laki-laki dan Perempuan)

Factors Affecting Sexual Behaviors - Quarter 1, Lesson 2, Health 8
Sex vs Gender vs Orientation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)