Mineralogi Petrografi - Acara 8 - Pengenalan XRD, XRF, dan SEM
Summary
TLDRThis video script covers a practical session on mineralogy and petrography, introducing key analytical techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It explains the principles behind each method, such as how XRD analyzes crystal structures through diffraction patterns, XRF identifies elemental concentrations, and SEM creates high-resolution images of sample surfaces. The script also highlights how these methods are applied in material analysis and geology, including identifying rock types and understanding their mineral composition.
Takeaways
- 😀 X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) are non-destructive techniques used to analyze and identify materials in mineralogy and petrology.
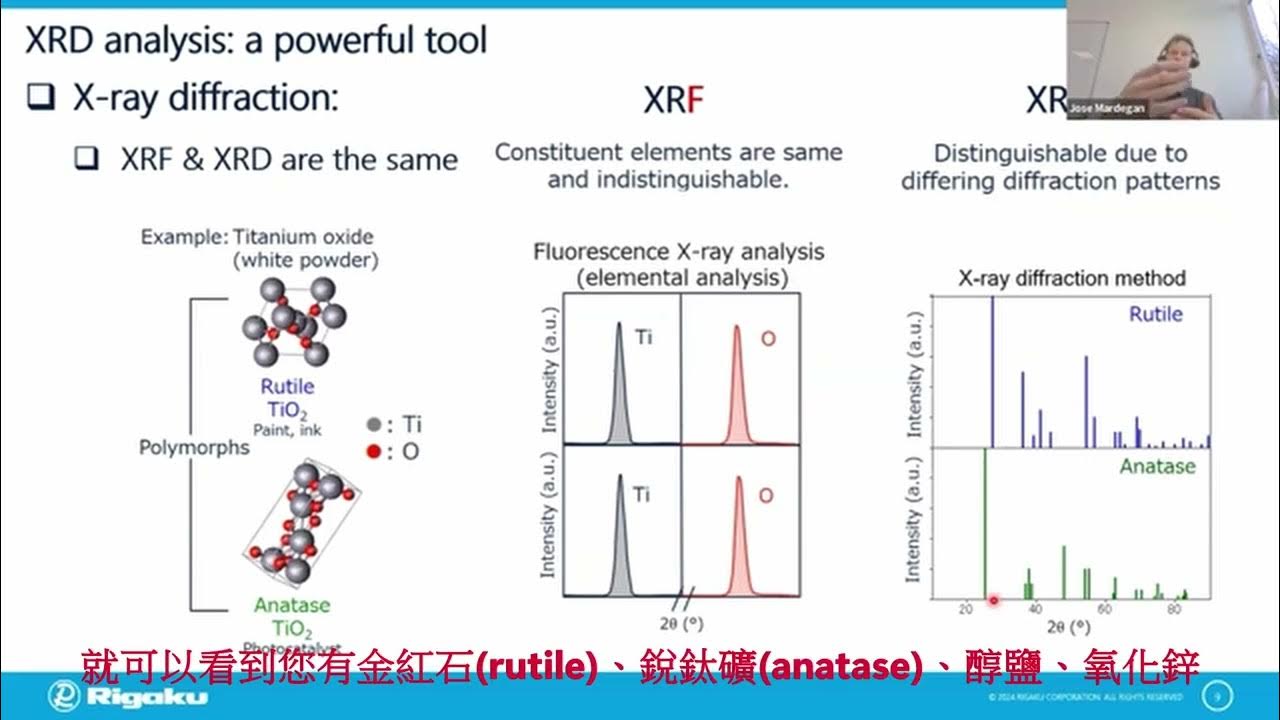
- 😀 XRD is used to identify the crystalline phases of materials, providing information about crystal dimensions and structures.
- 😀 XRF helps in determining the elemental composition of a sample by analyzing the emitted X-rays after material interaction.
- 😀 Spectroscopy is a method for analyzing materials based on the spectrum of light emitted or absorbed, which helps identify chemical elements and molecular structures.
- 😀 Microscopy, particularly Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), allows for high-resolution imaging of material surfaces and provides detailed physical and crystallographic information.
- 😀 Diffraction techniques, including X-ray and electron diffraction, help in understanding the atomic structure of crystalline materials.
- 😀 Thermal analysis is used to study the properties of materials as they change with temperature, revealing insights into material stability.
- 😀 XRD relies on X-rays produced from radioactive materials or electricity, and involves a diffractometer with components like an X-ray tube, focusing optics, sample holder, and a detector.
- 😀 The XRF technique uses electromagnetic radiation to interact with a sample, producing characteristic X-rays that are analyzed to determine elemental concentrations.
- 😀 In SEM, electron beams are used to examine the surface of samples, with high magnification and depth of field, enabling the study of sample morphology and composition.
- 😀 Samples analyzed by SEM must be prepared by coating them with a conductive material (like gold or platinum) to avoid interference from non-conductive elements.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of this mineralogy and petrology practical session?
-The main purpose of this practical session is to introduce and demonstrate techniques for identifying materials through X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
What are the four main types of material characterization techniques mentioned in the script?
-The four main types of material characterization techniques are spectroscopy, microscopy, diffraction, and thermal analysis.
What is the principle of spectroscopy as mentioned in the script?
-Spectroscopy is the study of methods used to analyze and generate a spectrum of results, which can then be used to analyze elements, atomic energy levels, molecular structure, and composition.
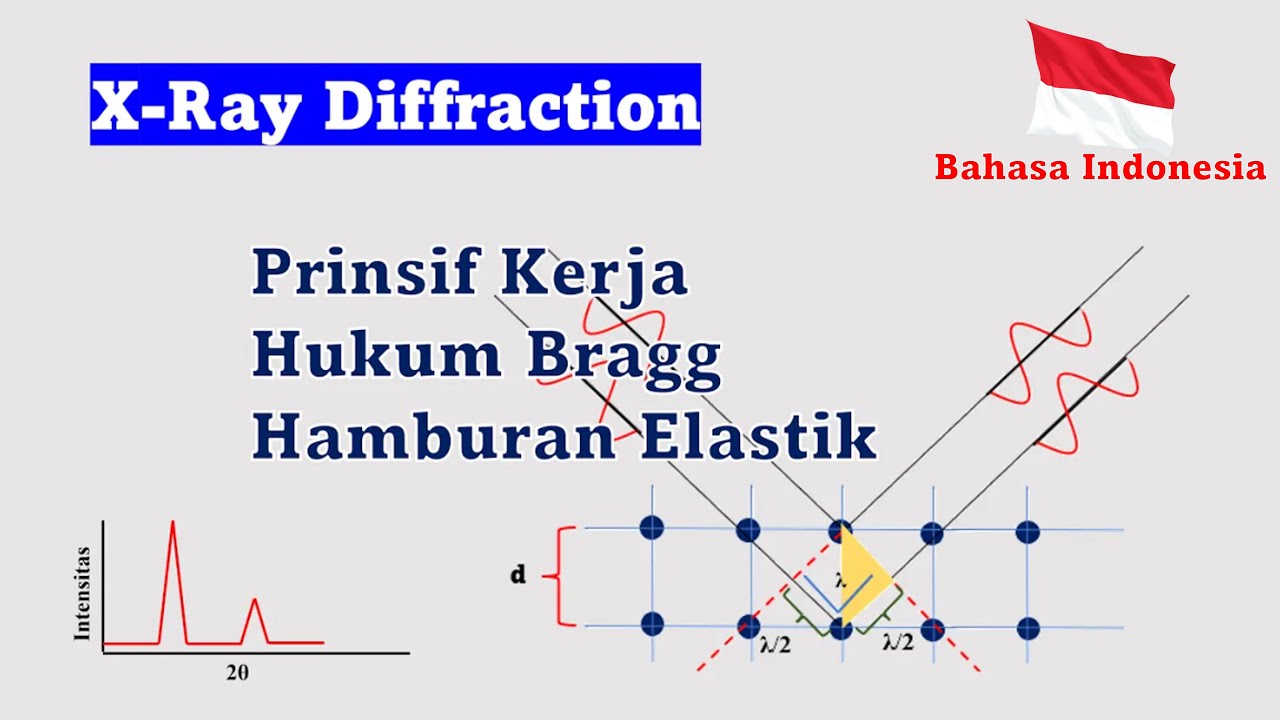
How does X-ray diffraction (XRD) work in material analysis?
-XRD is a non-destructive analytical technique used to identify the crystalline phases of a material. It works by diffracting X-rays through the crystal structure of a sample, measuring the intensity and angle of the diffracted rays to determine the crystal structure.
What is the significance of the diffraction pattern in XRD analysis?
-The diffraction pattern in XRD analysis provides valuable information about the atomic structure of a material, helping to identify the specific crystalline phases present in the sample.
How does X-ray fluorescence (XRF) differ from XRD in terms of material analysis?
-XRF is a non-destructive technique that identifies and quantifies elements in a material by measuring the fluorescent X-rays emitted from the sample when exposed to high-energy X-rays, while XRD identifies crystalline phases and the structure of the material.
What types of samples can be analyzed using XRF?
-XRF can analyze solid, powder, or liquid samples, and the sample preparation depends on its physical state. For powder samples, the particle size should be less than 400 microns, while solid samples need to have a flat surface, and liquid samples should be fresh and rapidly analyzed.
What is the role of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in material analysis?
-SEM is used to obtain high-resolution images of a sample's surface by detecting secondary electrons emitted when a focused electron beam interacts with the sample's surface. It helps to observe the physical structure and composition of materials at a microscopic level.
What is the principle behind scanning electron microscopy (SEM)?
-The principle behind SEM is the interaction of an electron beam with the sample surface, causing secondary electrons to be emitted. These electrons are then detected to form an image of the sample's surface with high magnification and resolution.
What is the significance of sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy (SEM)?
-For SEM, sample preparation is crucial because the sample must be clean, dry, and conductive. It often involves coating the sample with a thin layer of gold or platinum to improve conductivity and achieve accurate imaging.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)