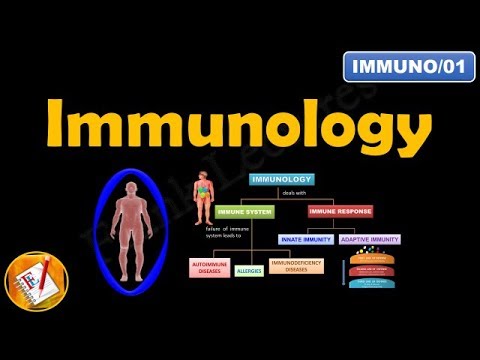
Imunitas Innat & Adaptif, Komponen, Aktivasi Respon Imun, dan Imunopatologi | Imunologi Dasar
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the intricate workings of the immune system, emphasizing both innate and adaptive immunity. It highlights the body's defense mechanisms, such as physical barriers, inflammation, and phagocytosis, as well as the roles of immune cells like macrophages and T-cells. The script delves into the concept of immunity, covering both natural and artificial immunity, including vaccination and antibody production. It also discusses immune-related issues like hypersensitivity, autoimmunity, and immunodeficiency. The explanation is engaging, presenting complex biological processes in an accessible way to help the audience understand the importance of immune health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The belief that food can be eaten if it falls within 5 seconds is incorrect, as microorganisms can still be present, and the body relies on its immune system for protection.
- 😀 The immune system is divided into innate immunity, which is fast but non-specific, and adaptive immunity, which is slower but specific and has memory.
- 😀 Adaptive immunity is triggered by the innate immune system and involves specific responses to pathogens, allowing the body to recognize and fight infections more efficiently in the future.
- 😀 Innate immunity includes physical barriers (like skin) and physiological processes (like stomach acid) to prevent pathogen entry, as well as cellular processes like phagocytosis and inflammation.
- 😀 Phagocytosis is the process where immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils consume and destroy microorganisms.
- 😀 Inflammation is the body's defense mechanism, triggered when tissues are damaged, resulting in symptoms like redness, heat, pain, and loss of function.
- 😀 Humoral components of the immune system include complement proteins, which help identify and clear pathogens, and lysozymes that break down bacteria.
- 😀 Adaptive immunity involves B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies (immunoglobulins) that specifically target pathogens, while T cells help regulate immune responses.
- 😀 Immunoglobulins (antibodies) are proteins that recognize specific markers (antigens) on pathogens, and there are different types, including IgA and IgG, each with distinct functions.
- 😀 Immunity can be acquired naturally (through infection or breastfeeding) or artificially (through vaccination or plasma donation), and these can be active or passive depending on the method.
Q & A
What was the common belief about dropped food when the speaker was a child?
-The common belief was that if food was dropped and picked up within five seconds, it was safe to eat because bacteria wouldn't have had enough time to grow and cause harm.
What does the immune system do in the body?
-The immune system defends the body against microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi that can invade and cause infections. It has various components that help identify and fight off these invaders.
What are the two types of immune systems mentioned in the script?
-The two types of immune systems mentioned are the innate immune system, which is fast but non-specific, and the adaptive immune system, which is slower but specific.
How does the adaptive immune system differ from the innate immune system?
-The adaptive immune system is slower and more specific, targeting specific pathogens, whereas the innate immune system responds quickly but doesn't distinguish between different types of invaders.
What role do antibodies play in the immune system?
-Antibodies are proteins that recognize specific antigens (unique markers of pathogens), and they help the immune system to identify and neutralize harmful invaders.
What are the main components of the immune system discussed in the script?
-The immune system includes physical barriers like the skin, physiological processes like stomach acid, cellular components like macrophages and neutrophils, and humoral components like antibodies and the complement system.
What is phagocytosis?
-Phagocytosis is the process where immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, engulf and digest harmful microorganisms or dead cells.
What happens during inflammation in the immune response?
-Inflammation is the body's response to tissue injury or infection, where it sends signals to recruit immune cells to the affected area to help fight off the invaders, leading to symptoms like redness, heat, pain, and swelling.
What are the differences between active and passive immunity?
-Active immunity is when the body actively produces antibodies after exposure to a pathogen or through vaccination, while passive immunity occurs when antibodies are transferred from one individual to another, such as from mother to child or through plasma donations.
What are the three types of immune system disorders mentioned?
-The three types of immune system disorders are hypersensitivity (overreaction to harmless stimuli, such as allergies), autoimmunity (where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells), and immunodeficiency (when the immune system is weakened, leading to increased vulnerability to infections).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)