Magnetic Particle Inspection
Summary
TLDRThe video script outlines the magnetic particle inspection method, a non-destructive testing technique for detecting near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials. It demonstrates the process of magnetizing a test piece and applying a fluorescent magnetic particle suspension to reveal defects, such as cracks, through visible clustering of particles. The method's effectiveness is maximized with ultraviolet light, and the necessity for the magnetic field to be oriented correctly relative to defects is emphasized. The script also covers the importance of magnetizing the sample in different directions to ensure comprehensive detection of surface and subsurface defects.
Takeaways
- 🧲 Magnetic particle inspection is a non-destructive testing method used to detect near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
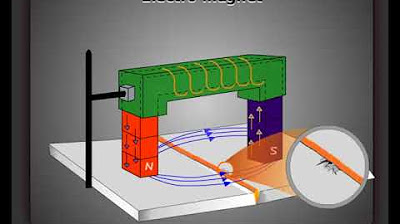
- 🔍 The procedure involves placing the test piece between the poles of an electromagnet and applying a suspension of magnetic particles.
- 💡 Defects are revealed when magnetic field lines leak from the surface and attract the magnetic particles, forming visible clusters.
- 🌞 The magnetic particle suspension contains pigments that fluoresce under ultraviolet light, enhancing the visibility of defects.
- 🌑 Defects are best visible under UV light and when the daylight is darkened, allowing for more precise inspection.
- 📐 The basic principle is to magnetize the workpiece in a way that field lines run parallel to its surface, except at points of inhomogeneity like cracks.
- 🔄 To detect all near-surface cracks, the sample must be magnetized in different directions, such as horizontal and perpendicular.
- 🔌 The current flow method is used to generate a circular magnetic field, which helps in detecting cracks in different orientations.
- 🛠️ The test sample is often a hardened sliding guide or a large gear wheel, which may develop cracks during manufacturing or operation.
- 🔧 Fatigue cracks in gear wheels can be detected using this method, which are typically caused by operational mismatches between gear wheels.
- 🔎 The inspection is crucial for identifying and preventing potential failures in critical components of machinery.
Q & A
What is magnetic particle inspection?
-Magnetic particle inspection is a non-destructive testing method used to detect near surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
How does the magnetic particle examination work?
-The examination works by magnetizing a ferromagnetic workpiece and applying a suspension of magnetic particles onto the test piece. The particles are attracted to areas of leakage fields caused by defects, indicating their presence.
What is the role of the electromagnet in the testing process?
-The electromagnet is used to magnetize the test piece, creating a magnetic field that helps in revealing defects through the application of magnetic particles.
Why are magnetic particles used in the inspection process?
-Magnetic particles are used because they are attracted to areas where the magnetic field lines leak due to defects, thus highlighting the presence of these defects.
How can defects be made more visible during the inspection?
-Defects can be made more visible by using a pigment that covers the magnetic particles and fluoresces under ultraviolet light, allowing for better detection even in daylight.
What is the significance of the magnetic field lines in the inspection process?
-Magnetic field lines are crucial as they must be perpendicular or at a certain angle to the defect to create a leakage field that attracts the magnetic particles and reveals the defect.
What is the purpose of using ultraviolet light during the inspection?
-Ultraviolet light is used to enhance the visibility of the magnetic particles that fluoresce, making it easier to detect defects, especially those not open to the surface.
Why is it necessary to magnetize the sample more than once?
-Magnetizing the sample more than once, at different angles, helps to ensure that all near surface cracks are detected, as defects oriented differently may not be visible with a single magnetization direction.
What is the current flow method mentioned in the script?
-The current flow method involves passing a high electric current through the sample to generate a circular magnetic field, which aids in detecting cracks oriented in a different direction than the initial magnetization.
What are fatigue cracks and how are they formed?
-Fatigue cracks are defects that form during the operation of mechanical components, such as gear wheels, due to repeated stress cycles, often as a result of a mismatch between interacting components.
How does the magnetic particle inspection help in quality control for manufactured parts?
-Magnetic particle inspection helps in quality control by detecting cracks and other defects in manufactured parts, ensuring that they meet the required safety and performance standards before they are used.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Lessons learnt while inspecting steam turbine blades

CVM - Y-2 AC Yoke | MT-Magnetic Particle Testing | การตรวจสอบรอยแตกร้าวด้วยอนุภาคแม่เหล็ก
magnetic particle testing

Macam-macam NDT (Non Destructive Test)

In The Materials Lab Non Destructive Testing Network Rail engineering education 15 of 15

Non-destructive testing (NDT) at TWI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)