Litosfer Bumi Teori Tektonik Lempeng
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating topic of the lithosphere, explaining its structure and components such as the Earth's crust, mantle, and core. The concept of plate tectonics is introduced, detailing the theory of continental drift by Alfred Wegener and the sea-floor spreading theory. Viewers learn about the dynamic interactions of tectonic plates, including divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries, as well as geological phenomena like earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanic activity. The video emphasizes the dynamic nature of Earth's surface and the processes driving these changes over time.
Takeaways
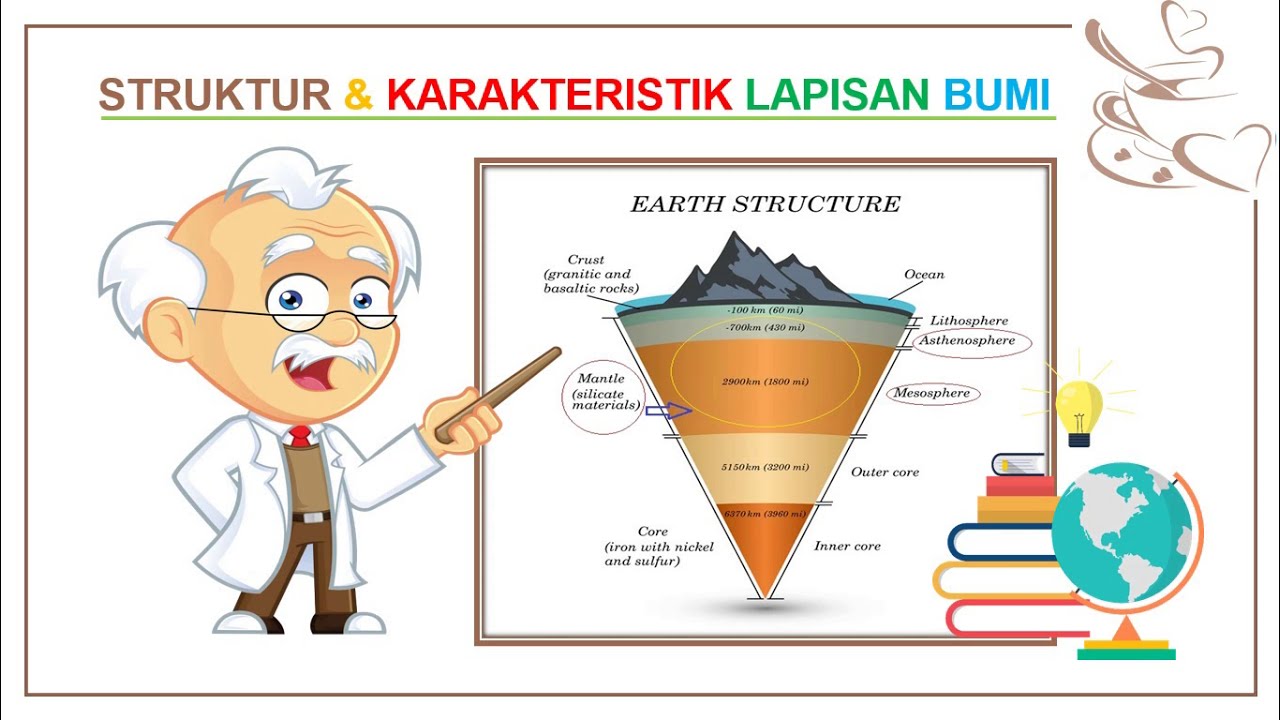
- 😀 Litosphere refers to the Earth's solid outer layer, consisting of the crust, mantle, and core.
- 😀 The Earth's crust is divided into two types: continental crust (on land) and oceanic crust (under the ocean).
- 😀 The mantle of the Earth is divided into the upper and lower mantles, with the lower mantle being hotter and more rigid.
- 😀 Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift, suggesting that Earth's continents were once a single supercontinent called Pangea.
- 😀 In the 1960s, scientists introduced the theory of sea-floor spreading, explaining how material beneath the Earth's crust moves and forms new oceanic crust.
- 😀 The theory of plate tectonics explains that the Earth's outer layer (lithosphere) is divided into several plates that can move and interact.
- 😀 Plate movements can cause various geological phenomena, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- 😀 Divergent boundaries occur when plates move apart, like the Indo-Australian plate moving away from the Antarctic plate.
- 😀 Convergent boundaries happen when plates move toward each other, causing phenomena like subduction zones and mountain formation, such as the Himalayas.
- 😀 The movement of tectonic plates is driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle, which are powered by the heat from the Earth's core.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere and where does it exist?
-The lithosphere is a layer of rock on Earth, derived from the Greek word 'lithos' meaning stone and 'sphere' meaning layer. It refers to the rigid outer shell of the Earth, which includes the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle.
What are the two types of Earth's crust, and how are they different?
-The Earth's crust is divided into two types: the continental crust, which is found on land, and the oceanic crust, which is found beneath the oceans. The continental crust is thicker and less dense than the oceanic crust.
What is the theory of continental drift, and who proposed it?
-The theory of continental drift, proposed by German meteorologist Alfred Wegener, suggests that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangea. Over millions of years, the continents drifted apart.
What is the theory of sea-floor spreading, and who introduced it?
-The theory of sea-floor spreading, proposed by scientist Harry Hess in the 1960s, explains that hot, less dense material from beneath the Earth's crust rises to the surface at mid-ocean ridges, pushing the oceanic crust apart and forming new crust.
What is the theory of plate tectonics and how does it relate to continental drift and sea-floor spreading?
-Plate tectonics is a theory that explains the movement of Earth's lithosphere, which is divided into tectonic plates. It builds on the concepts of continental drift and sea-floor spreading by showing that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are divided into rigid plates that move over the asthenosphere.
How does convection in the Earth's mantle drive tectonic plate movement?
-Convection occurs when the heat from Earth's core warms the mantle, causing material to become less dense and rise. As it reaches the surface, it cools and becomes denser, causing it to sink back down. This continuous cycle of rising and sinking material drives the movement of tectonic plates.
What happens when tectonic plates move apart?
-When tectonic plates move apart, it creates a divergent boundary. This can result in the formation of new crust, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. An example is the San Andreas Fault in California.
What occurs when tectonic plates collide?
-When tectonic plates collide, it leads to a convergent boundary. This can result in subduction (where one plate is forced beneath another), mountain building, and volcanic activity. An example is the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates, which formed the Himalayas.
What is subduction, and how does it occur?
-Subduction is the process that occurs when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, and the denser oceanic plate is forced beneath the continental plate. This can lead to the formation of deep ocean trenches and volcanic activity.
How do tectonic plate movements affect Earth's surface?
-Tectonic plate movements cause major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, the formation of mountain ranges, and ocean trenches. These movements continuously reshape the Earth's surface.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)