Printer Inkjet | Rekayasa menarik di belakangnya
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating workings of inkjet printers, explaining the science behind color mixing, the intricate mechanisms of inkjet technology, and how printers produce high-quality images. It covers the fundamental principles of additive and subtractive color mixing, revealing why using RGB colors in inkjet printing fails, and how printers utilize magenta, cyan, and yellow inks to create a wide range of colors. The video also highlights the role of black ink in creating darker shades and the importance of small droplet sizes for superior print quality. A comprehensive breakdown makes the complex process accessible and informative.
Takeaways
- 😀 Inkjet printers operate by ejecting small droplets of ink through nozzles, using heating elements that rapidly heat and evaporate ink to form bubbles that push the ink out.
- 😀 The primary difference between inkjet printers and display technology is that inkjet uses a subtractive color model (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) rather than an additive one (RGB).
- 😀 Inkjet printing works by layering ink droplets that absorb and reflect light differently based on their molecular structure, which results in color creation.
- 😀 To print color, the printer uses ink colors that are the inverse of the primary colors used in display technology: cyan, magenta, and yellow, instead of red, green, and blue.
- 😀 A key challenge in color printing is the use of subtractive color mixing, which doesn’t produce as clean a color mix as additive light-based mixing.
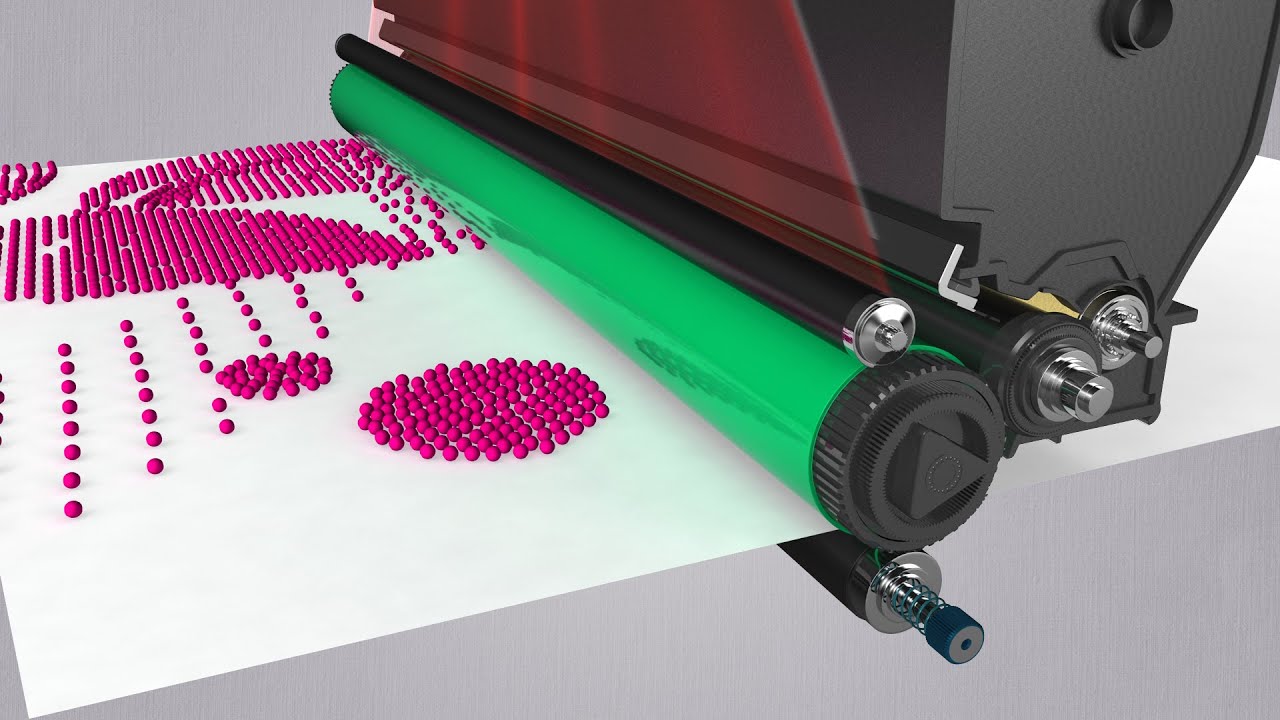
- 😀 The printer’s precision relies on tiny droplets of ink, with modern printers having more than 4,200 nozzles per print head to achieve high print quality.
- 😀 The inkjet printer uses a combination of moving belts, rollers, and stepper motors to precisely position the paper and the print head during printing.
- 😀 By varying the distance between ink droplets, printers can create the illusion of lighter or darker shades of color, allowing for a broader range of hues and more nuanced prints.
- 😀 The addition of black ink (K) to the printing process helps produce darker shades and more detailed prints, improving the overall print quality.
- 😀 The drop size and precision of modern inkjet printers significantly affect the quality of the print, with smaller droplets allowing for higher resolution and finer details.
Q & A
How do inkjet printers create precise images?
-Inkjet printers use tiny droplets of ink that are ejected through nozzles. The droplets are controlled by small heating resistors that heat the ink and create bubbles, forcing the ink out in a controlled manner to form precise dots, resulting in a printed image.
What is the role of the heating resistor in an inkjet printer?
-The heating resistor in an inkjet printer rapidly heats up when electrical current passes through it, reaching around 100°C per microsecond. This causes the ink to vaporize, forming bubbles that push the ink droplets out of the nozzle.
Why does ink form a second droplet when leaving the nozzle?
-The ink droplet elongates due to the viscosity of the ink, and as it stretches, a second droplet forms nearby. Over time, these droplets can merge due to surface tension and other factors.
What is the significance of the nozzle's internal pressure?
-The internal pressure inside the nozzle prevents ink from leaking continuously. It is essential for creating the controlled ejection of ink droplets needed for precision in printing.
How does the stepper motor contribute to the printing process?
-The stepper motor drives the movement of the print head and paper through the printer. It ensures that the print head moves along a precise path, enabling accurate dot placement and overall image reproduction.
What is the difference between additive and subtractive color mixing?
-Additive color mixing involves light, where different colors of light combine to create a new color. Subtractive color mixing, on the other hand, involves pigments or inks, where colors absorb certain wavelengths of light and reflect others, affecting the final visible color.
Why can't traditional RGB color mixing work in inkjet printing?
-In inkjet printing, the colors mix subtractively, not additively like in RGB displays. Using RGB colors in printing results in poor color output because of the way light interacts with inks, which absorb and reflect different wavelengths.
What are the key colors used in inkjet printers, and why?
-Inkjet printers use cyan, magenta, and yellow as the primary colors instead of red, green, and blue. This is because subtractive color mixing, used in printing, requires the inverse of RGB to produce accurate colors.
How are darker shades like dark green achieved in inkjet printing?
-Darker shades, like dark green, are achieved by combining regular color inks with black ink (often represented as 'K'). The black ink helps to deepen the color by creating shadows and enhancing the contrast.
How do modern printers improve the quality of prints?
-Modern printers use smaller ink droplets and higher nozzle counts (e.g., 2100-4200 nozzles per print head) to increase the precision of ink application, allowing for higher resolution prints with better color accuracy and finer detail.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How do printers work? (Color Laser Printer & inkjet printer)

Which printers work with cardstock? Choosing cards and printers. Why some card won't print well

IGCSE Computer Science 2023-25 - Topic 3: HARDWARE (5) - OUTPUT DEVICES

Printers Explained - Laser, Inkjet, Thermal, & Dot Matrix

Perangkat Eksternal Peripheral Input Output PC

Stampa digitale inkjet: campi di utilizzo illimitati // Daniele Cogo
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)