Gastrointestinal | Teeth Anatomy
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed exploration of tooth anatomy, covering key components such as the crown, neck, and root, along with the enamel, dentin, pulp cavity, and root canal. It also highlights important structures like the cementum, periodontal membrane, and alveolus. Additionally, the video delves into maxillary and mandibular dentition, explaining the arrangement of different teeth such as molars, premolars, canines, and incisors. The video concludes with an overview of the pulp cavity and nerve pathways, including the inferior alveolar nerve, artery, and vein, providing a comprehensive understanding of tooth structure and function.
Takeaways
- 😀 The crown of the tooth is the visible part, covered by enamel, and is the hardest substance in the human body.
- 😀 The neck of the tooth is the area where the tooth meets the gums (gingiva), and connects the crown to the root.
- 😀 The root is the part of the tooth that anchors it into the jawbone, extending below the neck.
- 😀 Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth and is the hardest material in the body, protecting the tooth.
- 😀 Dentin is a protein-rich material beneath the enamel, forming the bulk of the tooth structure.
- 😀 The pulp cavity contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue, providing nourishment and sensation to the tooth.
- 😀 The root canal is a small passage that carries blood vessels, nerves, and other structures to and from the pulp cavity.
- 😀 The cementum is a material covering the root, anchoring the tooth to the surrounding bone and periodontal ligaments.
- 😀 The alveolus is the socket in the jawbone that holds the tooth securely in place.
- 😀 Gingiva (gums) protects the tooth and prevents infection, while the periodontal membrane and ligaments help anchor the tooth in its socket.
Q & A
What is the crown of the tooth, and how is it different from the root?
-The crown of the tooth is the top portion, above the gum line, and is covered with enamel. The root is the part of the tooth embedded in the jawbone, beneath the gum line, and anchors the tooth in place.
What is the neck of the tooth?
-The neck of the tooth is the region where the crown meets the root, and it is located near the gum line, where the gingiva firmly surrounds the tooth.
What is the function of enamel, and why is it important?
-Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth and is the hardest substance in the body. Its primary function is to protect the tooth from wear, decay, and damage from acids and other external factors.
What is dentin, and how does it differ from enamel?
-Dentin is the inner layer of the tooth beneath the enamel. It is a protein-rich material that is softer than enamel and forms the bulk of the tooth's structure, providing support and strength.
What is the pulp cavity, and what does it contain?
-The pulp cavity is the central part of the tooth that contains the pulp. The pulp is made up of connective tissue, nerves, arteries, and veins, and it supplies nutrients and sensations to the tooth.
What is the role of the root canal?
-The root canal is a small passageway that extends from the pulp cavity down through the root of the tooth. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue, allowing them to travel up and down to support the tooth's living cells.
What is the difference between the superior and inferior alveolar arteries?
-The superior alveolar artery supplies blood to the maxillary teeth, while the inferior alveolar artery supplies blood to the mandibular teeth. These arteries deliver essential nutrients to the teeth's pulp and surrounding structures.
What is cementum, and what is its function?
-Cementum is a protein-rich material that covers the root of the tooth and helps anchor the tooth to the surrounding bone via the periodontal ligament. It plays a crucial role in tooth stability.
What is the alveolus, and why is it important?
-The alveolus is the socket in the jawbone where the tooth sits. It provides a secure and stable position for the tooth and is surrounded by the bone and periodontal ligament.
What is gingiva, and what role does it play in oral health?
-The gingiva is the gum tissue that surrounds the tooth and provides a protective barrier against bacteria and microorganisms. Healthy gingiva is crucial for preventing conditions like gingivitis and ensuring the tooth remains securely anchored.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Differences Between Primary and Permanent Dentition | Pedodontics | Animated Explanation

Differences between Deciduous teeth & Permanent teeth

MORFOLOGI AKAR

Development of the Teeth
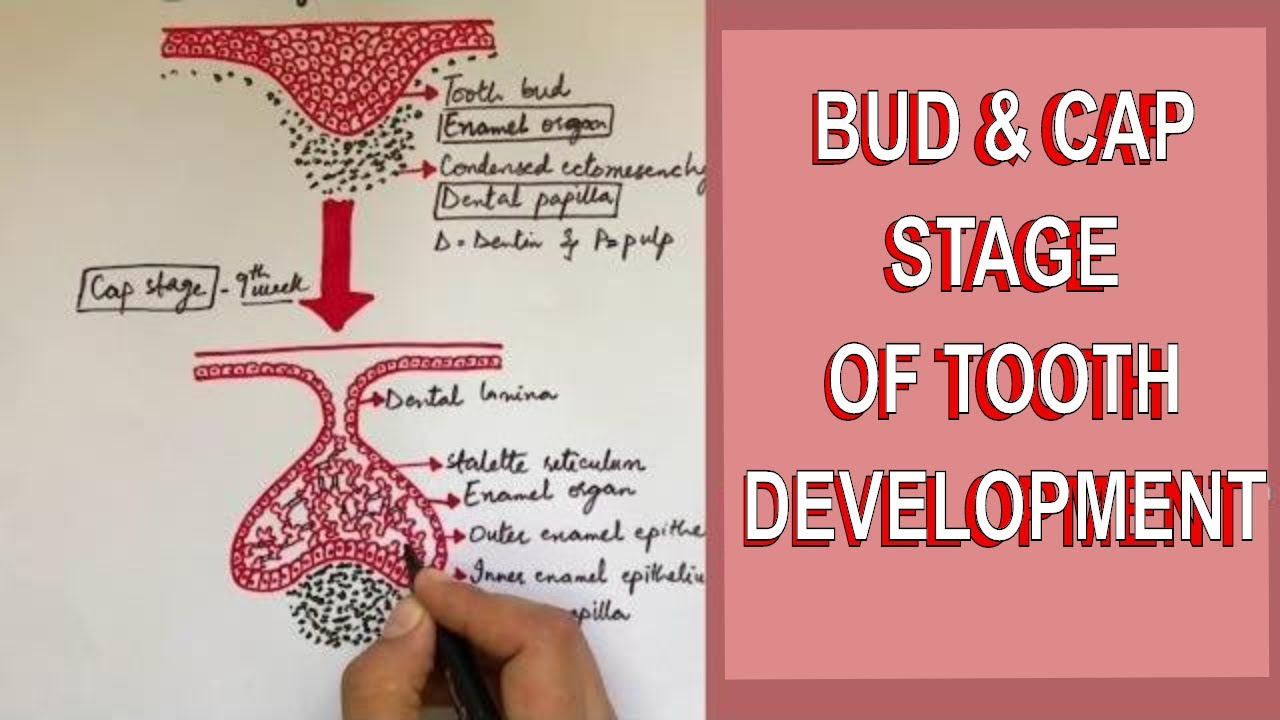
Development of Tooth - Part 1: Initiation, Bud and Cap stage of Tooth development

Dentacademy - Anatomi Umum - Sistem Mastikasi - Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)