Pressure Swing Adsorption Process For Air Purification|| PSA Cycle|| Aspen Adsorption
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) process for air purification is explored. The tutorial covers setting up the process using simulation tools, configuring component properties, and defining key parameters such as adsorption and desorption cycles. Detailed steps include adjusting gas dynamics, setting up column properties, and analyzing breakthrough curves to monitor performance. The cycle alternates between adsorption and desorption, ensuring continuous operation. The video also guides the viewer through the simulation setup, result analysis, and plotting key data like nitrogen and oxygen concentrations. Ideal for anyone learning about gas separation and PSA technology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Overview: The lecture focuses on the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) process for air purification.
- 😀 Comparison: The current topic builds upon the previously covered Temperature Swing Adsorption (TSA) process.
- 😀 SP Absorption Setup: The configuration of SP Absorption involves selecting components from the property system and defining their properties using the SPEN file.
- 😀 Process Flow Sheet: The PSA process flow sheet includes various components such as the bottom tank, top tank, and absorption column, each with specific designations and connections.
- 😀 Component Definition: The field gas consists of 79% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, with a pressure of 3.45 bar for the feed gas.
- 😀 Stream Specifications: The pressure for the West stream and product stream is set to 1 atm for both, ensuring standard conditions.
- 😀 Bed Configuration: The bed is defined with specific parameters such as vertical orientation, one-dimensional dimension, and material balance equations like Aron or Caron models.
- 😀 Column Details: The absorption column’s design includes factors like column height, diameter, and mass transfer coefficient, with initial conditions set for simulation.
- 😀 PSA Cycle: The PSA process is divided into two steps: adsorption and desorption, with cycles of 1000 seconds each, controlled by manipulated variables such as feed and product wall specifications.
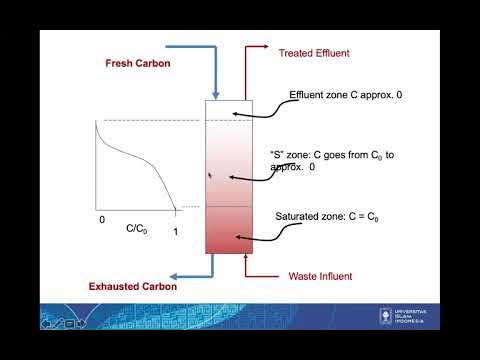
- 😀 Breakthrough Curve: The simulation results in a breakthrough curve that shows the nitrogen and oxygen composition in the product stream over time, aiding in performance analysis.
- 😀 Solid Loading: The solid loading distribution is tracked at different column nodes to monitor nitrogen and oxygen loading at various stages of the column (bottom, middle, top).
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is the Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA) process for the purification of air.
What process was discussed in the previous lecture?
-The previous lecture focused on the Temperature Swing Absorption (TSA) process.
How does the speaker set up the property configuration for the PSA system?
-The speaker sets up the property configuration by opening the SP Absorption module, selecting the S-property Sy system, and adding components using SpanPlus or the property definition file.
What are the key components specified in the process flow sheet?
-The key components specified in the process flow sheet include the top tank, bottom tank, bed, and product streams.
How are the material streams connected in the PSA process?
-The material streams are connected to the bed by using the connection gas material feature in the SP Absorption software.
What parameters are specified for the feed stream?
-The feed stream consists of 79% nitrogen and 21% oxygen with a pressure of 3.45 bar.
What are the specifications for the product stream?
-The product stream pressure is set to 1 atm, and the product wall active specification is also set accordingly.
What details are provided for the absorption column in the simulation?
-The absorption column is detailed with specifications such as the number of layers, type (vertical), dimension (one-dimensional), heat exchanger presence, material balance equation, kinetic model, and mass transfer coefficients.
What are the two steps in the Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA) cycle?
-The two steps in the PSA cycle are absorption and desorption. Both steps last for 1000 seconds each.
What are the main variables manipulated during the absorption and desorption steps?
-During absorption, the feed wall is closed, and the product wall is active. During desorption, the feed wall and product wall are closed, while the WTE wall is open with a constant CV value.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Adsorption Columns & Equipment - How do they Work? (Lec127)

2 Hydrogen Generation Plant via Natural Gas Reforming

Nitrogen Plant working principle #N2 Plant kaise kam karta hai#Nitrogen Plant kya hota hai
Pertemuan 18 Adsorpsi Bagian 2, SOSP TL, Prodi TL UII, 2020-2021

Hydrostatic Pressure (Fluid Mechanics - Lesson 3)

Surface Area Analysis of Carbon Materials
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)