VIDEO Le leggi della Dinamica AMALDI ZANICHELLI
Summary
TLDRThis engaging video explores Newton's three laws of motion using relatable examples from daily life, space experiments, and astronaut demonstrations. Through experiments with objects in motion, gravity, and mass, viewers learn how forces affect movement. The video also highlights the importance of these laws in scientific research and space exploration. Featuring astronaut demonstrations aboard the ISS, the script makes complex scientific concepts accessible, showing how understanding Newton's laws is crucial for the future and encouraging young people to engage with science and research.
Takeaways
- 😀 Newton's three laws of motion are essential for understanding how forces and objects interact in everyday life and in space.
- 😀 Newton discovered that an object accelerates only when a force is applied to it, and this was highlighted through the example of a falling apple.
- 😀 The first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- 😀 Inertia is the tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. A stationary object stays still, and a moving object continues moving unless acted on by an outside force.
- 😀 The second law of motion explains that the force applied to an object is related to its mass and the acceleration it experiences. A heavier object requires more force to accelerate.
- 😀 On the International Space Station (ISS), astronauts experience minimal gravity, which makes them feel weightless even though their mass remains unchanged.
- 😀 Weight is different from mass: weight is the force of gravity acting on an object, while mass is the amount of matter in the object.
- 😀 The second law of motion can be observed by comparing how objects with different masses accelerate when the same force is applied.
- 😀 The third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This was demonstrated by astronauts pushing off each other in space.
- 😀 Understanding Newton's laws is crucial for various scientific fields, including space exploration, where the laws help propel rockets and guide spacecraft operations.
Q & A
What are Newton's three laws of motion?
-Newton's three laws of motion are: 1) An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force (First Law). 2) The force applied on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration (Second Law). 3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction (Third Law).
Why did Isaac Newton's observation of a falling apple lead to an important discovery?
-Newton realized that for an object to accelerate, a force must be applied to it. When the apple fell, he understood that the force acting on it was gravity, which helped him formulate his laws of motion.
What is inertia, as explained in the script?
-Inertia is the tendency of an object to remain in its current state—whether at rest or in motion—unless acted upon by an external force. This concept is demonstrated by objects continuing to move or stay still unless a force is applied.
How does gravity affect objects differently on Earth and the ISS (International Space Station)?
-On Earth, gravity is strong and pulls objects toward the ground, giving them weight. On the ISS, the effect of gravity is minimal, so objects experience a sensation of weightlessness, even though their mass remains unchanged.
What role does mass play in Newton's second law of motion?
-Mass is a key factor in the second law of motion, which states that force equals mass times acceleration. Objects with greater mass require more force to achieve the same acceleration as lighter objects.
Why do lighter objects fall faster in some experiments, while heavier objects might fall slower?
-In real-world experiments, air resistance (or friction) affects the fall of lighter objects more than heavier ones, causing them to fall slower. However, in the absence of air resistance, such as in a vacuum, all objects would fall at the same rate regardless of their mass.
What is the significance of the concept of action and reaction in the third law of motion?
-The third law states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction. This is seen when one astronaut pushes another in space; both will move in opposite directions with equal force but different speeds due to their masses.
How does friction affect the demonstration of Newton’s laws on Earth?
-Friction acts as a resistive force that slows down moving objects. It complicates the demonstration of Newton's laws because it introduces an additional force that needs to be accounted for in experiments, such as with objects of different weights or surfaces.
Why do astronauts experience weightlessness on the ISS despite having mass?
-Astronauts feel weightless on the ISS because they are in a state of free fall due to minimal gravitational pull at that altitude, although they still have mass. The sensation of weightlessness occurs because they, along with the ISS, are falling at the same rate.
What experiment demonstrates Newton's second law using objects of different masses?
-In the experiment with three balls—wood, brass, and ping-pong—Newton's second law is demonstrated by showing that objects with more mass move more slowly when the same force is applied, illustrating the relationship between mass and acceleration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Newton's Laws Of Motion (1) : The Law Of Inertia

STEMonstrations: Newton's 2nd Law of Motion

HUKUM NEWTON | IPA KELAS 8

BrainPop Newton's Laws

What is Newton's Third Law of Motion | Action and Reaction Forces with Examples | Dr. Binocs Show
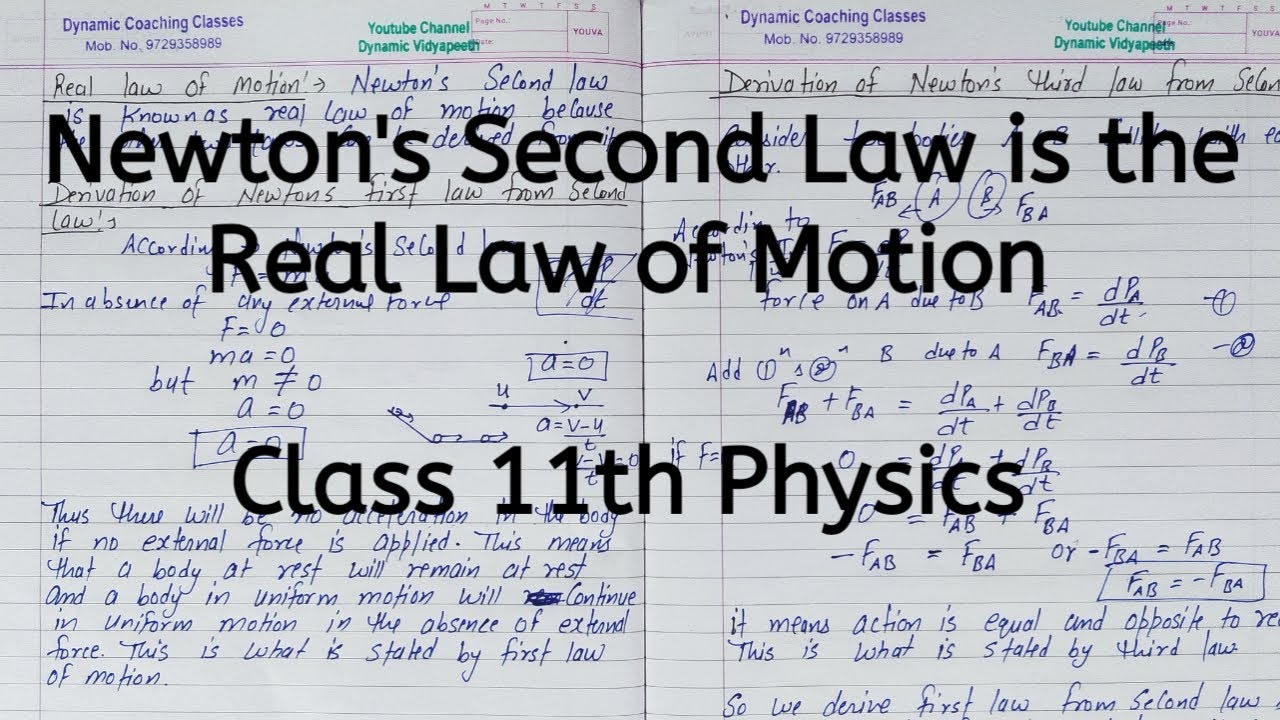
Newton's Second Law is the Real Law of Motion | Chapter 4 | Laws of Motion | Class 11 Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)