06 - As Leis de Newton.
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into Newton's laws of motion, exploring the fundamental relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It traces the development of classical mechanics from Copernicus to Galileo, highlighting the breakthroughs of Kepler and Newton. Newton's three laws of motion are explained, showcasing how they define the movement of objects, including the influence of gravity and inertia. The video also emphasizes the elegance and simplicity of Newton's equation, F = ma, which governs all motion, offering insight into how these principles laid the groundwork for modern physics and our understanding of the universe.
Takeaways
- 😀 Newton's three laws of motion provide a foundation for understanding the mechanics of the universe and govern everything from the movement of objects on Earth to the motion of celestial bodies.
- 😀 The first law of motion, or the law of inertia, states that a body will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
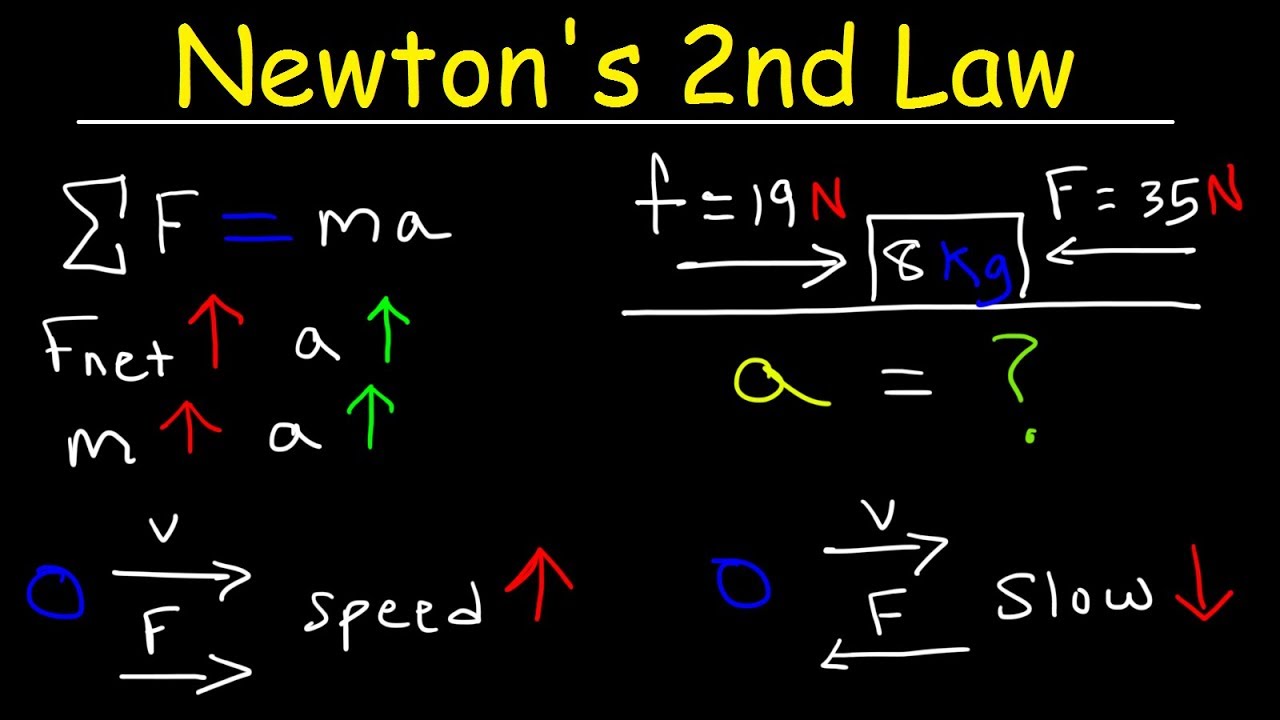
- 😀 The second law of motion, represented by the equation F = ma (Force equals mass times acceleration), is key to understanding how forces affect the motion of objects.
- 😀 The third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, meaning all objects interact with each other through forces.
- 😀 The equation F = ma is powerful, as it links force, mass, and acceleration, allowing for the calculation of motion under different conditions.
- 😀 Galileo's observations about projectile motion led to the realization that projectiles follow a parabolic path, influenced by gravity, which is described by Newton's laws.
- 😀 The concept of acceleration is essential in understanding motion, and it is a rate of change of velocity, which itself is a derivative of time.
- 😀 Despite its simplicity, Newton's equation F = ma reveals complex principles, such as the fact that force and acceleration are vectors, and the need for directional alignment in calculations.
- 😀 Newton's laws not only clarified terrestrial mechanics but also unified the understanding of motion both on Earth and in the heavens, governing the movement of planets and comets.
- 😀 The impact of Newton’s laws extended beyond scientific theory and altered our understanding of the physical world, replacing older Aristotelian concepts that were rooted in mystical explanations.
Q & A
What is the core concept of the script?
-The core concept of the script revolves around the understanding of classical mechanics, particularly Newton's laws of motion and their application to various real-world phenomena, like projectile motion and gravity. The script discusses how Newton's laws explain the movement of objects both on Earth and in space.
What role did Isaac Newton play in the development of physics?
-Isaac Newton revolutionized physics by formulating the laws of motion, which provided a unifying explanation for the movement of objects both on Earth and in space. His work established the foundation for classical mechanics, which remains central to our understanding of physical laws.
How does Newton's second law explain motion?
-Newton's second law states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma). This law explains how a force changes the motion of an object, with the direction and magnitude of the force determining the object's acceleration.
What is acceleration, and how is it related to Newton's laws?
-Acceleration is the rate of change of an object's velocity. It is a key component of Newton's second law (F = ma), as the force applied to an object causes it to accelerate. The script explains that acceleration is not just velocity but the rate at which an object’s speed increases or decreases.
How do Newton's laws relate to projectile motion?
-Newton's laws, particularly the second and third laws, govern the motion of projectiles. The script demonstrates how gravity acts on a projectile, causing it to follow a curved, parabolic trajectory. The horizontal motion of the projectile remains constant, while the vertical motion is influenced by the constant acceleration due to gravity (g).
What is the significance of Galileo’s contributions to projectile motion?
-Galileo’s discoveries laid the groundwork for understanding projectile motion. He demonstrated that objects moving horizontally and vertically at the same time follow independent paths. This was a crucial step in understanding that projectiles follow a curved trajectory, which Newton later formalized in his laws.
Why is Newton's third law important in understanding interactions between objects?
-Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law is fundamental in understanding the interactions between objects. For instance, when a projectile is launched, the force it exerts on the air is met with an equal and opposite force, which affects its motion.
How does the script explain the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration?
-The script explains that the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is captured by the equation F = ma. It emphasizes that for an object to accelerate, a force must be applied, and the object's mass influences how much acceleration is produced by a given force.
What is the significance of the equation F = ma in understanding the universe?
-The equation F = ma is central to understanding the physical universe because it describes how objects move under the influence of forces. It encapsulates the basic principles of motion, explaining how forces cause acceleration in objects, which is crucial for predicting the behavior of everything from projectiles to planets.
What philosophical debate is mentioned in the script regarding the understanding of force and motion?
-The script touches on the philosophical debate about the nature of motion, particularly the shift from Aristotle’s view of motion as needing a continuous force to keep objects moving, to the understanding of inertia and Newton’s laws. This change in perspective marked a transition from a static to a dynamic understanding of the physical world.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)