14.2 Central Banks and Monetary Policy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Paul Hanley explains the central bank's role in controlling monetary policy through tools such as standing facilities, reserve requirements, and open market operations. He discusses how central banks influence the money supply and interest rates, impacting the economy. Through expansionary and contractionary monetary policies, the central bank can either inject or withdraw money, affecting borrowing costs and economic activity. Hanley uses visual diagrams to demonstrate how changes in money supply influence equilibrium interest rates and borrowing, offering an engaging and insightful look at how central banks manage economic stability.
Takeaways
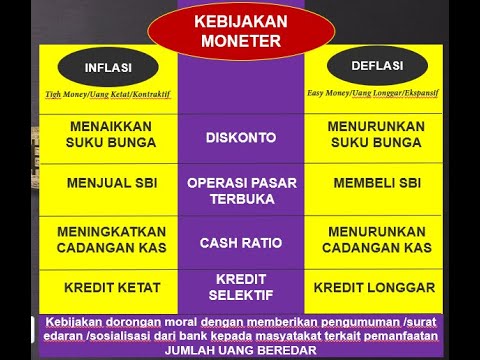
- 😀 Central banks control monetary policy through tools like standing facilities, reserve requirements, and open market operations.
- 😀 Standing facilities allow commercial banks to borrow money from central banks overnight at a marginal lending rate or deposit excess reserves at a deposit rate.
- 😀 Reserve requirements are the minimum reserves a bank must hold as a fraction of total deposits to ensure liquidity and solvency.
- 😀 Open market operations involve buying and selling government bonds to control the money supply in the banking system.
- 😀 Purchasing government bonds by a central bank injects cash into the banking system, increasing reserves and money supply.
- 😀 Selling government bonds reduces reserves in the banking system, decreasing the money supply.
- 😀 Expansionary monetary policy is when a central bank buys government bonds, injecting money into the system and lowering interest rates.
- 😀 Lower interest rates from expansionary monetary policy reduce the cost of borrowing, encouraging borrowing and spending in the economy.
- 😀 Contractionary monetary policy occurs when a central bank sells government bonds, reducing money supply and increasing interest rates.
- 😀 Higher interest rates from contractionary monetary policy raise the cost of borrowing, reducing borrowing and spending in the economy.
- 😀 Both expansionary and contractionary policies influence the money supply and interest rates, directly affecting economic activity through changes in borrowing and spending.
Q & A
What is the primary function of central bank monetary policy?
-The primary function of central bank monetary policy is to control the money supply and indirectly influence interest rates in the economy, thereby managing economic stability.
What are standing facilities in the context of central bank monetary policy?
-Standing facilities are tools that allow commercial banks to borrow money from the central bank at a marginal lending rate if they are short of funds, or deposit excess reserves at the central bank to earn interest at the deposit rate.
How do reserve requirements work in monetary policy?
-Reserve requirements are the minimum amount of reserves that a bank must hold in liquid form, such as cash, as a fraction of its total deposits. For example, if the reserve requirement is 10%, a bank must keep 10% of the deposited amount as reserves.
What is the role of open market operations in monetary policy?
-Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government bonds by the central bank. Purchasing bonds injects money into the banking system, while selling bonds withdraws money, affecting the money supply and interest rates.
What is the impact of expansionary monetary policy on the money supply?
-Expansionary monetary policy increases the money supply by purchasing government bonds, which raises bank reserves, allowing banks to offer more loans. This leads to a decrease in interest rates and increased borrowing and expenditure in the economy.
How does contractionary monetary policy affect the money supply?
-Contractionary monetary policy reduces the money supply by selling government bonds. This decreases bank reserves, limiting the amount banks can lend. As a result, interest rates rise, and borrowing and expenditure decrease.
What happens to the equilibrium interest rate in expansionary monetary policy?
-In expansionary monetary policy, the money supply increases, which shifts the money supply curve to the right. This leads to a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate, making borrowing cheaper and stimulating economic activity.
How do central banks use repurchase agreements to control the money supply?
-Repurchase agreements (repos) are short-term transactions where the central bank buys or sells government bonds from or to banks with an agreement to reverse the transaction after a specified period, usually one week. This helps adjust the money supply by injecting or withdrawing funds from the banking system.
What is the relationship between the money supply and interest rates in monetary policy?
-There is an inverse relationship between the money supply and interest rates. When the money supply increases, interest rates tend to decrease, making borrowing cheaper. Conversely, when the money supply decreases, interest rates increase, raising the cost of borrowing.
How does a decrease in bank reserves affect potential loans and the money supply?
-A decrease in bank reserves reduces the amount of money that banks can lend. This lowers the potential for loans, leading to a decrease in the money supply as fewer loans are made and less money circulates in the economy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)