Alat Reproduktif Wanita
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the anatomy and reproductive processes of the female body, starting with the internal and external reproductive organs. It explains the role of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina in reproduction. The video delves into oogenesis, detailing how egg cells form and mature, and the hormonal regulation of ovulation. It also discusses the menstrual cycle, including the roles of FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone in the development of follicles, the thickening of the endometrium, and menstruation. The content is informative and outlines the intricate workings of female reproduction, highlighting the connection between hormones and fertility.
Takeaways
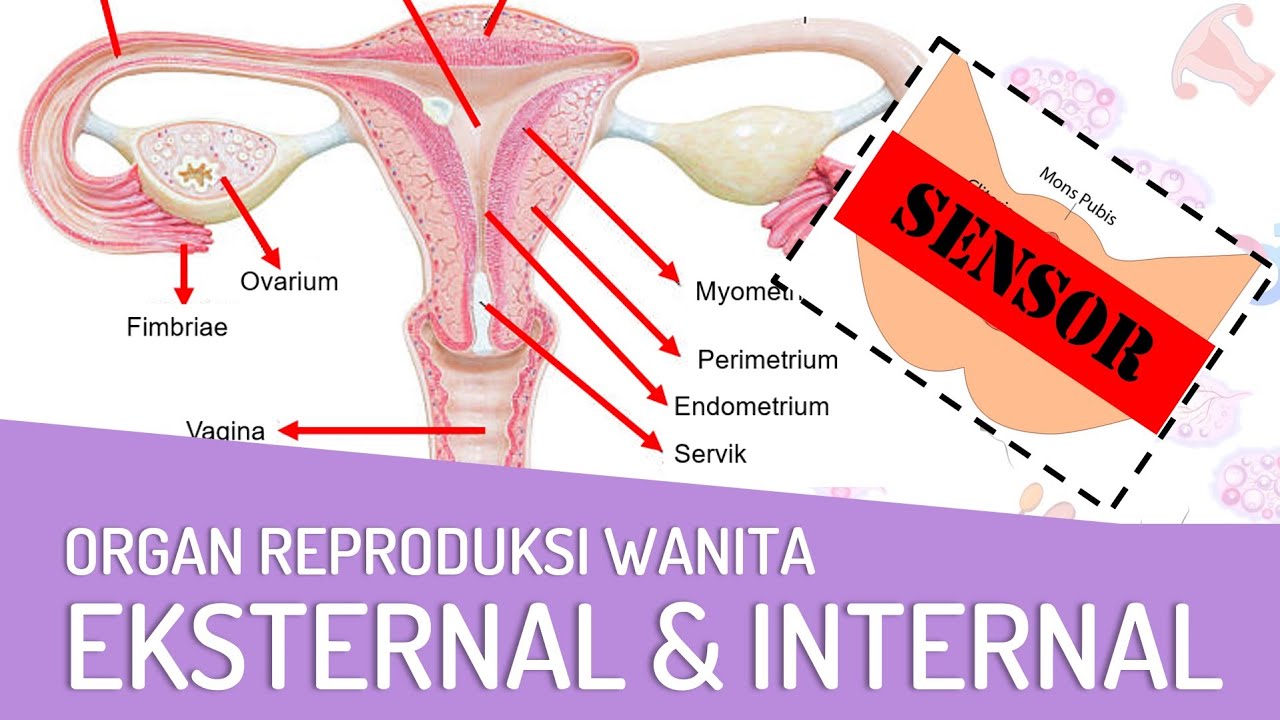
- 😀 The female reproductive system consists of both internal and external genitalia, with the internal components including ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
- 😀 The ovaries contain follicles, which hold immature eggs (oocytes) that develop and release estrogen, playing a key role in reproduction.
- 😀 The fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, catch eggs released from the ovaries and transport them toward the uterus.
- 😀 The uterus is a thick, muscular, hollow organ where fertilized eggs implant and develop into embryos.
- 😀 The cervix connects the uterus to the vagina and serves as the gateway between the internal and external genitalia.
- 😀 The vagina is a muscular canal lined with epithelial tissue and folds, providing an area for sperm entry and menstruation.
- 😀 The external genitalia include the vulva, labia, and clitoris, with the clitoris functioning similarly to the male penis due to its erectile tissue.
- 😀 Oogenesis, or egg formation, begins in fetal life, where primordial germ cells develop into oogonia and later oocytes.
- 😀 At birth, females already have their total oocyte count, which decreases over time, with only about 400,000 remaining by puberty.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormonal fluctuations, with FSH and LH from the pituitary gland stimulating follicle growth, ovulation, and the formation of the corpus luteum.
Q & A
What are the main parts of the female reproductive system discussed in the script?
-The main parts of the female reproductive system discussed are the internal reproductive organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina) and the external reproductive organs (vulva, labia, clitoris).
What is the role of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
-The ovaries are responsible for producing and releasing eggs (oocytes) and secreting hormones such as estrogen, which helps regulate the reproductive cycle.
What is the process of oogenesis?
-Oogenesis is the process through which egg cells (oocytes) are formed. It begins during fetal development, continues through puberty, and occurs in stages involving meiosis, with the primary oocyte maturing into a secondary oocyte ready for ovulation.
How do the fallopian tubes contribute to fertilization?
-The fallopian tubes (or oviducts) capture the egg released from the ovary during ovulation. They are also the site where fertilization occurs if sperm meets the egg.
What happens to the egg if it is not fertilized?
-If the egg is not fertilized, it degenerates and is eventually expelled from the body along with the uterine lining during menstruation.
What is the function of the uterus?
-The uterus provides a space for the implantation and growth of a fertilized egg. It has a thick, muscular lining (endometrium) that supports this process.
What hormones regulate the menstrual cycle?
-The menstrual cycle is regulated by several hormones, including Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinizing Hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone.
What is the role of the corpus luteum?
-After ovulation, the ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone and estrogen to prepare the endometrium for possible implantation. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates.
How does the menstrual cycle affect the endometrium?
-The menstrual cycle causes the endometrium to thicken and then shed if fertilization does not occur. This thickening is driven by estrogen and progesterone, which prepare the lining for implantation.
What triggers ovulation during the menstrual cycle?
-Ovulation is triggered by a surge in Luteinizing Hormone (LH), which occurs after the estrogen levels rise, signaling the release of the mature egg from the ovary.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Organ Reproduksi Wanita [Eksternal & Internal] dan Fungsinya

ANATOMI FISIOLOGI SISTEM REPRODUKSI WANITA

Struktur dan Fungsi Sistem Reproduksi pada Manusia#videopembelajaranipa @nova_scienceart9251

Resumão: SISTEMA REPRODUTOR FEMININO

dr Ariyandy Fisiologi Reproduksi Pada Wanita PART 1

DUNIA REMAJA: Sistem Reproduksi Manusia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)