🧪 CARACTERÍSTICAS ATÔMICAS
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging video, Professor Gabriel Cabral breaks down key concepts of atomic structure, including atomic number, mass number, protons, neutrons, and isotopes. With a fun and approachable style, he explains how atomic number identifies elements and how mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. The video also covers how to calculate neutrons and the significance of isotopes—atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Gabriel encourages viewers to stay focused and provides tips for mastering these concepts in chemistry, specifically for the ENEM exam. His energetic teaching style makes complex topics more accessible and enjoyable.
Takeaways
- 😀 The atomic number represents the number of protons in an element's nucleus, and it identifies the element itself.
- 😀 The atomic number is like an element's 'ID card,' differentiating one element from another based on its number of protons.
- 😀 A change in the number of protons alters the identity of the element (e.g., hydrogen to helium as the number of protons increases).
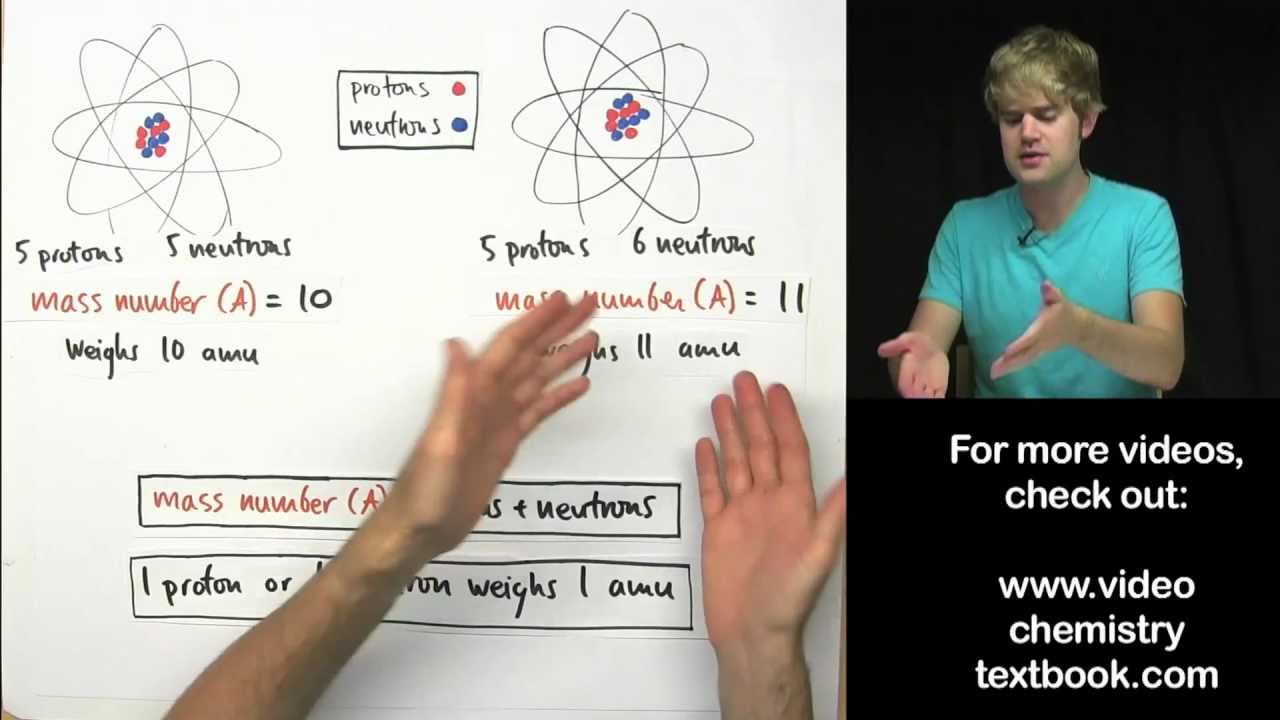
- 😀 The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, giving the total number of particles.
- 😀 To calculate the mass number, you simply add the number of protons and neutrons.
- 😀 Example: For an atom with 3 protons and 4 neutrons, the mass number is 7 (3 + 4 = 7).
- 😀 Every element can be represented with a symbol, with the mass number at the top and the atomic number at the bottom.
- 😀 Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, which results in different mass numbers.
- 😀 To calculate the number of neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the mass number: Neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number.
- 😀 For example, if the mass number is 35 and the atomic number is 17, the number of neutrons is 18 (35 - 17 = 18).
- 😀 Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are referred to as isotopes, and they are identified by their mass numbers (e.g., Cl-35 and Cl-37).
Q & A
What is the atomic number of an element?
-The atomic number is the number of protons in an element's nucleus. It identifies the element and determines its place in the periodic table.
How do you calculate the mass number of an element?
-The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
What is the difference between the atomic number and the mass number?
-The atomic number refers to the number of protons, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons combined.
How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom?
-To find the number of neutrons, subtract the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number.
What are isotopes?
-Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers.
Can you give an example of two isotopes of the same element?
-Yes, for example, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37. Both have 17 protons, but the number of neutrons differs, giving them different mass numbers.
Why do atoms of the same element have different mass numbers?
-Atoms of the same element have different mass numbers because they contain different numbers of neutrons, leading to variations in their mass.
What is the symbol representation of an element?
-The symbol representation of an element consists of the element's chemical symbol, with the mass number on top and the atomic number on the bottom.
What is the atomic number of hydrogen?
-The atomic number of hydrogen is 1, meaning it has one proton in its nucleus.
How do you distinguish between isotopes of the same element?
-Isotopes of the same element are distinguished by their mass numbers, which differ due to the varying number of neutrons, though the atomic number remains the same.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Isotopes and Isobars | Atoms and Molecules | Don't Memorise

Struktur Atom | Elektron Proton Neutron | Notasi Atom | No Massa | Isotop Isobar Isoton Isoelektron

LAMBANG ATOM

Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial

ESTRUTURA ATÔMICA - PRÓTONS, NÊUTRONS E ELÉTRONS
What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)