Population Genetics: When Darwin Met Mendel - Crash Course Biology #18
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker introduces the principles of population genetics, blending the ideas of Gregor Mendel and Charles Darwin. They explain how genetic changes in populations happen over time through processes like natural selection, sexual selection, mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow. By using a hypothetical example of earwax traits, the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is explored, showing how allele frequencies remain stable in a population when no evolutionary forces are at play. This engaging explanation connects Mendel’s genetics with Darwin’s theory of evolution, using both math and real-world examples to illustrate how populations evolve.
Takeaways
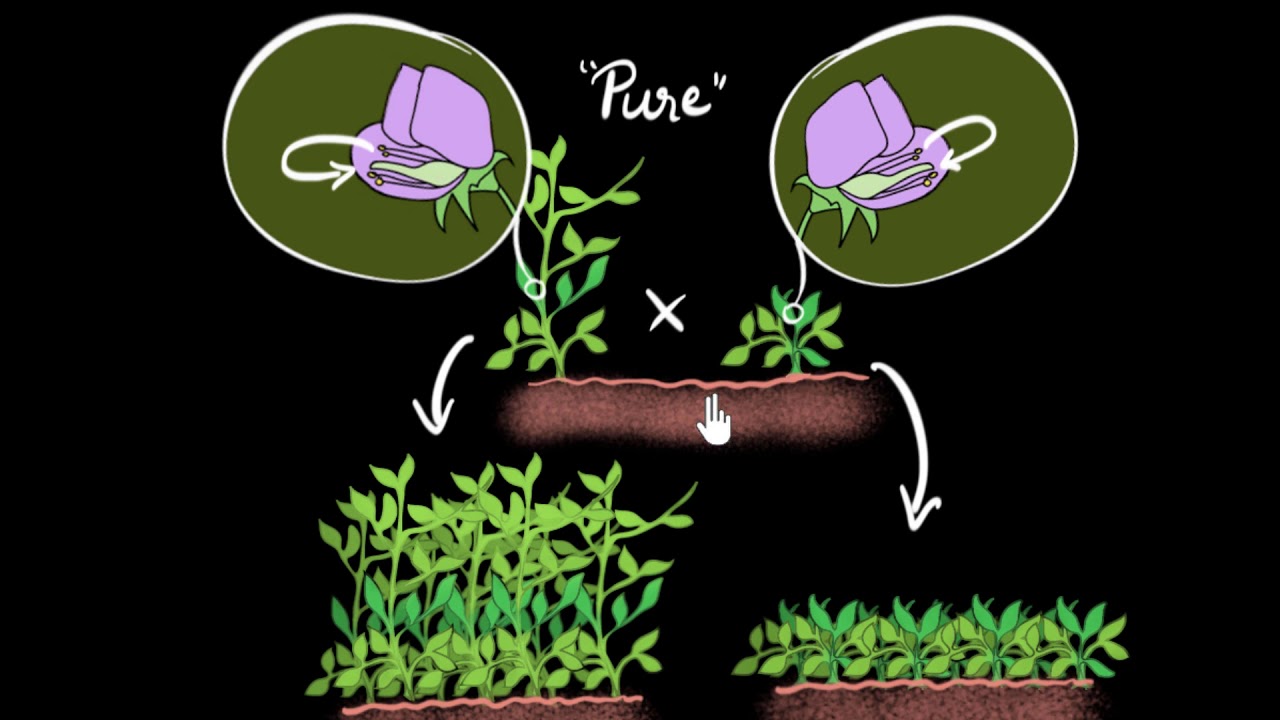
- 😀 Mendel discovered the basic principles of genetics, including the idea that both parents contribute one allele for each gene to their offspring.
- 😀 Some alleles are dominant and always expressed, while others are recessive and only show up when paired with another recessive allele.
- 😀 Darwin's theory of natural selection did not have an understanding of heredity, leaving a gap in explaining how traits were passed on to offspring.
- 😀 Population genetics studies how the genetic makeup of a population changes over time, leading to evolution.
- 😀 A population is defined as a group of individuals of the same species that can interbreed.
- 😀 Allele frequency refers to how often a particular allele appears in a population, and changes in allele frequency drive evolution.
- 😀 The five main factors that change allele frequency in a population are natural selection, sexual selection, mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow.
- 😀 Natural selection increases the frequency of alleles that make individuals more fit for survival, while sexual selection increases the frequency of alleles that make individuals more attractive mates.
- 😀 Mutation introduces new alleles into a population, which can sometimes be beneficial, helping organisms survive and reproduce.
- 😀 Genetic drift causes changes in allele frequencies by random chance, and its effect is more pronounced in small populations.
- 😀 Gene flow occurs when individuals from one population migrate and introduce new alleles into another population, influencing allele frequencies.
Q & A
What is the significance of Gregor Mendel's work in genetics?
-Gregor Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity, establishing that both parents contribute alleles to their offspring. His work laid the foundation for understanding genetic inheritance and how traits are passed down.
How does Darwin's theory of natural selection relate to Mendel's findings?
-Darwin's theory of natural selection explains how certain traits become more common in a population over time. However, Darwin didn't understand how traits were inherited. Mendel's discoveries in genetics complement Darwin’s theory by explaining how traits are passed down genetically.
What is population genetics and why is it important?
-Population genetics is the study of how genetic variation changes within a population over time, leading to evolution. It helps explain the mechanisms behind natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, gene flow, and sexual selection.
What is an allele frequency, and why is it important in population genetics?
-Allele frequency refers to how often a particular allele appears in a population. Changes in allele frequency are central to how populations evolve over time.
What are the five main factors that influence allele frequency in a population?
-The five main factors influencing allele frequency are: natural selection, sexual selection, mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow.
What is sexual selection and how does it affect allele frequency?
-Sexual selection is when certain traits increase an individual's chances of mating, even if those traits don’t contribute directly to survival. These traits become more common in the population because individuals with them are more likely to reproduce.
How do mutations contribute to evolution?
-Mutations are random changes in DNA that can create new alleles. While some mutations may be harmful, others can be beneficial by improving an organism's ability to survive and reproduce, and those beneficial mutations can spread through the population.
What is genetic drift and how does it affect small populations?
-Genetic drift is the change in allele frequency due to random chance, which is more pronounced in small populations. Events like natural disasters can drastically alter allele frequencies in a small population.
What is gene flow and how does it influence genetic diversity?
-Gene flow occurs when individuals from different populations interbreed, introducing new alleles into a population. This can increase genetic diversity and affect the overall allele frequencies of a population.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, and under what conditions does it apply?
-The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium describes a population where allele frequencies remain constant over generations. For this to occur, there must be no natural selection, no sexual selection, no mutations, a large population size, and no gene flow.
How is the Hardy-Weinberg equation used to calculate allele frequencies in a population?
-The Hardy-Weinberg equation (p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1) is used to calculate the frequency of genotypes in a population. By knowing the frequency of the recessive allele (q^2), we can calculate the frequency of the dominant allele (p), and subsequently, the frequencies of the homozygous and heterozygous genotypes.
What does the scenario of 'hot surfers' moving to an island demonstrate in terms of population genetics?
-The 'hot surfers' example illustrates how nonrandom mating (such as preference for certain mates) can influence genetic frequencies. When individuals with a particular trait (like dry earwax) move into a population, it can alter the genetic makeup of that population.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Gregor Mendel: The Father of Modern Genetics
Mendel's experiment (monohybrid cross) | Heredity & Evolution | Biology | Khan Academy

Mendel e a Ervilha - Os Seis Experimentos que Mudaram o Mundo

História de GREGOR MENDEL - GENÉTICA
Genetics - Lost and Found: Crash Course History of Science #25

A Genética da variabilidade | Filosofia das Origens #4
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)