Are Molten Salt Reactors the Future of Nuclear Power?
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the challenges of relying on renewable energy sources like wind and solar, highlighting their intermittency and the need for constant energy generation. It examines the limitations of current nuclear power, including its historical association with nuclear weapons, and the potential of thorium molten salt reactors. The video discusses the benefits of these reactors, such as safety, efficiency, and reduced radioactive waste, while also addressing the corrosion issues that have hindered their development. Finally, it emphasizes global progress in thorium reactor research, especially in China, and its potential as a reliable energy source for the future.
Takeaways
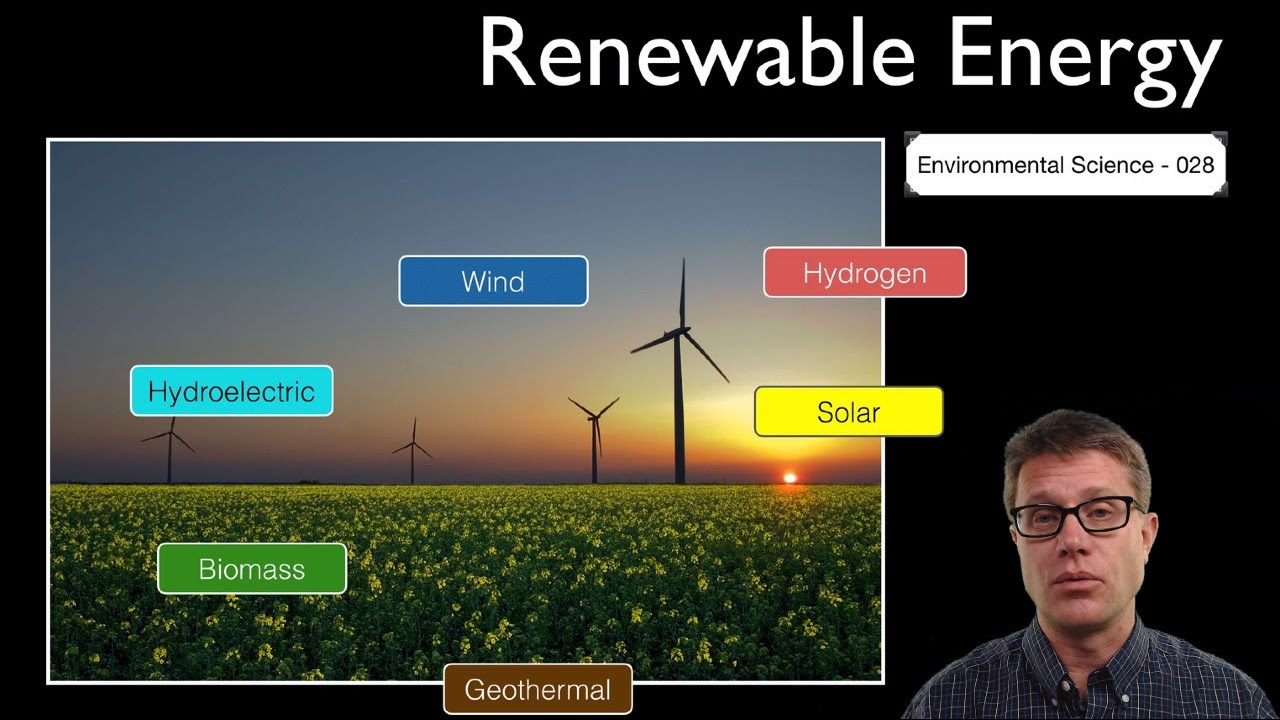
- 😀 Wind and solar power are growing, but their reliability is limited due to factors like night-time and weather conditions.
- 🌞 Solar power is not continuous, as the sun sets every night, and cloud cover can drastically reduce its output.
- 💨 Wind power is also subject to variability, with lulls in wind lasting from hours to days.
- 🔋 While batteries help store excess renewable energy, they are still not ideal for a fully green energy grid.
- 🌍 There are limited alternatives for continuous energy generation, including hydroelectric, geothermal, and nuclear power, with tidal power being a future hope.
- ⚛️ Nuclear fission, the same power behind atomic bombs, has been the backbone of nuclear energy since the 1950s, despite challenges in public acceptance and safety concerns.
- 🚨 Major nuclear accidents like Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima have caused nuclear power to decline, but recent events, such as the Ukraine war, have led to a resurgence in interest.
- 🛑 Nuclear power is tied to nuclear weapons production, as the technology used for nuclear reactors can also be adapted for creating weapons-grade plutonium.
- 🔮 Thorium reactors, using a more abundant fuel, were experimented with in the past but faced issues with material corrosion, limiting their widespread adoption.
- 🌐 Recent advancements in material science have made thorium molten salt reactors more viable, with new alloys showing promise for improved durability and resistance to corrosion, which could make them more widely used in the future.
Q & A
What are the limitations of relying solely on wind and solar power for a 100% green energy supply?
-Wind and solar power are intermittent; the sun goes down every night and cloud cover can reduce solar output. Wind can also be variable, with lulls lasting from hours to days, making it difficult to rely solely on them for continuous, reliable energy.
What alternatives to wind and solar power exist for continuous energy generation?
-Hydroelectric, geothermal, and tidal power are alternatives that can generate energy continuously. However, these are often geographically restricted. Nuclear power, particularly nuclear fission, is another viable option for reliable energy generation.
Why has nuclear power been in decline since the 1980s?
-Nuclear power faced setbacks due to major accidents such as Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima, which led to a decline in public trust and political support for nuclear energy.
What is the connection between nuclear power and nuclear weapons?
-The technology used to create nuclear power plants can also be used to produce plutonium for nuclear weapons. This dual-use nature of nuclear technology has led to concerns about the proliferation of nuclear weapons.
What are molten salt reactors, and how are they different from traditional nuclear reactors?
-Molten salt reactors use a mixture of molten salt and nuclear fuel to generate energy. Unlike traditional water-cooled reactors, they have built-in safety features, such as a negative temperature coefficient, which reduces reactivity when the temperature increases, preventing meltdowns.
What was the Aircraft Reactor Experiment (ARE) and what did it demonstrate?
-The Aircraft Reactor Experiment, conducted in the 1950s, was a prototype designed to explore the possibility of using a small nuclear reactor to power supersonic bombers. It ran for four days at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, demonstrating the feasibility of a molten salt reactor for aircraft power.
What challenges did the MSRE (Molten Salt Reactor Experiment) face during its operation?
-The MSRE faced issues with the corrosion of materials due to the high-temperature salt mixture and neutron radiation. Despite running for four years, these problems limited its long-term viability for commercial use.
Why was the molten salt reactor program shut down in favor of uranium cycle reactors?
-The molten salt reactor program was shut down due to material science limitations, specifically the corrosion issues caused by salt and radiation. Uranium cycle reactors, despite their potential for creating weapons-grade plutonium, were considered more scalable and reliable at the time.
How have advances in material science contributed to the potential of molten salt reactors today?
-Recent advancements in material science, particularly in the understanding of salt corrosion and radiation effects, have led to the development of better alloys. These innovations could significantly improve the lifespan and safety of molten salt reactors, making them more viable for commercial use.
What role does thorium play in the future of nuclear energy?
-Thorium is an alternative to uranium as a nuclear fuel. It is more abundant and produces less radioactive waste. Several countries, including China, are experimenting with thorium molten salt reactors, which could provide a safer and more sustainable energy solution compared to traditional uranium-based reactors.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)