Músculo Esquelético 2/6: Tecido Conjuntivo, Irrigação Sanguínea e Inervação | Anatomia e etc
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the speaker explores the characteristics of skeletal muscle, focusing on its connective tissue layers, blood supply, and innervation. The video explains the different layers of connective tissue surrounding muscle fibers, such as endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium, and how they extend to form tendons. The importance of blood vessels and motor neurons in muscle function is also discussed, as well as the concept of motor units. The speaker emphasizes the need for proper vascularization and neural stimulation for efficient muscle contraction and overall muscle health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The focus of today's lesson is on skeletal muscle tissue, specifically the connective tissue, blood supply, and nerve innervation in skeletal muscles.
- 😀 The Black Friday event is offering a 24-hour window for registration to an anatomy conference, starting at noon on Saturday.
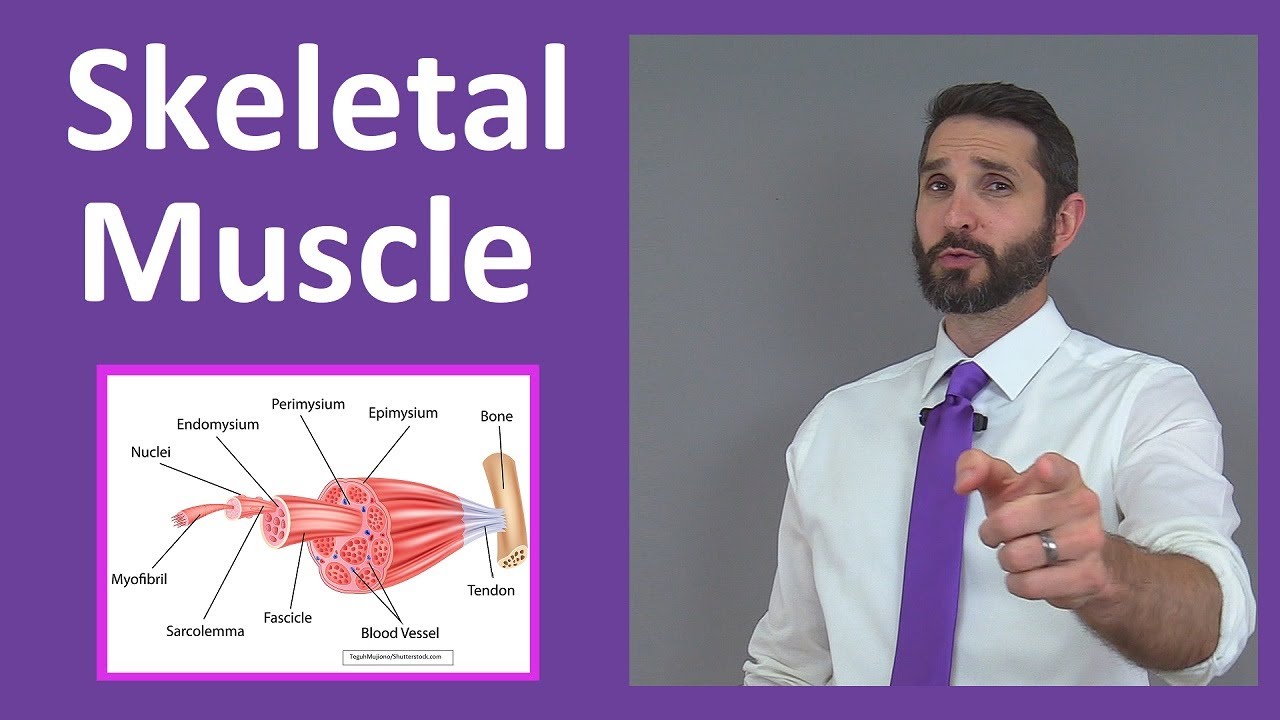
- 😀 Skeletal muscles are surrounded by different layers of connective tissue, starting with the endomysium, which covers each muscle fiber.
- 😀 Muscle fibers are organized in parallel and grouped into bundles, which are wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.
- 😀 The entire muscle is composed of these fiber bundles and is encased in the epimysium, which covers the whole muscle.
- 😀 Tendons connect skeletal muscles to bones and are extensions of the connective tissue layers (endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium).
- 😀 Fascial tissue surrounds groups of muscles, keeping them together and separating different muscle groups.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles require a rich blood supply to function properly, providing the energy and nutrients needed for muscle contraction.
- 😀 Muscle contraction also produces waste products that need to be removed from the muscle and the body, a process facilitated by the blood supply.
- 😀 A motor neuron stimulates muscle fibers to contract, and a motor unit is the combination of one motor neuron and the muscle fibers it controls.
Q & A
What is the focus of the lecture in the transcript?
-The lecture focuses on the skeletal muscle, specifically the connective tissue components, blood supply, and innervation involved in muscle function.
What is the significance of the 'endomysium' in skeletal muscle?
-The 'endomysium' is a connective tissue layer that covers each individual muscle fiber, providing support and protection.
What is the role of the 'perimysium' in muscle structure?
-The 'perimysium' is the connective tissue that surrounds a bundle of muscle fibers, known as a fascicle, and helps in organizing the muscle fibers into functional groups.
What does the 'epimysium' do in skeletal muscle?
-The 'epimysium' is the outermost connective tissue layer that surrounds the entire muscle, helping to maintain the structure and integrity of the muscle as a whole.
What is the role of tendons in skeletal muscle function?
-Tendons connect skeletal muscles to bones and are composed of connective tissue, including extensions of the 'endomysium,' 'perimysium,' and 'epimysium' to ensure muscle-to-bone attachment.
What is fascia muscular and what is its function?
-Fascia muscular is a dense connective tissue that covers groups of muscles, helping to keep them together and separate different muscle groups based on their function.
Why is a good blood supply essential for skeletal muscles?
-Skeletal muscles require a good blood supply to deliver oxygen and nutrients necessary for muscle contraction and energy production, and to remove waste products produced during muscle activity.
How do neurons interact with skeletal muscles to stimulate contraction?
-Neurons, specifically motor neurons, send electrical impulses called action potentials to muscle fibers, which triggers muscle contraction. Each motor neuron stimulates multiple muscle fibers, creating a 'motor unit.'
What is a motor unit in muscle physiology?
-A motor unit consists of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates. When the motor neuron is stimulated, all fibers in the motor unit contract simultaneously.
How do capillaries contribute to muscle function?
-Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that surround muscle fibers, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach the muscle cells, and waste products are removed, facilitating proper muscle function and recovery.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)