Michael Faraday's Experiment #class 10 physics
Summary
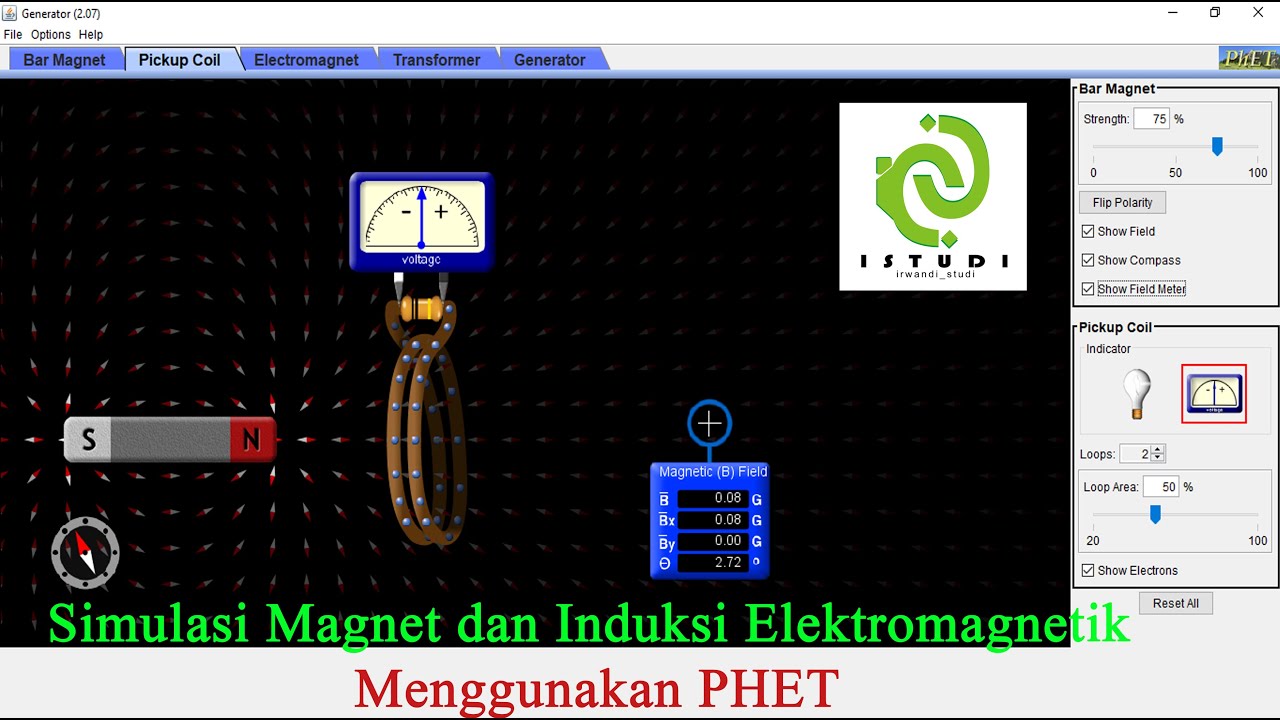
TLDRIn this video, the concept of Michael Faraday's experiment on electricity generation is explained. The experiment demonstrates how moving a bar magnet through a circular coil induces electricity. The strength of the induced current depends on factors such as the speed of movement, the number of coils, and the polarity of the magnet. The video illustrates how the voltage, as indicated by a voltmeter, increases with faster movements and more coils, causing brighter light. The explanation also touches on the magnetic field's role in the induction process, leading to the production of induced currents.
Takeaways
- 😀 Michael Faraday's experiment demonstrates how electricity is produced through the movement of a bar magnet within a circular coil.
- 😀 A voltmeter is used in the experiment to measure the potential difference produced by the movement of the magnet.
- 😀 The production of electricity occurs when the bar magnet moves in and out of the circular coil, creating an electric current.
- 😀 The rate of deflection on the voltmeter increases when the magnet is moved faster, demonstrating a higher intensity of electricity.
- 😀 Changing the polarity of the magnet does not change the fact that electricity is produced.
- 😀 The amount of electricity produced depends on how quickly the magnet is moved in the experiment.
- 😀 Using a coil with fewer loops results in a lower current and a dimmer light bulb.
- 😀 The more coils in the circular coil, the higher the electricity produced, as seen in the voltmeter readings and the brightness of the bulb.
- 😀 The experiment illustrates the principle of electromagnetic induction, where moving a magnet through a coil induces an electric current.
- 😀 The induced current is a result of the movement of the magnet creating a disturbance in the magnetic field, allowing electrons to flow through the coil.
Q & A
What is the main objective of Michael Faraday's experiment as described in the script?
-The main objective of Michael Faraday's experiment is to demonstrate how electricity is produced through the movement of a bar magnet inside a circular coil, illustrating electromagnetic induction.
What equipment is required to perform this experiment?
-The experiment requires a circular coil, a voltmeter to measure the potential difference, and a bar magnet to create the magnetic field.
How does the motion of the bar magnet affect the electricity produced in the experiment?
-The electricity is generated when the bar magnet is moved in and out of the circular coil. The speed of the movement influences the intensity of the electricity produced.
What happens when the bar magnet is moved slowly in the coil?
-When the bar magnet is moved slowly, the deflection on the voltmeter is small, indicating that less electricity is generated. The bulb also glows with a dimmer light.
How does rotating the bar magnet around the coil affect the electricity produced?
-Rotating the bar magnet around the circular coil increases the intensity of the electricity produced, as evidenced by more significant deflections on the voltmeter and a brighter bulb.
What role does the number of coils in the circular coil play in the experiment?
-The number of coils in the circular coil affects the amount of electricity produced. A higher number of coils generates more electricity, which is reflected in the increased brightness of the bulb and greater voltmeter deflection.
What happens when the polarity of the bar magnet is reversed?
-When the polarity of the bar magnet is reversed, the production of electricity remains the same. This indicates that the direction of the magnetic field doesn't alter the overall induction process.
What is the term used to describe the current produced in this experiment?
-The current produced in this experiment is called the induced current, which is generated due to the motion of the magnet within the magnetic field.
How does the speed of movement of the bar magnet influence the electricity produced?
-The faster the bar magnet is moved, the greater the amount of electricity is generated, as seen in the increased deflections on the voltmeter and brighter light in the bulb.
What does the magnetic field of the bar magnet do in the experiment?
-The magnetic field of the bar magnet interacts with the circular coil, causing electrons to move through the coil and generate an induced current, which flows through the connected wire.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GGL INDUKSI PADA SUATU KUMPARAN

Faraday's Law of Induction Demonstration - Penn Physics

Electromagnetic induction (& Faraday's experiments)

michael faraday | law of electromagnetic induction | faraday's law of induction
Simulasi Magnet dan Induksi Elektromagnetik Menggunakan PHET

GAYA GERAK LISTRIK | KELAS XII | FISIKA ITU MUDAH [Nabila Ratna Az-Zahra]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)