Keseimbangan Cairan, Elektrolit dan Asam Basa Part 2
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the body's fluid regulation mechanisms, focusing on key hormones such as ADH, aldosterone, and atrial natriuretic peptide. It outlines how ADH helps conserve water when plasma osmolarity is high due to dehydration. Additionally, aldosterone regulates sodium and potassium balance by stimulating sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, while atrial natriuretic peptide promotes sodium and water excretion when there is excess fluid. The script also explores how changes in blood volume and sodium intake influence these hormone-driven processes to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
Takeaways
- 😀 ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) is released by the pituitary gland and plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance in the body.
- 😀 When the plasma osmolarity increases due to dehydration, ADH levels rise, causing the kidneys to conserve water and produce concentrated urine.
- 😀 Alcohol consumption inhibits ADH, leading to increased urination as the body loses more water.
- 😀 Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect changes in plasma osmolarity and regulate ADH release accordingly.
- 😀 High ADH levels result in more water being absorbed by the kidneys, reducing plasma osmolarity and restoring fluid balance.
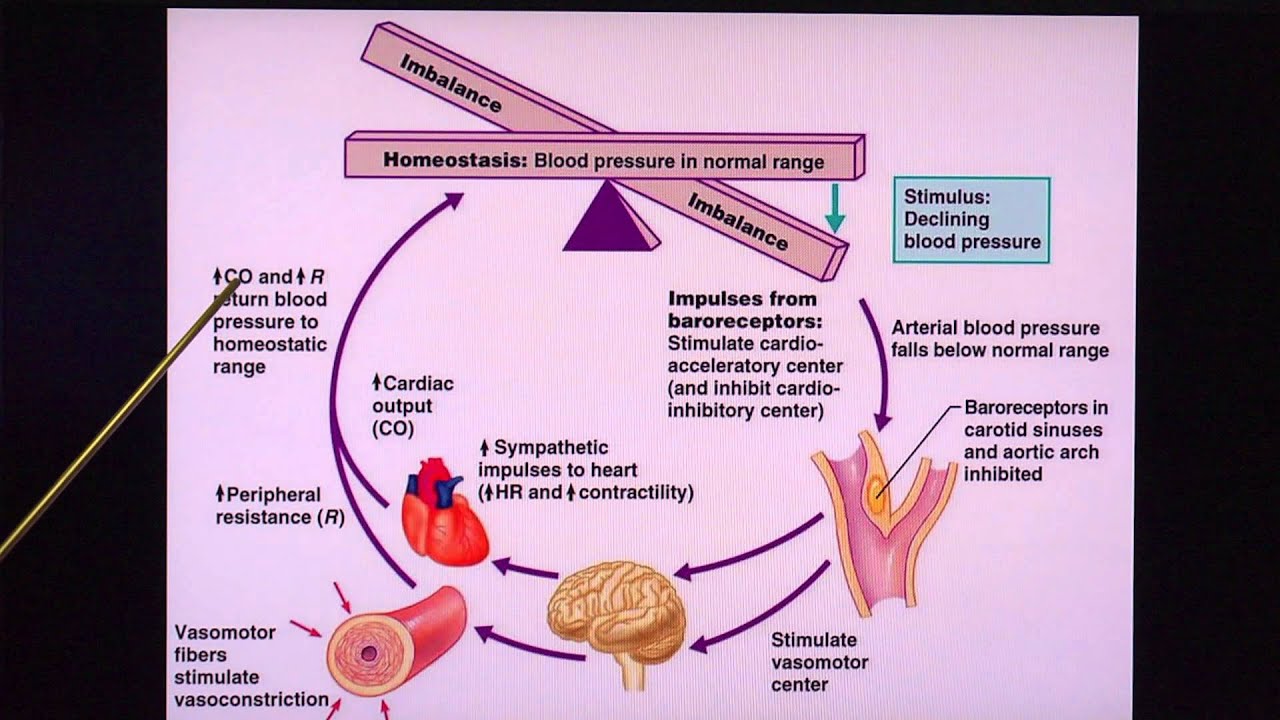
- 😀 The body releases ADH in response to low blood volume or low blood pressure, signaling the kidneys to conserve water and maintain fluid balance.
- 😀 The body regulates sodium and chloride balance using three hormones: Angiotensin II, Aldosterone, and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP).
- 😀 Angiotensin II and Aldosterone work to conserve sodium and chloride, which also helps conserve water by osmosis, especially during dehydration.
- 😀 Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) promotes the excretion of sodium and chloride, leading to water loss and decreased blood volume, often in cases of excess fluid.
- 😀 Aldosterone, secreted by the adrenal cortex, helps retain sodium during low sodium levels or high potassium levels, maintaining electrolyte balance.
- 😀 High sodium intake (e.g., from salt) increases plasma sodium levels, leading to water moving out of cells, increasing blood volume, and triggering mechanisms to regulate fluid balance, such as ANP and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition.
Q & A
What is the role of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) in fluid balance?
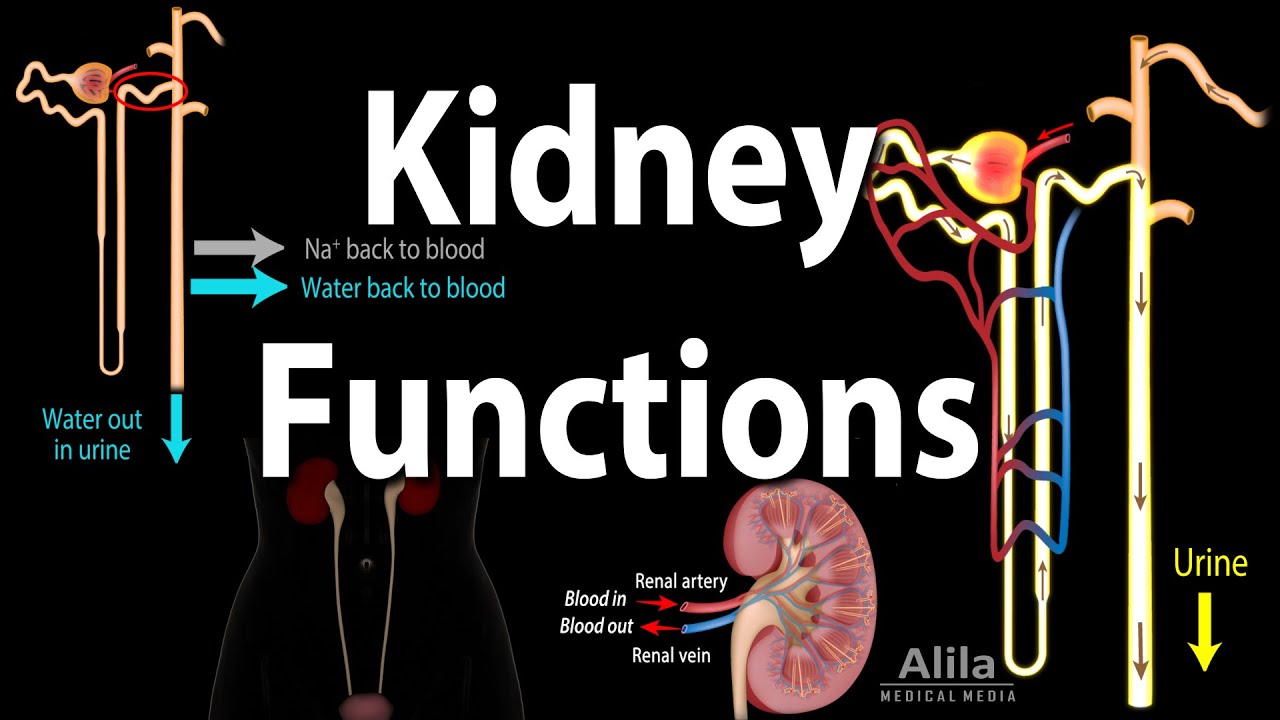
-ADH is released by the pituitary gland in response to high plasma osmolarity, which typically occurs when the body is dehydrated. ADH acts on the kidneys, particularly the collecting ducts, to increase water reabsorption, helping to conserve body fluids and dilute the urine.
How does alcohol consumption affect ADH secretion?
-Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, which leads to reduced water reabsorption in the kidneys. This results in increased urine output and frequent urination, contributing to dehydration.
What triggers the release of ADH?
-ADH release is triggered by increased plasma osmolarity, which can occur during dehydration or when there is a high concentration of sodium in the blood. This triggers osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus to signal the pituitary gland to release ADH.
What is the effect of high ADH levels on urine?
-High ADH levels cause the kidneys to reabsorb more water, resulting in more concentrated urine and less frequent urination. This helps conserve water in the body during dehydration.
What happens when the body experiences excessive fluid intake?
-When the body has excess fluid, the hypothalamus inhibits ADH release, which decreases water reabsorption in the kidneys. This results in the excretion of a larger volume of dilute urine to restore fluid balance.
How do osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus regulate fluid balance?
-Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect changes in plasma osmolarity. When the plasma becomes more concentrated (due to dehydration), they stimulate ADH release. Conversely, when fluid intake is excessive, they inhibit ADH release to allow for the excretion of excess water.
What is the role of aldosterone in regulating sodium and fluid balance?
-Aldosterone, secreted by the adrenal cortex, increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, which in turn helps retain water. This hormone is released when sodium levels drop or potassium levels rise in the blood, helping restore electrolyte balance and conserve fluid.
What happens when the body is dehydrated regarding sodium reabsorption?
-During dehydration, aldosterone is released to promote sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. Since water follows sodium through osmosis, this process helps conserve both sodium and water, restoring fluid balance.
How does atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) influence fluid balance?
-ANP is released when the heart atria are stretched due to increased blood volume. It promotes sodium and water excretion by the kidneys, leading to a reduction in blood volume and helping to alleviate fluid overload.
What role does the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) play in fluid regulation?
-The RAAS is activated when blood volume or blood pressure drops. Renin is released, which leads to the production of angiotensin II, stimulating aldosterone secretion. This process helps increase sodium and water reabsorption, thereby restoring blood volume and blood pressure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hormones in body fluid homestasis (ADH/vasopressin, Aldosterone and Natriuretic peptides)

ATRIAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE! ANP! The Kidneys and high blood pressure explained!

Guyton and Hall Medical Physiology (Chapter 29)REVIEW Urine Concentration and Dilution || StudyThis!
Regulation of Blood Pressure

Mekanisme Osmoregulasi dan Termoregulasi - Biologi sma kelas 11 bab.sistem hormonal/endokrin
Kidney Homeostatic Functions, Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)